Dr. T.V. Ramachandra
Centre for Sustainable Technologies, Centre for infrastructure, Sustainable Transportation and Urban Planning (CiSTUP), Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA. E-mail : tvr@iisc.ac.in Tel: 91-080-22933099/23600985, Fax: 91-080-23601428/23600085 Web: http://ces.iisc.ac.in/energy
Bharath H. Aithal
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA. E-mail: bharathh@iisc.ac.in
Bharath Setturu
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA. E-mail: setturb@iisc.ac.in
Vinay .S
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA. E-mail: svinay@iisc.ac.in
Citation:Ramachandra T V, Bharath H Aithal, Bharath Setturu, Vinay S, 2018, Waste Management, ENVIS Technical Report 143, ENVIS, CES, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012, Pp 312.
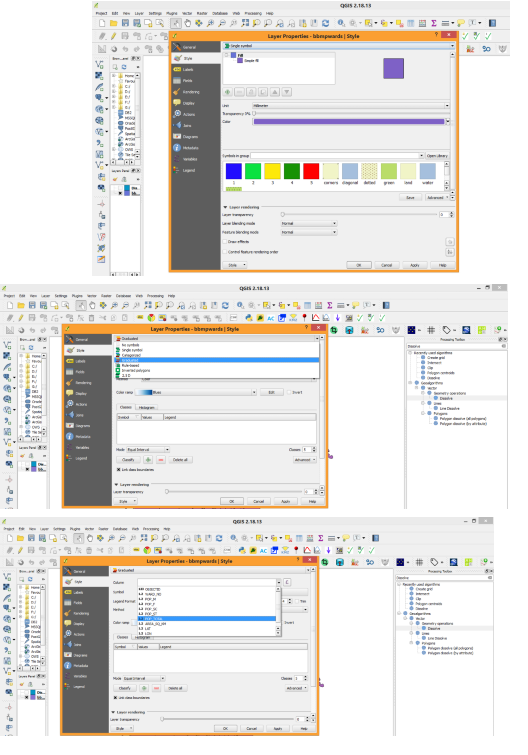
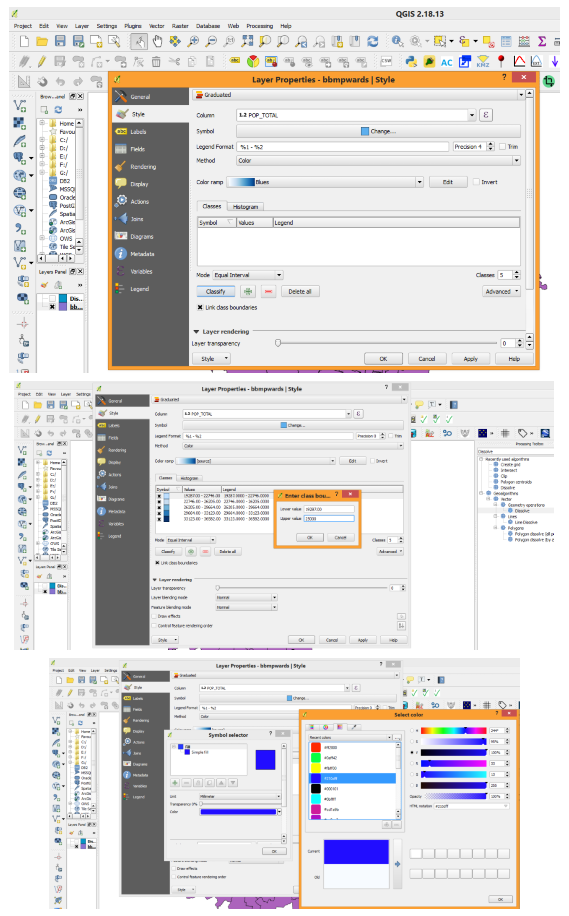
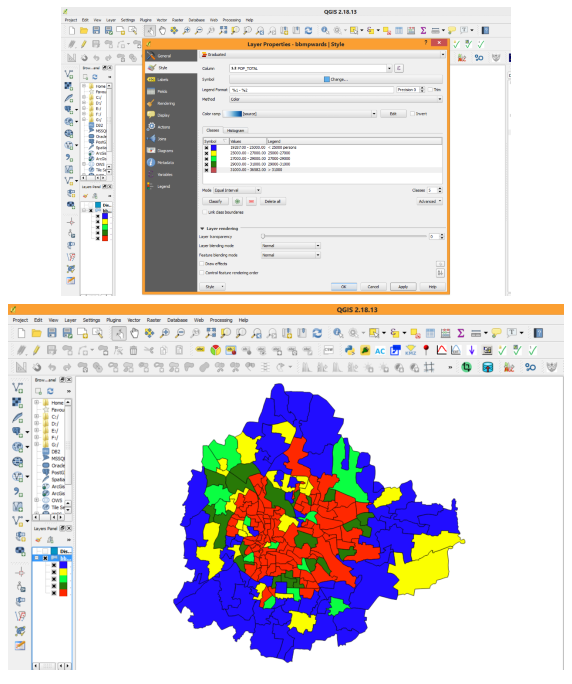
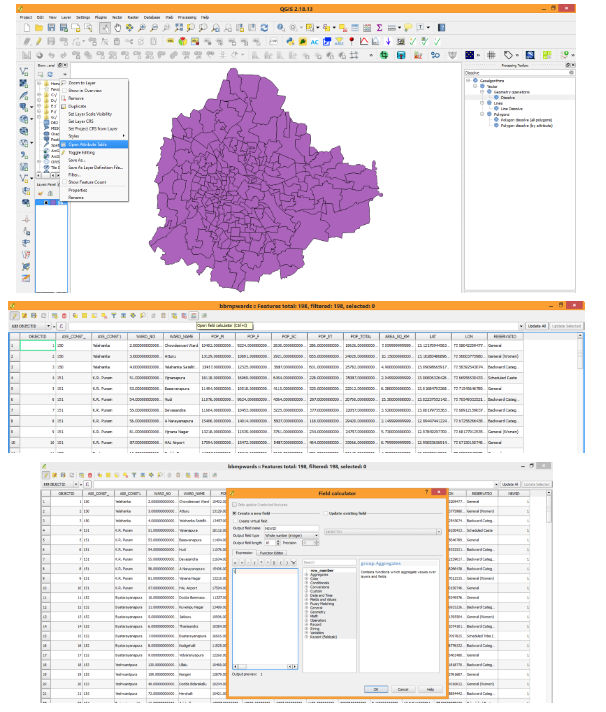
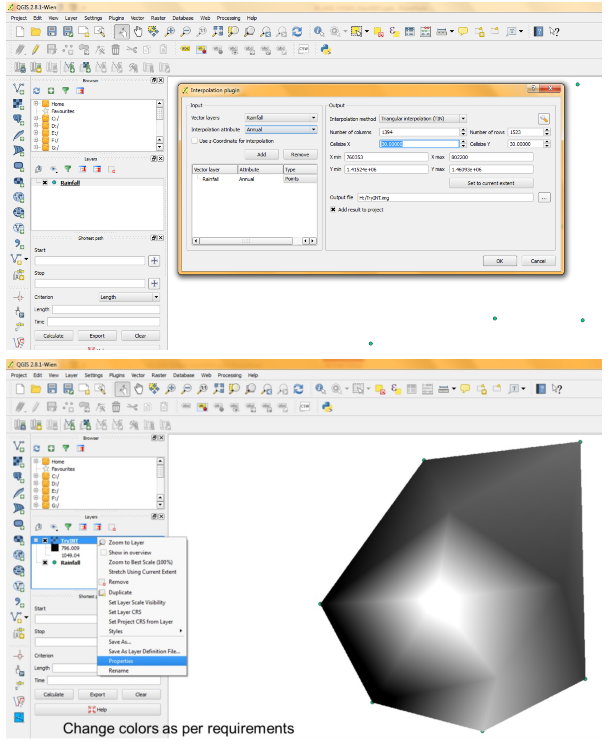
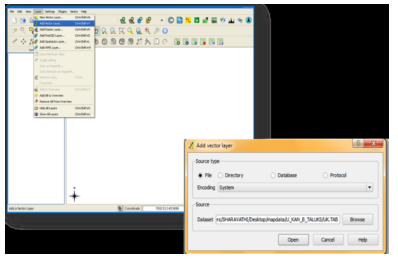
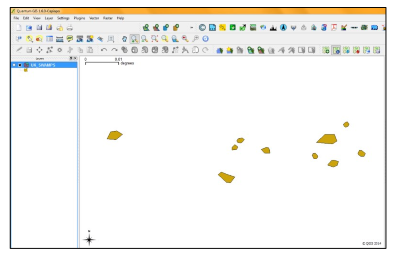
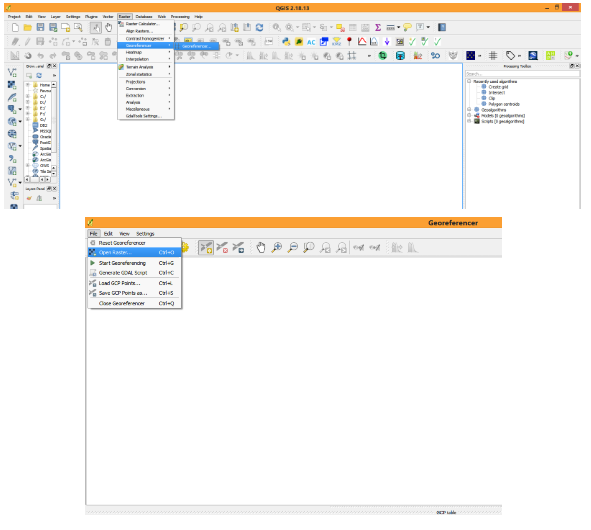
| ||||||||||||||||||||||