|
10.0 |
Mahadayi –Mandovi River |
1 |
Geography |
River Mahadayi is Spread across the Districts of Goa, Karnataka and Maharashtra. Originating at Khanpur (Belgaum-Karnataka), Mahadayi flows for a distance of nearly 117 km (http://thesurveyofindia.gov.in, Survey of India Topographic sheets) before it joins Arabian Sea at Panji (North-Goa) (Figure 1).
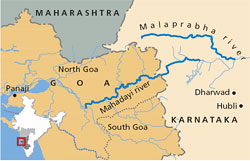
Figure 1: Mahadayi River
Tributaries of Mahadayi include, Kalasa Nala, Surla Nala, Haltar Nala, Poti Nala, Mahadayi Nala, Pansheer Nala, Bail Nala, Andher Nala and many more. Mahadayi river has a catchment area of 2032 sq.km.
Topography of Mahadayi river: Elevation ranges between < 0m and > 980m w.r.t Mean Sea Level, slope of the catchment varies up to 150%. Very high slope we observed in the Ghats (Braganja Ghats).
The variations in the terrain has led to formation of various water falls such as the Doodhsagar falls,Vajra poha falls etc.
Rock types: Granites to schists, shale, quartzite’s, Phyllites. Charnockites. etc.
Ores: Iron, limestone, bauxite, quartz, limestone, sand, clay, lime shell, Manganese, Asbestos, Mica, Lead, Cadmium,
Soil: Kanhaplic Rhodustalfs, Kanhaplic Hapustalfs, Typic Kandiustalfs, Ustoxic Kanhaplustalfs, Typic Ustropepts, Ustic Kandihumults, Ustic Haplohumults, Kandic Paleustalfs, Typic Rhodustalfs, Typic Chromusterts, Rhodic Paleustalfs, Ustic Palehumults, etc. |
2 |
Rainfall and Water Yield |
Rainfall assessment in Mahadayi catchment indicates that rainfall in the catchment is orographic with annual rainfall varying spatially between 1918 mm at the plains(Khanapur), to over 5425 mm at the Ghats (Gavalli).
Water yield in the catchment is 3164 M.cum to 5703 M.cum. |
3 |
Anthropology |
Major Population is contained at towns such as Belgaum, Panji.
Communities: Kumri Marati, Goudas, Konkanis. Havyaka Brahmin, , Kurubas, Siddis, Daivajna, Muslims, Christians, etc. |
4 |
Land use |
Table 1 depicts land use changes in the catchment
Table1: Land use in Mahadayi Catchment
Land use |
|
Forest |
36.6% |
Non Agriculture Land |
4.10% |
Barren and Uncultivable land |
4.60% |
Cultivable waste land including fallow land |
19.7% |
Permanent pastures and other grazing land |
0.60% |
Land under miscellaneous trees and crops |
0.30% |
Gross Sown Area |
35.3% |
|
5 |
Agriculture, Irrigation |
Variety of Paddy, Sugar cane, Banana, Arecanut, Coconut, Mango, spices, Cashew nut etc. |
6 |
Diversions |
No major diversion works in the catchment, however numerous small scale check dams are built for irrigation practice. |
7 |
Bio Diversity |
Bivalves: EIA of Proposed Mahadayi HEP,1997
Flora: Forest types found in the district are: Evergreen, Semi Evergreen, Moist Deciduous, Scrub, Thorny, un wooded with following species.
Acacia sp., Artabotrys hexapetalus, Atlantia recemosa, Bombax sp, Butea monosperma, Calophyllum wightianum, Calophyllum elatum, Carallia brachiata, Careya arborea, Cassia fistula, Cinnamomum zeylancium, Dalbergia latifolia, Dillenia pentagyana, Diospyros candolleana, Diospyros montana, Embilca officinalis, Euphoria longana, Ficus benghalensis, Ficus religiosa, Glycosmis sp., Holigarna arnotiana, Hopea parviflora, Ixora brachiata, Lagerstroemia lanceolata, Lygodium sp., Lophopetalum wightianum, Macaranga peltata, Mallotus philippensis, Mangifera indica, Memecylon edula, Mimusops elengi, Myristica sp., Olea dioica, Pongamia sp., Pongamia pinnata, Randia dumetorum, Spatholobus sp., Strobilanthes sp., Symploca sp., Syzygium cumini, Tectona grandis, Terminalia chebula, Terminalia paniculata, Terminalia tomentosa, Vitex negundo, Xanthium sp., Ziziphus oenoplia, Artocarpus hirsutus, Falconeria sp, Garcinia indica, Holigarna sp, Madhuca indica, Syzygium sp, etc
Fauna: : EIA of Proposed Mahadayi HEP,1997
Mammals: Tiger, Black Panther, Leopard, Bison, Gaur, Hare, Wild Boar, Sloth Bear, Deer, Thar, Bonnet Macaque, Lion Tailed Macaque, Giant Squirrel, Hanuman Languor, Wroughton’s Freetailed bat (endemic-endangered), Sambar, Chital, Porcupine, Giant Squirrel, Barking Deer, Mouse Deer,
Reptiles: Snakes (Vipers, Cobra, Rat snake, Crate, King cobra, Python, Wolf snake, Blind snake, Shield tail snake, Boa, Banded kurki, Russel Kurki snake, Flying snake, coral snake, Russel viper, rat snake, etc), Monitor Lizard. |
9 |
References |
- Survey of India Topographic Sheets, 1:50000 scale, http://thesurveyofindia.gov.in
- Water Resource Information System of India, http://www.india-wris.nrsc.gov.in.
- Google Earth, https://www.google.com/earth/.
- Census of India, 2001 and 2011, http://censusindia.gov.in.
- Environmental Impact assessment of proposed Mahadayi Hydroelectric Project, KPCL, Bangalore September 1997
|
|
T.V. Ramachandra
Centre for Sustainable Technologies, Centre for infrastructure, Sustainable Transportation and Urban Planning (CiSTUP), Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail : tvr@iisc.ac.in
Tel: 91-080-22933099/23600985,
Fax: 91-080-23601428/23600085
Web: http://ces.iisc.ac.in/energy
Vinay S.
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: svinay@iisc.ac.in
Bharath Settur
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: setturb@iisc.ac.in
Bharath H. Aithal
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: bharathh@iisc.ac.in
Citation: Ramachandra T V, Vinay S, Bharath Settur and Bharath H. Aithal, 2017. Profile of Rivers in Karnataka, ENVIS Technical Report 129, Sahyadri Conservation Series 71, Energy & Wetlands Research Group, CES, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012
| Contact Address : |
| |
Dr. T.V. Ramachandra
Energy & Wetlands Research Group,
Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
Tel : 91-80-23600985 / 22932506 / 22933099
Fax : 91-80-23601428 / 23600085 / 23600683 [CES-TVR]
E-mail : tvr@iisc.ac.in, energy@ces.iisc.ac.in,
Web : http://wgbis.ces.iisc.ac.in/energy |
|