| |
ENVIS Technical Report: 86, February 2015 |
 |
FISH MORTALITY IN JAKKUR LAKE: CAUSES AND REMEDIAL MEASURES |
 |
Energy and Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560012, India.
*Corresponding author: cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in
|
|
Macrophytes, the aquatic macroscopic plants confine themselves to the shallow euphotic zone of the water bodies. In the littoral zone, macrophytes are the chief exploiters of plant nutrients from the sediments, which otherwise, are lost temporarily from the water. The nutrients so logged in the body material are released only after death, decay and subsequent mineralization, thus, they play a role in nutrient dynamics and primary productivity of shallow systems. Therefore, seasonal growth rate patterns and population dynamics of macrophytes are very important. Macrophytes grow profusely when there is enough room for colonization and abundant availability of nutrients,. They assimilate nutrients directly into their tissues. The inlet, middle, outlet and shoreline portion of lake is covered by macrophytes. There were mainly 7 species found in the lake. Alternanthera philoxeroides, Ludwigia perennis, Typha angustata, Cyperus sp, Lemna gibba, Eichhornia crassipes (water hyacinth), Pistia stratiotes were the main macrophyte species found in the lake (Figure 7). Alternanthera philoxeroides sand Eichhornia crassipes were the dominant macrophytes present in the lake. These indicate high amount of nutrient and other pollution load in the lake.Water hyacinth wide spread occurrence in the fresh water lakes is harmful to fishing (depleting DO) depleting water content from the water bodies and interfering in water utilization and other activities. Water hyacinth by its abundance of leaves, dense vegetation and innumerable rootlets in tertiary manner obstruct water flow and displaces many other macrophytes, and suppresses the phytoplankton growth.
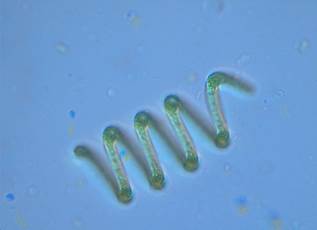
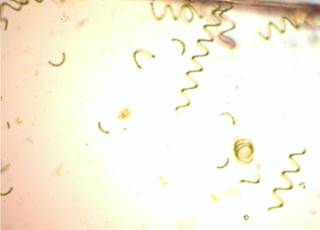
Algal specie found in the lake: During our earlier studies (Ramachandraet.al, 2013) there was a good diversity of algae (64 species) found in the lake. During this study the lake was dominated by Spirulina spp (figure 8).
Figure 7: Macrophyte found in Jakkur lake |

|

|
Alternanthera philoxeroides |
Ludwigia perennis |

|

|
Typha angustata in inlet |
Water hyacinth and Pistia in the middle |

|

|
Treated (in channel) and untreated sewage water entering the lake |
Untreated sewage inlet |

|

|
Died and decaying macrophytes and algae in the shoreline of lake |
Cyperus sp in the inlet of lake |

|

|
Thick algal growth in the middle of lake |
Macrophyte cover in the outlet of lake |
|
|
Figure 8: Algae (Spirulina spp) found in Jakkur lake |
|
T.V. Ramachandra
Centre for Sustainable Technologies, Centre for infrastructure, Sustainable Transportation and Urban Planning (CiSTUP), Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail : cestvr@ces.iisc.ac.in
Tel: 91-080-22933099/23600985,
Fax: 91-080-23601428/23600085
Web: http://ces.iisc.ac.in/energy
Sudarshan P.Bhat
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: asulabha@ces.iisc.ac.in
Sincy V.
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: sincy@ces.iisc.ac.in
Asulabha K S
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: sudarshan@ces.iisc.ac.in
Kruthika Lakkangoudar
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: bharath@ces.iisc.ac.in
Rahaman M.F.
Energy & Wetlands Research Group, Centre for Ecological Sciences, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore – 560 012, INDIA.
E-mail: bharath@ces.iisc.ac.in
Citation: Ramachandra T V, Sudarshan P. Bhat, Asulabha K S, Sincy V, Kruthika L. and Rahaman M F, 2015.Fish mortality in Jakkur lake: Causes and Remedial Measures, ENVIS Technical Report 86, CES, Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore 560012
| |