| Back | Materials and Methods |
Next |
Biosorbent material
Bengal gram husk (bgh), seed coat of Cicer arientinum was collected from a legume seed-splitting mill. The bgh was washed extensively in running tap water to remove dirt and other particulate matter. Washing and boiling in distilled water repeatedly to remove colour followed this. The washed and boiled bgh was oven dried at 105º C for 24 hrs, stored in dessicator and used for biosorption studies in the original piece size.
Preparation of stock solution
An aqueous stock solution (1000 mg/l) of Cr (VI) ions was prepared using K2Cr2O7 salt. pH of the solution was adjusted using 0.1 N HCl or NaOH. Fresh dilutions were used for each study.
Biosorption studies
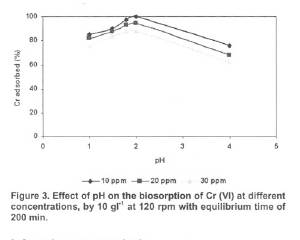
The biosorption capacity of bgh was determined by contacting various concentrations (10 - 100 mgl-1 ) of 100 ml Cr solution in 250 ml conical flasks, with 1 gram of bgh. The mixture was shaken in a rotary shaker at 120 rpm followed by filtration using Whatman filter paper (No. I). The filtrate containing the residual concentration of Cr was determined spectrophotometrically at 540 nm after complexation with 1,5 diphenylcarbazide (Eaton et al.1995). For the determination of rate of metal biosorption by bgh from 100 ml (at 10,20,50,100 mgl-1 the supernatant was analysed for residual Cr after the contact period of 15, 30, 60, 120, 180, 240 and 300 min. The effect of pH on Cr sorption by bgh was determined at pH values of 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7. The effect of different doses of bgh ranging from 1 to 40 g/l at varied Cr (VI) concentrations was determined.
Adsorption isotherm studies were carried out with thirteen different initial concentrations ranging from 20 to 600 mg/l of Cr (VI) while maintaining the adsorbent dosage at 1g/100ml. Langmuir and Freundlich models were applied to the adsorption isotherm and different constants were generated. The Langmuir and Freundlich adsorption parameters and correlation coefficient were also calculated from the adsorption isotherm data.
Infrared spectra analysis
In order to determine the functional groups responsible for metal uptake, an un-reacted bgh sample and bgh pre-treated with 100 mg/l chromium solution were analysed using a Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR). FTIR technique is used mainly to identify functional groups (like carboxyl, hydroxyl, etc.) that are capable of adsorbing metal ions.
All the experiments were carried out in triplicate and the mean values with standard deviation are presented. The maximum deviation was 2.0% (standard deviation ± 2%).