ENVIS Technical Report: 89, July 2015 |
 |
Biodiversity, Ecology, Energy, Landscape Dynamics & Hydrology of Agastya Foundation Campus, Kuppam
| 
|
| Ramachandra T. V.* |
Harish R.Bhat |
Bharath H. Aithal |
Rao G. R. |
Sudarshan P.Bhat |
| Vinay S. |
Ganesh Hegde |
Gouri Kulkarni |
Vishnu D. Mukri |
|
|
Kingdom |
Animalia |
Phylum |
Arthropoda |
Class |
Arachnida |
Order |
Araneae (Spiders) |
Suborder |
Mygalomorphae and Araneomorphae |

|

|
Spiders with more than 41000 species occur almost everywhere in the globe. They are able to live in all climate zones, in or on water, air and ground. Spiders are related to scorpions, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, ticks and mites, all are ARACHNIDS, 8-legged animals. These arachnids are generally predators (catch live prey), except for some parasites (ticks and some mites). Spiders come in many different sizes, shapes and colours, and exist everywhere. Spiders are known for their venom and silk.
- VENOM is used in attack and defense: to catch live food, and to protect against predators, parasites, and aggressive relatives. Most spider venom is completely harmless to humans, and only very few spider species can be lethal to people.
- SILK: Spiders are unique for possessing silk glands; 3 pairs of spinnerets used for silk production. Spider silk is an elastic, strong and sometimes adhesive material. Spiders use silk for many purposes: to protect their young, catch food, make homes and move around. They are the only animals that use silk in almost every part of their daily lives. Silks differ depending on the temperature and speed at which they are spun, on the spider’s diet, and on the purpose of the silk.
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
Agelenidae (FUNNEL WEB SPIDERS) |
Genus |
Agelena (2 genera have been reported from India) |
Species |
515 species worldwide, 10 are reported from India |
>  |
Morphological characters: |
8 eyes, hairy bodies and long legs, oval abdomens (rear part) with elongated last pair of spinnerets. |
Habitat preference |
grasslands, meadows, gardens and house walls. |
Web |
irregular and flat sheet-like web, with a tube extending from one edge to a retreat; the funnel in which the spider awaits for prey. |
Prey preference: |
walking and jumping insects. |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
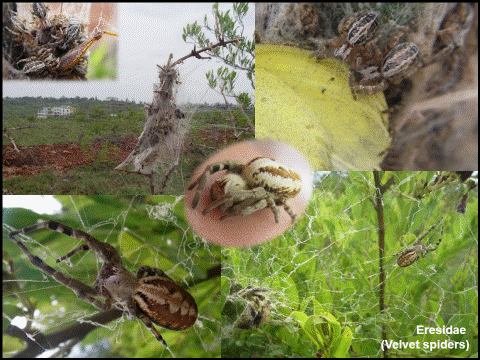
Eresidae |
Genus |
Stegodyphus is the only genus reported from India |
Species |
100 species, 4 of which are reported from India |
|
Morphological characters: |
8-eyes, robust looking spiders with a square cephalothorax (head region), body covered with hair, giving a velvet appearance. |
Habitat preference: |
ground or bushes, shrubs and trees |
Web: |
sock-like silken retreat in the ground, or sheet webs on bushes, shrubs and trees connected to a small tubular or large irregular retreat |
Prey preference: |
insects |
3 species are social, live in groups like ants, take care of common young, catch prey and feed together, and maintain the web together. Colonies of one of these species are easy to spot in bushes and trees around Agastya campus. |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
Araneidae (ORB WEAVERS) |
Genus |
Argiope, Araneus, Cyclosa, Cyrtophora, Gasteracantha and others (29 genera are reported from India) |
Species |
3000 species worldwide, 154 are reported from India |

