|
Agastya foundation campus is located at Kuppam. Monthly rainfall variation is depicted in figure 1. The region receives about 626 mm annual rainfall and mostly during north eastern monsoon.
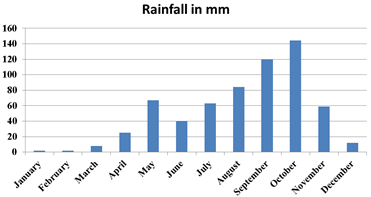
Figure 1. Rainfall dynamics in Agastya Foundation
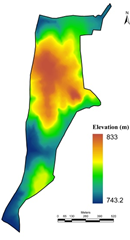
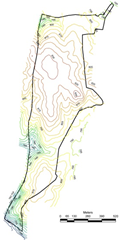
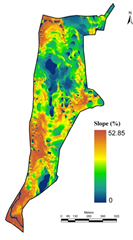
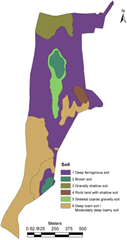
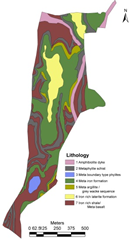
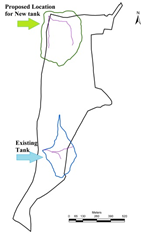
The digital elevation model (figure 2a) was developed using the contour information (figure 2b) provided by Agastya foundation. Figure 2c depicts the slope variation based on the digital elevation model generated using CARTOSAT 2.5 m spatial resolution data. This aided in order to delineate the stream network. Figure 2d depicts the soil profile and Figure 2e gives the lithological details of the campus. Integration of these spatial data aided in the identification of locations (Figure 2f) suitable for optimal harvesting of rainwater. This also helps in addressing water stress in the campus during post monsoon. Among these two locations, lake/tank already exists in the campus behind discovery center (near the Karnataka border). The catchment of this lake is about 8.03 Ha (19.85 acre), with catchment yield of about 25 million liters. A new lake is proposed across two streams that connects near the north western boundary. This lake will have catchment area of 16.05 Ha (36.68 acre), with yield of 50 million liters (with an annual rainfall of 320 mm). Table 1 provide the information of different depths of the tank with water holding capacities
.
Table 1: Volumetric storage in relation with bund height
FRL |
Depth (m) |
Surface Area(sq.m) |
Volume (cum) |
775.25 |
0.00 |
|
0.00 |
777.5 |
1.75 |
76.05 |
42.19 |
780 |
4.25 |
161.02 |
847.13 |
782.5 |
6.75 |
2736.89 |
6213.52 |
785 |
9.25 |
4226.2 |
14062.23 |
787.5 |
11.75 |
6275.38 |
26562.52 |
790 |
14.25 |
9291.98 |
43930.35 |
|
|
|
a.Digital Elevation Model |
b. Contour Map |
c. Slope |
|
|
|
d. Soil |
e. Lithology |
f. Catchment and drainage |
Figure 2: Topography
Proposed lake/tank in the campus:
- The sub surface is gravelly, and drains of water easily, it is recommended to use clay soil for pitching up to the FRL with minimal thickness over 25 to 30mm, compacted and supported by grasses (the same can be made for all the ponds in the campus in order to avoid seepage of water to the substrata).
- Depth of about 11 m would have storage capacity of 26 Million liters.
- Slope of the shore could be 1:100 and with grass turfing to enhance hydrological function of the shore
- Riparian vegetation of native species helps (mix of shrubs and tree species suitable for aquatic ecosystems) in rejuvenating water sources.
- Watershed based approach with plating of native species of grass, shrub and trees in the catchment would aid in the infiltration of water as well as retaining of water.
- RCC based arch dam (instead of earthen gravity dam) taking advantage of valley (for the existing lake same could be followed).
| 







