|

|
|

VARIATION OF A NUTRIENT IN A TAIL REACH DRAIN AREA OF AN AGRICULTURAL FIELD
S. Suraj Kumar1 and M. Manoj Kumar2

|

|
|


 ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
 INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
 METHODOLOGY:-I. INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
METHODOLOGY:-I. INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
 II. ANALYSIS OF SOIL SAMPLES
II. ANALYSIS OF SOIL SAMPLES
 III. WELL-WATER ANALYSIS
III. WELL-WATER ANALYSIS
 CONCLUSION
CONCLUSION
 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
 REFERENCES
REFERENCES
 TABLE 1: INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
TABLE 1: INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
 TABLE 2A: SOIL ANALYSIS PRIOR TO APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
TABLE 2A: SOIL ANALYSIS PRIOR TO APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
 TABLE 2B: SOIL ANALYSIS AFTER APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
TABLE 2B: SOIL ANALYSIS AFTER APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS
 TABLE 3: GROUND WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
TABLE 3: GROUND WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS
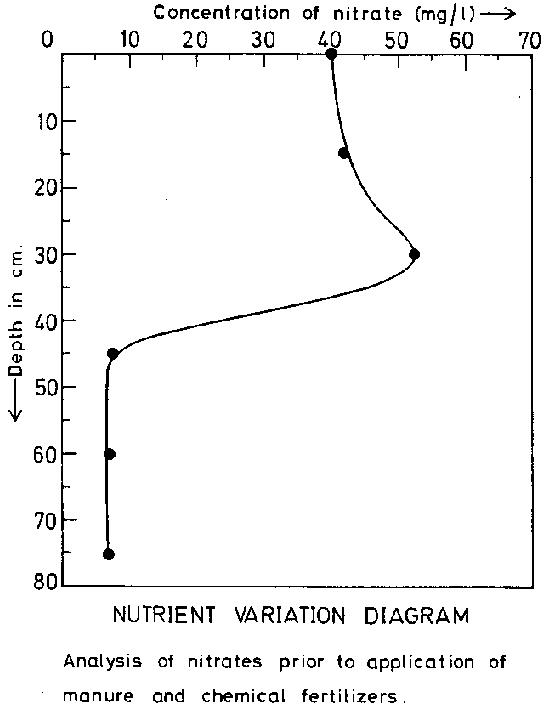
 FIGURE-1: NUTRIENT VARIATION DIAGRAM
FIGURE-1: NUTRIENT VARIATION DIAGRAM
| ABSTRACT: |




|
Nitrates and total dissolved solids considered as the main nutrient parameters are analyzed in the agricultural field. These nutrients have their sources originating from water from the lake, field solids, organic manure and fertilizers by the farmers. These nutrients percolate at a considerable rate and have all chances of deteriorating ground water quality. High nitrate concentration in drinking water causes health hazards. Hardness of water also increases as concentration of total dissolved solids increases. This investigation is carried out in agricultural fields, which are irrigated by Mandakalli lake (located near Mysore city). Domestic requirement such as drinking, etc. is met through ground water from bore wells.
The inlet leading to these agricultural fields has been measured for nitrates and total dissolved solids (TDS). The soil samples in a trial pit in the tail reach area have also been analyzed at different depths for nitrates (for variation of nitrates) prior to and after application of organic manure and chemical fertilizers.
| INTRODUCTION: |




|
Water constitutes one of the important physical environments of man, having direct bearing on his health. Water is precious to man and therefore WHO refers to "Control of Water Supplies to ensure that they are pure and wholesome" as one of the principal objectives of environmental sanitation. But every area on earth does not receive treated, pure and wholesome water. Water sources (surface and ground) have become increasingly contaminated due to industrial and agricultural activity (Veissman and Hammer, 1993).
This study deals with an approach to estimate the variation in concentration of nitrate and TDS in the tail reach drain area of an agricultural field and to assess the quality of ground water source in a particular area. The study site is located near Mandakalli lake in Mysore district. The lake water is utilised for agricultural activities.
This lake receives water mainly from rain, and fishery is undertaken by private agencies throughout the year. This has led to contamination of water, due to the addition of nutrients for fish. All agricultural fields nearby derive water from this lake for irrigation. Paddy is grown in almost all command areas. Water is completely absorbed in the tail end of fields without joining any stream. This water is partly utilized in the fields and the rest percolates into the soil strata reaching the ground water. The farmers use manure and chemical fertilizers in their fields, which have nitrates as their main nutrient. The residual nitrates and other nutrients get into the soil layers. Water, which percolates and joins ground water extracts nitrate from soil and contaminates the ground water (Sawyer et al., 1994). Residents in this area use ground water through open wells and bore wells for drinking and other domestic purposes. Nitrates and total dissolved solids in the groundwater need to be estimated as it is used for cooking and washing purposes.
| OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY: |