|
Morphological characters: |
8-eyes with long hairy legs, very large abdomen (rear end of the body), that are brightly colored with various patterns, and sometimes irregularly shaped |
Habitat preference: |
grasslands, meadows, gardens, forests |
Web: |
an orb web is a circularly shaped web, constructed in a spiral way. The web is made of silk which spiders developed for the specific purpose of trapping flying insects, and it can reach great sizes. Spiders sometimes add decorations in form of denser silk in different patterns, or leaves, branches or stones |
Prey preference: |
flying insects |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
Oxyopidae (LYNX SPIDERS) |
Genus |
Oxyopes, Peucetica and others (4 genera are reported from India) |
Species |
430 species worldwide, 69 of which are reported from India |

|
Morphological characters: |
8-eyes with slender abdomens and extremely spiny legs. |
Habitat preference: |
plants, flowers and shrubs |
Web: |
these are actively hunting spiders without a catching web. They chase or ambush prey. Some hide in flowers and jump to catch flying insects. |
Prey preference: |
Lynx spiders are important in agricultural systems as biological control agents, as they feed on pest insects |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
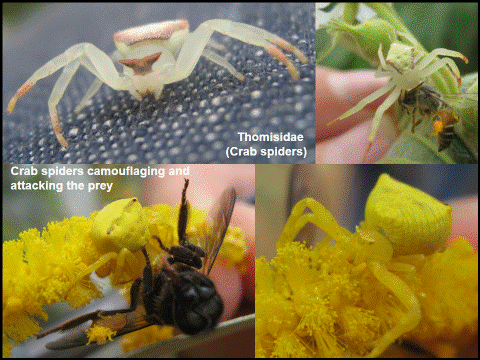
Thomisidae (CRAB SPIDERS) |
Genus |
Thomisus and others (38 genera are reported in India) |
Species |
2120 species worldwide, 164 are reported in India |
|
Morphological characters: |
8-eyes, squat shaped spiders, which move sideways. The first 2 pairs of legs are larger, stouter and spinier than the last 2 pairs. Many species are pink, yellow or white and camouflage the flowers they occupy |
Habitat preference: |
Gardens and meadows, mainly on flowers, but sometimes on tree barks. |
Web: |
These spiders have no catching web as they ambush prey. |
Prey preference: |
Mainly pollinators (flying insects visiting flowers) |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
Sparassidae (GIANT CRAB SPIDERS) |
Genus |
Heteropoda, Olios and others (11 genera are reported from India) |
Species |
1093 species worldwide, 85 are reported from India |

|
Morphological characters: |
8-eyes, medium to large sized spiders with long legs and are often camouflaged. They run sideways and are active during the night. |
Habitat preference: |
ground litter or dry leaves and tree trunks |
Web: |
they build silken retreats, but do not spin webs |
Prey preference: |
Cockroaches |
Suborder |
Araneomorphae |
Family |
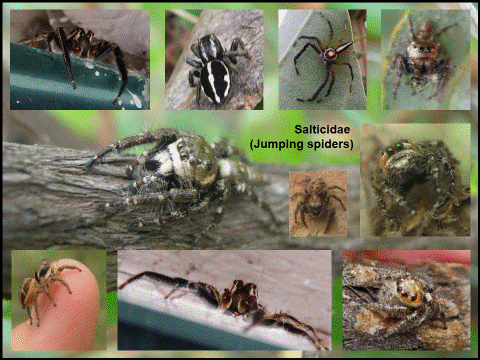
Salticidae (JUMPING SPIDERS) |
Genus |
Carhotus, Salticus and others (66 genera are reported from India) |
Species |
5300 species worldwide, 192 of which are reported in India |
|
Morphological characters: |
8 eyes in 2 rows (4+4) with an excellent eyesight, two of their eyes are conspicuously large; small to medium sized very hairy spiders of various colors They are active during the day. |
Habitat preference: |
Litter, grassland, bushes, trees, rocks and under stones |
Web: |
They make a silk safety line while jumping and moving around, but do not spin a web. |
Prey preference: |
They actively stalk and attack insects, like ants, or other spiders. |
| |










