SEDIMENTATION RATES
In the sludge settling experiments, it was observed that the
sediments near the inlet regions in zones Z1 and Z2 were
consisted of 3 different types of sludge. However the
sediments near the outlet regions were similar. In the non-
monsoon seasons (08) the sludge near the high flow regions
were having a higher C content (which is attributed to
particulate organic matter and rapid sludge formation). The
sludge near the inlet zones was highly organic as seen in the
earlier (Dec, 08 samples) but as we approach towards the
outlets an improved and a matured sludge (Fig. 9) was
observed. This is primarily due to unprecedented discharge of
untreated sewage and due to external input from the catchment
and surface run off which is in agreement with earlier studies
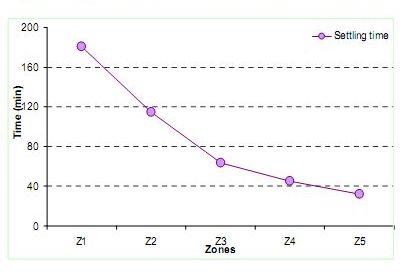
[31]. Figure 10 shows the time taken for the sludge for 90%
settling. It is well observed that the sludge settles fast near the
outlets unlike the inlet where it takes a much longer time.
However the Organic content of the sludge was found to be
significantly higher in Dec, 09 which showed a higher organic
C content throughout and was more prominent towards the
bund region and the outlets. This links to the morphometry of
the lake which has the deepest portions near the bund. The
sedimentation rate is lowest in the deepest part of the lake, but
increases progressively towards the inlets and the shorelines on
either side of the lake.
Figure 9. Correlation between % C and % N content in the sediments
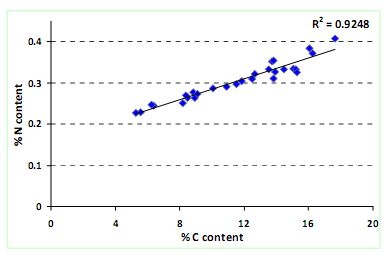
Figure 10. Time required for 90% of the sludge for settling