|
Pollution Monitoring in Urban Wetlands of Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu
|
 |
Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore
Web: http://ces.iisc.ac.in/energy/, http://ces.iisc.ac.in/biodiversity Email: cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in, energy@ces.iisc.ac.in
|
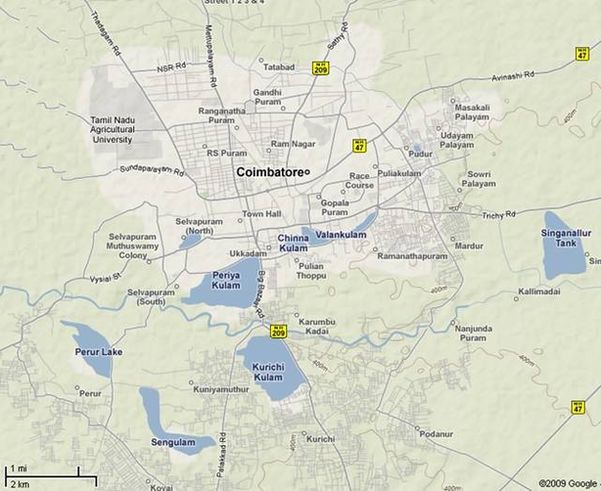
Study Area Coimbatore also referred popularly as Manchester of India is an important industrial city, located in Tamil Nadu (10°55’-11°10’ N, and 77°10’ - 76°50’ E) at an average altitude of 470m, ranking 11th in terms of population (Figure 1). There are more than 30,000 small, medium and large industries including textile mills and foundries in the city employing about 40% of the population. The growing industrial sector and ensuing immigration of people pose heavy burden on the city infrastructure that did not grow in proportion. The city does not have facilities for treatment of industrial, municipal and domestic wastes. Wetlands and Noyyal River have been used for disposal of wastes of the city. Natural drainage networks have been converted to storm water drains for letting the sewerage into wetlands without any treatment. In Coimbatore city there are 28 wetlands, mostly fed by the river Noyyal. The river, flowing through the city on its south, originates in the Vellingiri hills in Western Ghats, located on the south-western side of the city. Some of these wetlands are seasonal and have also been used as dumping yard for garbage and industrial wastes during dry period (Mohan Raj et al., 2000). During the monsoon, with the inflow of water, this activity leads to contamination of groundwater sources. Six wetlands selected for biomonitoring (Figure 1) are: Vedapatti (VPP), Pallapalayam (PPL), Sundakamuthur (SMS), Perur (PRP), Noyyal (NLP) and Singanallur (SNP).
|
Citation: Karthick B, Alakananda B, and Ramachandra T V, 2009. Diatom Based Pollution Monitoring in Urban Wetlands of Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu. ENVironmentl Information System (ENVIS) Technical Report No. 31. Centre for Ecological Science, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore |
|
| E-mail | Sahyadri | ENVIS | GRASS | Energy | CES | CST | CiSTUP | IISc | E-mail | |