 |
Sankey Lake: waiting for an Immediate Sensible Action
| 
|
| T.V. Ramachandra* |
Asulabha .K S |
Sincy .V. |
Vinay .S |
Sudarshan p. Bhat |
Bharath H. Aithal
|
Wetlands (and lakes) constitute the most productive ecosystems with a wide array of goods and services. These ecosystems serve as life support systems; serve as habitat for a variety of organisms including migratory birds for food and shelter. They aid in bioremediation and hence aptly known as ‘kidneys of the landscape’. Major services include flood control, wastewater treatment, arresting sediment load, drinking water, protein production, and more importantly recharging of aquifers apart from aiding as sinks and climate stabilizers. The wetlands provide a low cost way to treat the community’s wastewater, while simultaneously functioning as wild fauna sanctuary, with public access. These ecosystems are valuable for education and scientific endeavours due to rich biodiversity.
Bangalore city (Karnataka State, India) has been experiencing unprecedented urbanisation and sprawl due to concentrated developmental activities in recent times with impetus on industrialisation for the economic development of the region. This concentrated growth has resulted in the increase in population and consequent pressure on infrastructure, natural resources and ultimately giving rise to a plethora of serious challenges such as climate change, enhanced green-house gases emissions, lack of appropriate infrastructure, traffic congestion, and lack of basic amenities (electricity, water, and sanitation) in many localities, etc. Temporal data analysis reveals that that there has been a growth of 925% in urban areas of Bangalore across four decades (1973 to 2013). Sharp decline in natural resources – 78% decline in trees and 79% decline in water bodies highlight unplanned urbanisation process in the city. Urban heat island phenomenon is evident from large number of localities with higher local temperatures. The city once enjoyed salubrious climate (about 14-16 °C during peak summer – May month in early 18th century), now has been experiencing higher temperatures (34 to 37° C) with altered micro climate and frequent flooding during rainy days. The study reveals the pattern of growth in Bangalore and its implication on local climate (an increase of ~2 to 2.5 ºC during the last decade) and also on the natural resources, necessitating appropriate strategies for the sustainable management of natural resources (water bodies, tree cover, etc.). The frequent flooding (since 2000, even during normal rainfall) in Bangalore is a consequence of the increase in impervious area with the high-density urban development in the catchment and loss of wetlands and vegetation.
Urban ecosystems are the consequence of the intrinsic nature of humans as social beings to live together (Ramachandra et al., 2012; Ramachandra and Kumar, 2008). The process of urbanisation contributed by infrastructure initiatives, consequent population growth and migration results in the growth of villages into towns, towns into cities and cities into metros. Urbanisation and urban sprawl have posed serious challenges to the decision makers in the city planning and management process involving plethora of issues like infrastructure development, traffic congestion, and basic amenities (electricity, water, and sanitation), etc. (Kulkarni and Ramachandra, 2006). Apart from this, major implications of urbanisation are:
- Loss of wetlands and green spaces: Urbanisation (925% concretisation or paved surface increase) has telling influences on the natural resources such as decline in green spaces (78% decline in vegetation) including wetlands (79% decline) and / or depleting groundwater table. Quantification of number of trees in the region using remote sensing data with field census reveal 1.5 million trees and human population is 9.5 million, indicating one tree for seven persons in the city. This is insufficient even to sequester respiratory carbon (due to breathing which ranges from 540 -900 g per person per day).
- Floods: Conversion of wetlands to residential and commercial layouts has compounded the problem by removing the interconnectivities in an undulating terrain. Encroachment of natural drains, alteration of topography involving the construction of high-rise buildings, removal of vegetative cover, reclamation of wetlands are the prime reasons for frequent flooding even during normal rainfall post 2000.
- Decline in groundwater table: Studies reveal the removal of wetlands has led to the decline in water table. Water table has declined to 300 m from 28 m over a period of 20 years after the reclamation of lake with its catchment for commercial activities. In addition, groundwater table in intensely urbanized area such as Whitefield, etc. has now dropped to 400 to 500m.
- Heat island: Surface and atmospheric temperatures are increased by anthropogenic heat discharge due to energy consumption, increased land surface coverage by artificial materials having high heat capacities and conductivities, and the associated decreases in vegetation and water pervious surfaces, which reduce surface temperature through evapotranspiration.
- Increased carbon footprint: Due to the adoption of inappropriate building architecture, the consumption of electricity has increased in certain corporation wards drastically. The building design conducive to tropical climate would have reduced the dependence on electricity. Adoption of building architecture unsuitable for Bangalore climate has contributed to higher electricity consumption and hence higher GHG (Greenhouse gases). Per capita electricity consumption in the zones dominated by high rise building with glass facades require 14000-17000 units (kWh) per year compared to the zones with eco-friendly buildings (1300-1500 units/person/year)Higher energy consumption, enhanced pollution levels due to the increase of private vehicles, traffic bottlenecks have contributed to carbon emissions significantly. Apart from these, mismanagement of solid and liquid wastes has aggravated the situation.
