|
Faunal assemblages in Myristica swamps of Central Western Ghats, Karnataka, India |
 |
| Sameer Ali, M D Subash Chandran and T V Ramachandra Energy and Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560 012 E Mail: cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in |
| Citation: Sameer Ali, Subash Chandran M. D. and Ramachandra T. V., 2008. Faunal assemblages in Myristica swamps of Central Western Ghats, Karnataka, India, In Environment Education for Ecosystem Conservation, Ramachandra (ed.), Capital publishing company, New Delhi, Pp 94-112. |
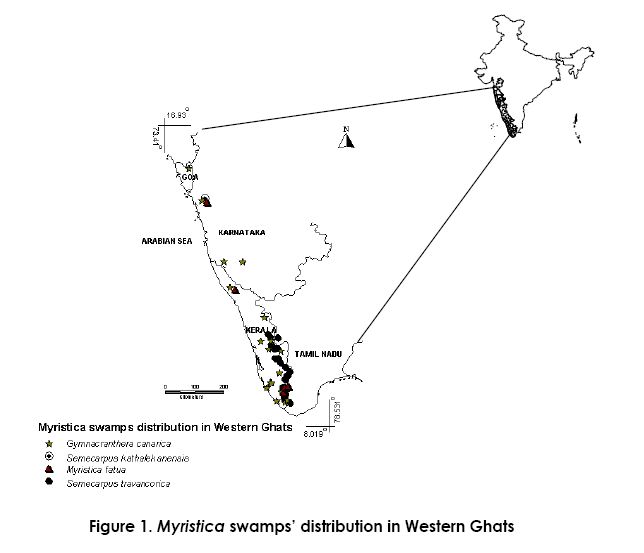
Introduction Tropical forests, which harbour most of the world’s plant diversity, continue to be destroyed at unprecedented rates (Myers et al., 2000; Pittman & Jorgenson 2002). The faunal species associated with these forests are also affected due to one or another reason. The wet evergreen forests of the Western Ghats of India are one of the global biodiversity hotspots, being rich in biodiversity and endemic species (Myers et al., 2000), it is also under the threat of deforestation. It harbours some of the relic elements in the remnant forests, which are in patchy distribution. Myristica swamps are one such threatened ecosystems occurring in these remnant forests of Western Ghats. They are undoubtedly priceless assets for the evolutionary biologist, since many features of Myristicaceae are primitive in origin and hence regarded as ‘living fossils’. What are Myristica swamps? Myristica swamp is any freshwater swamp where any one or both of the exclusive swamp growing trees of the family Myristicaceae namely Gymnacranthera canaria or Myristica fatua var. magnifica are present. These swamp species may occur in association with some other, usually evergreen trees having varied degrees of flood tolerance. Distribution of Myristica swamps Varghese and Kumar (1997) differentiate between two types of swamps having Myristicaceae, in the Travancore region: 1. Myristica swamp forest, restricted to below 300 m, fringing sluggish streams. 2. Tropical sub-montane hill valley swamp forest- found as narrow strips of water-logged areas. Whereas, the former has M. fatua as well as G. canarica, in the latter, G. canarica is found along with Mastixia arborea and several others. Such bifurcation of these swamps does not have enough justification. The Atlas of Endemics of the Western Ghats (India) by Ramesh and Pascal (1997) shows that G. canarica and M. fatua occur from sea level to 700 m and 1000 m altitudes respectively. More detailed studies on the Myristica swamps of Uttara Kannada in Central Western Ghats have been made recently. These swamps are isolated and situated in localities from near sea level to about 450 m altitude (Figure 1)(Chandran et al., 1999; Chandran and Mesta, 2001).
|
| E-mail | Sahyadri | ENVIS | GRASS | Energy | CES | CST | CiSTUP | IISc | E-mail |