| Sahyadri Conservation Series: 23 |
ENVIS Technical Report: 53, May 2013 |
 |
Status of Forest in Shimoga District, Karnataka |
 |
1Energy and Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560012, India.
2Member, Western Ghats Task Force, Government of Karnataka, 3Member, Karnataka Biodiversity Board, Government of Karnataka
*Corresponding author: cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in
FOREST ENCROACHMENTS IN SHIMOGA DISTRICT
As per Section 32 of the National Forestry and Tree Planting Act (NFTPA) of 2003 encroachment is the entry of people with their activities into forest reserves without permission. The entry can be deliberate or unknowingly for the purpose of grazing cattle, cultivation, settlement, construction or any other human activities(National Forestry Authority http://www.nfa.org.ug). At present forest encroachment is the major threat to biodiversity because it not only causes the habitat loss of species but also results in the more devastating effects through fragmentation.The encroachment of forest land for agricultural purposes is mainly because of relatively rich and virgin forest soils. However leaching in forest soils is much faster when exposed to the high temperatures and heavy rainfall of the tropical region and gets exhausted much faster. These factors force the encroachers to open new land annually.Forest encroachment will result in several ecological and economic effects. The ecological effects of forest encroachment will include; reduction in the forest cover, forest fragmentation, reduction in forest biodiversity, changes in vegetation type (composition and abundance), curtailment of natural regeneration of the forest, spread of invasive alien species, destruction of ecosystems/habitats, species extinction, etc. The economic effects of forest encroachment will include reduction in the quality and quantity of products from forests, reduction in the Total Economic Value (TEV) of the forests, increases the cost of forest management
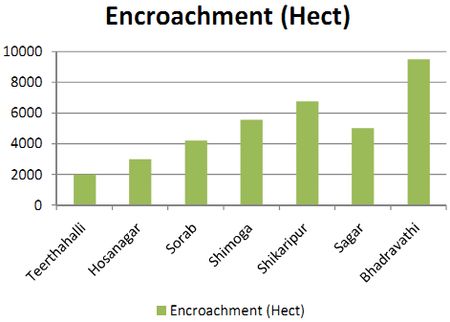
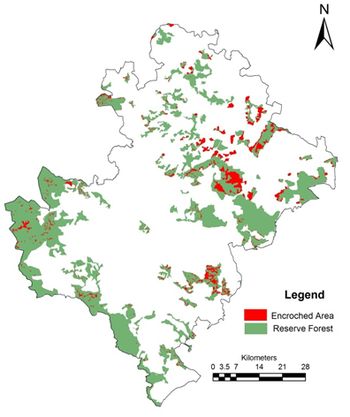
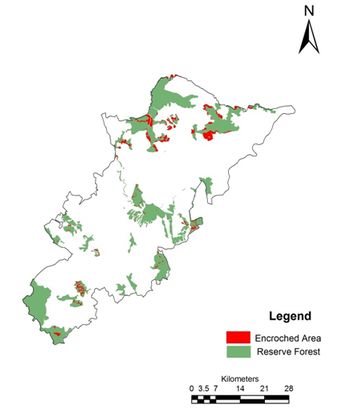
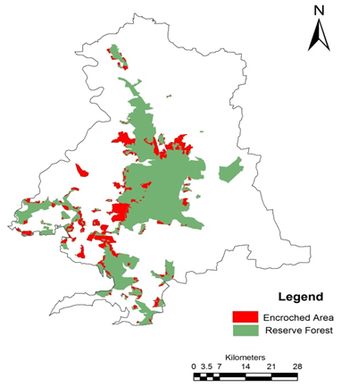
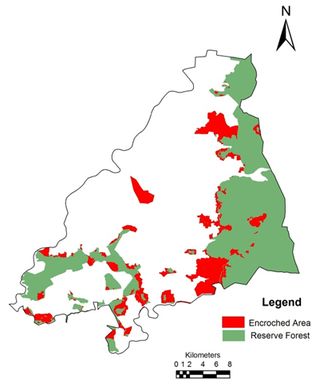
Forest vegetation decreased from 43.83% (1973) to 22.33% (2012). The results highlight conversion of forests to agriculture, industrial and cascaded developmental activities acted as major driving forces of degradation.Forest fragmentation analysis indicated that domination of forests receded during post 90’s with the formation of patch and edge forest in all three divisions. Land use changes from forests to non-forests with intensified human interference had been very high especially in Bhadravathi division. Interior forest decreased by 12% during 4 decades. The extent of interior forests ranges from 12.91 (Shimoga) followed by 4.76 (Sagar) and 3.79 % (Bhadravathi). During the last four decades the interior forest declined from 22.9 (1973) to 13 % (2012) in Shimoga, and 15.90 (1973) to 4.76% (2012) in Sagar, and 4.10 (1973) to 3.79 % (2012) in Bhadravathi divisions. Encroachment of forest land (36105 hectares) and conversion to agricultural land is the principal cause of degradation at local levels apart from land releases for major developmental activities. Table 1 lists talukwise encroachment of forest land in Shimoga. Bhadravathitalukhas highest number of encroachments (26.36%), followed by Shikaripur (18.77), Shimoga (15.42), Sagar (13.92), Sorab (11.66%), Hosanagar (8.35%), and Teerthahalli (5.51%). Figure 1 depicts the locations of encroachment in the district (talukwise) while Figure 2 provides the spatial distribution of divisionwise encroachment.
|
Total Encroachment |
|
| Taluk |
Acres |
Hectares |
| Teerthahalli |
4917.15 |
1990.75 |
| Hosanagar |
7448.09 |
3015.42 |
| Sorab |
10399.12 |
4210.17 |
| Shimoga |
13751.08 |
5567.24 |
| Shikaripur |
16738.40 |
6776.68 |
| Sagar |
12416.79 |
5027.04 |
| Bhadravathi |
23508.72 |
9517.7 |
| Total |
89179.35 |
36105.00 |
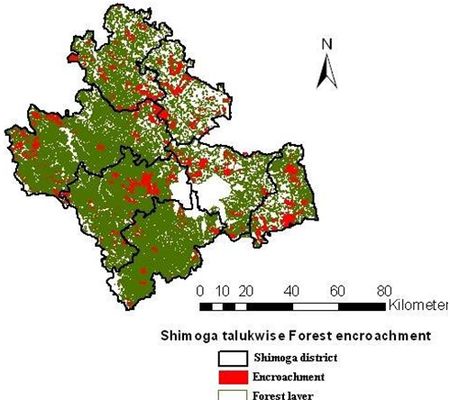
Figure 1: Spatial distribution of forest encroachments in Shimoga
|
|
T.V. Ramachandra
Centre for Sustainable Technologies,
Centre for infrastructure, Sustainable Transportation and Urban Planning (CiSTUP),
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail : cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in
Tel: 91-080-22933099/23600985,
Fax: 91-080-23601428/23600085
Web: http://ces.iisc.ac.in/energy
Subash Chandran M.DEnergy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail:
mds@ces.iisc.ac.in
Sudarshan P. Bhat
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail:
bhat.sudarshanp@gmail.com
Bharath H. Aithal
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail:
bharath@ces.iisc.ac.in
G. R. Rao
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail:
grrao1@gmail.com
Vishnu Mukri
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail:
vishnumukri@gmail.com
Citation: Ramachandra T.V, Subash Chandran M.D, Sudarshan P. Bhat, Bharath H. Aithal, Rao G.R. and Vishnu Mukri, 2013. Status of Forest in Shimoga District, Karnataka., Sahyadri Conservation Series 23, ENVIS Technical Report : 53, May 2013, Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560 012.
| Contact Address : |
| |
Dr. T.V. Ramachandra
Energy & Wetlands Research Group,
Centre for Ecological Sciences,
New Biological Sciences Building, 3rd Floor, E-Wing, Lab: TE15
Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
Tel : 91-80-22933099 / 22933503(Ext:107) / 23600985
Fax : 91-80-23601428 / 23600085 / 23600683 [CES-TVR]
E-mail : cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in, energy@ces.iisc.ac.in,
Web : http://wgbis.ces.iisc.ac.in/energy |