Unplanned urbanisation has drastically altered the drainage characteristics of natural catchments, or drainage areas, by increasing the volume and rate of surface runoff. Drainage systems are unable to cope with the increased volume of water, and are often blocked due to indiscriminate disposal of solid wastes. Encroachment of wetlands, floodplains, etc. obstructs flood-ways causing loss of natural flood storage.
Threats faced by Wetlands in Bangalore
The rapid development of urban sprawl has many potentially detrimental effects including the loss of valuable agricultural and eco-sensitive (e.g. wetlands, forests) lands, enhanced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions from increasing private vehicle use (Ramachandra and Shwetmala, 2009). Vegetation has decreased by 32% (during 1973 to 1992), 38% (1992 to 2002) and 63% (2002 to 2010).
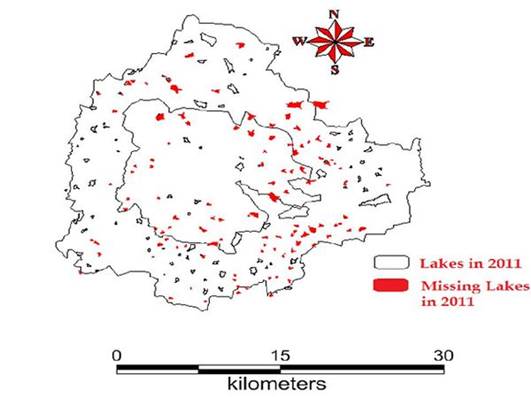
Figure 1: Lakes encroached by land mafia
Disappearance of water bodies or sharp decline in the number of water bodies in Bangalore is mainly due to intense urbanisation and urban sprawl. Many lakes (54%) were encroached for illegal buildings. Field survey of all lakes (in 2007) shows that nearly 66% of lakes are sewage fed, 14% surrounded by slums and 72% showed loss of catchment area. Also, lake catchments were used as dumping yards for either municipal solid waste or building debris (Ramachandra, 2009a; 2012a). The surrounding of these lakes have illegal constructions of buildings and most of the times, slum dwellers occupy the adjoining areas. At many sites, water is used for washing and household activities and even fishing was observed at one of these sites. Multi-storied buildings have come up on some lake beds that have totally intervene the natural catchment flow leading to sharp decline and deteriorating quality of water bodies. This is correlated with the increase in built up area from the concentrated growth model focusing on Bangalore, adopted by the state machinery, affecting severely open spaces and in particular water bodies. Some of the lakes have been restored by the city corporation and the concerned authorities in recent times. Threats faced by lakes and drainages of Bangalore:
-
Encroachment of lakebed, flood plains, and lake itself;
-
Encroachment of rajakaluves / storm water drains and loss of interconnectivity;
-
Lake reclamation for infrastructure activities;
-
Topography alterations in lake catchment;
-
Unauthorised dumping of municipal solid waste and building debris;
-
Sustained inflow of untreated or partially treated sewage and industrial effluents;
-
Removal of shoreline riparian vegetation;
-
Pollution due to enhanced vehicular traffic;
-
Too many para-state agencies and lack of co-ordination among them.
-
Different custodians for upstream and downstream lakes in the valley (Figure 2 and Table 1).