|
The objectives of this study are:
To study and analyze the objectives mentioned above, the water quality at the inlet to the field has been analyzed for nitrates and TDS. The soil samples in a trial pit in the tail reach drain area have also been analyzed at different depths to know the variation of nitrates and TDS prior to and after application of manure and chemical fertilizers. To assess the input of these parameters on the ground water quality, the water samples from open wells nearby have also been analyzed.
|
METHODOLOGY:
I. INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS |




|
The water sample at the inlet to the agricultural field from the lake has been collected and analysed for nitrates and TDS. Nitrates have been analysed by PDA method and total dissolved solids by gravimetric method (APHA 1995).
The results of the analysis, given in Table 1, show the concentration of nitrates as almost negligible (as it is below detectionable limit (BDL)). According to WHO standards, the standard specified for nitrates in water is 10 mg/l. The concentration of TDS is 460 mg/l which is also tolerable as the limit specified for water to be utilized for all purposes should be less than or equal to 500 mg/l.
| II. ANALYSIS OF SOIL SAMPLES |




|
Tail reach drain area of the agricultural field was identified and an area of 60cm x 60cm was set up. Soil samples were collected in polythene bags starting from ground level vertically downwards with an interval of 15cm. Six samples were collected up to a depth of 75cm. This has been done prior to and after the application of manure and chemical fertilizers.
The soil samples have been dried and sieved using mechanical shaker and the residue of 150mm diameter has been used for soil extraction for further analysis of nitrates and TDS. The results are given in Table 2. According to the results obtained, the concentration of the nitrates increases significantly to a certain depth and constantly decreases at higher depths. The profile of this nutrient variation diagram is shown in Fig. 1[Nutrient Variation Diagram 1].
| III. WELL-WATER ANALYSIS |




|
A sample of the nearby well water was collected to analyze the concentration of nitrates and TDS in ground water. It was observed from the analysis that the water contains 9.5 mg/L of nitrates, which is below objectionable limits. The major part of nitrate concentration in this water is due to the application of nitrate rich fertilizers. The TDS concentration was found to be 650 mg/L, which is higher than the acceptable limits of 500 mg/L (Table 3).
| CONCLUSION: |




|
The study broadly reveals the following:
1. It is found that the characteristics of soil below the agricultural land attenuates nitrates to a greater extent and prevents the contamination of ground water.
2. The ground water quality confirms the attenuation capacity of the soil (9.5 mg/l < 10mg/l).
3. During peak application of chemical fertilizers there may be chances for the nitrate level to exceed the prescribed limits at certain depths.
4. The analysis of TDS confirms that the ground water is moderately hard (650 mg/l > 500 mg/l).
5. The scope of this study is limited. Intensive study for variation of other nutrients like phosphates, sulfates, chlorides, etc., can be carried out to assess the ground water quality.
| ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: |




|
We sincerely thank our beloved Principal, SJCE, Mysore for having provided the laboratory facilities. We also thank Dr.H.S.Ramesh, Prof. Department of Environmental Engineering, for having given us the moral support.
| REFERENCES: |




|
| TABLE 1: INLET WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS |




|
|
Nutrients |
Concentration (mg/L) |
|
Nitrates |
BDL |
|
TDS |
460 |
| TABLE 2A: SOIL ANALYSIS PRIOR TO APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS |




|
|
Depth (cm) |
Nitrate concentration (mg/L) |
TDS concentration (mg/L) |
|
0 |
40 |
100 |
|
15 |
42.1 |
103.4 |
|
30 |
52.5 |
99.23 |
|
45 |
7.5 |
122.53 |
|
60 |
7.2 |
143.6 |
|
75 |
7.1 |
151.723 |
| TABLE 2B: SOIL ANALYSIS AFTER APPLICATION OF MANURE AND CHEMICAL FERTILIZERS |




|
|
Depths (cm) |
Nitrate concentration (mg/L) |
TDS concentration (mg/L) |
|
0 |
43.6 |
93.2 |
|
15 |
50.0 |
91.43 |
|
30 |
32 |
103.62 |
|
45 |
9.5 |
119.52 |
|
60 |
9.2 |
152.2 |
|
75 |
9 |
151.6 |
| TABLE 3: GROUND WATER QUALITY ANALYSIS |




|
|
Nutrients |
Concentration (mg/L) |
|
Nitrates |
9.5 |
|
TDS |
650 |
| FIGURE-1: NUTRIENT VARIATION DIAGRAM |




|
| ADDRESS: |


|
1.) B.E. (5th semester) Student,
Department of Environmental Engineering,
SJCE,
Mysore,
Karnataka,
India.
2.) M.Tech (III Semester) student,
Department of Environmental Engineering,
SJCE,
Mysore,
Karnataka,
India.
|
|