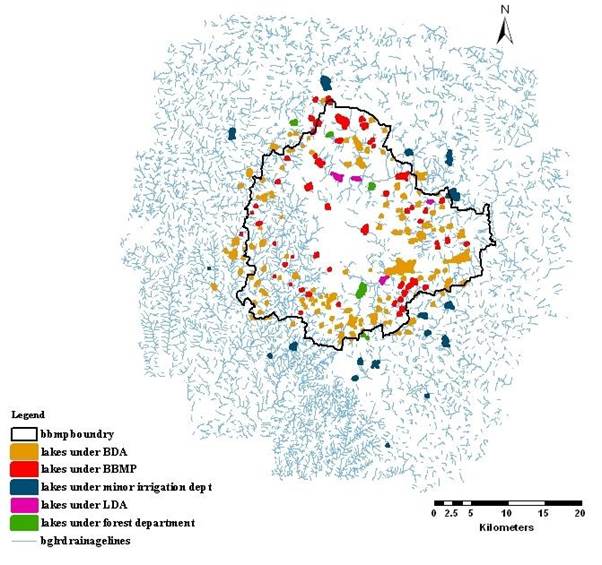
Figure 2: Spatial spread of lakes and custodians (too many – BBMP, BDA, LDA…. But too less effort to protect these lakes)
Table 1: Lakes with BBMP (A: Area in acres, G: Gunta, T: Total)
Sl.No
|
Name of the lake |
Taluk |
Hobli |
Name of the village
Survey No. |
Extent (A-G) as per RTC |
1 |
Agrahara Lake |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Agrahara -33 |
15-34 |
2 |
Allalasandra kere |
B'lore North |
Yalahanka |
Allalsandra -15 |
41-23 |
3 |
Ambalipura Kelagina kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Ambalipura-40 & 41 |
3-0, 4-09
T-7-09 |
4 |
Amblipura Melinakere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Ambalipura-36 |
12-16 |
5 |
Attur kere |
B'lore North |
Yalahanka |
Attur kere-81
Ananthapura-92
Ramagondanahalli- 39
Kempanahalli-12 |
56-29
6-15
7-22
19-18
T-90-04 |
6 |
Avalahalli |
B'lore North |
Yalahanka |
Avalahalli -10 & Singanayakanahalli 64 |
11-01
2-10
T-13-11 |
7 |
Bhimmana katte |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Halagevaderahalli-138 |
1-23 |
8 |
Bayappanapalya Kunte (Munniyappana katte) |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Vajarahalli -36 |
2-31 |
9 |
Challakere Lake |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Challakere - 85 |
38-05 |
10 |
Chinnapanhalli kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Chinnapanahalli 15 & 17 |
11-33
11-10 |
11 |
Chokkanahalli lake |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Chokkanahalli Sy-2 |
8-02 |
12 |
Dasarahalli kere (Chokkasandra) |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Dasarahalli - 24
Chokkasandra - 5 |
3-29
24-04
T-27-33 |
13 |
Deepanjali kere |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Devatige Ramanahalli-32 |
7-22 |
14 |
Devsandra kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Devasandra 31 |
16-08 |
15 |
Doddabommasandra |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Dodda Bommasandra-56
Kodigehalli- 175
Thindlu - 53 |
39-10
49-21
35-28
T-124-19 |
16 |
Doddakanenahalli kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Doddakanenahalli - 109 |
18-14 |
17 |
Dore kere |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Uttarahalli -22
Vasanthapura -06 |
19-11
'9-06
T-28-17 |
18 |
H Gollahalli Lake (Varahasandra Lake) |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Kengeri Gollahalli-9
Varahasandra-9
Hemgepura-25 |
7-08
4-33
7-25
T-19-26 |
19 |
Halagevaderahalli Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Halagevaderahalli-1 |
17-10 |
20 |
Handrahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Handrahalli -8 |
16-06 |
21 |
Haraluru kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Haraluru-95 |
34-70 |
22 |
Herohalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Herohalli-99 |
34-33 |
23 |
Harohalli lake |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Harohalli-91 |
74-32 |
24 |
Jogi kere |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Mallasandra-30 |
3-20 |
25 |
J.P. Park (Mathikere) |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Jalahalli-32
Mathikere-59
Thaniranahalli-01
Kasaba Yeshwanthpura-114 |
47-26
--
20-39
--
T- |
26 |
Kaikondanahalli kere |
B'lore East |
Varthuru |
Kaikondanahalli -8
Kasavanahalli -70 |
18-18
30-05
T-48-23 |
27 |
Kalkere Agra kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram & Bidarahalli |
Kalkere-45
Kyalasanahalli-36
Beelisivale-101 & 106 Horamavu Agra-36 |
73-11
51-19
0-37 & 0-14
61-11
T-187-12 |
28 |
Kammagondanahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Kammagondanahalli-18
Shettyhalli-67
Myadarahalli (Medarahalli)-26 |
15-26
5-32
1-32
T-23-10 |
29 |
Kasavanhalli |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Kasavanahalli-50
Haralur-32 |
21-30
33-18
T-56-08 |
30 |
Kattiganahalli Kere-136 |
B'lore North |
Jala |
Kattiganahalli -136 |
25-28 |
31 |
Kattiganahalli Kere-31 |
B'lore North |
Jala |
Kattiganahalli -31 |
20-10 |
32 |
Kempambudhi Lake |
B'lore North |
B'lore |
Kempambudhi-2 |
|
33 |
Kodigehalli kere |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Kodigehalli - 30 |
9-25 |
34 |
Kogilu Lake |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka
Jala |
Kogilu - 84
Kattigenahalli - 117 |
40-04
38-24
T-78-28 |
35 |
Koudenahalli kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Koudenahalli -27 |
55-05 |
36 |
Kudlu Chikere |
Anekal Taluk |
Sarjapura |
Koodlu-70 |
13-05 |
37 |
Kudlu doddakere |
Anekal Talulk
and B'lore South |
Sarjapur & Begur |
Koodlu-150
Parapanaagrahara-37 |
26-38
17-01
T-43-39 |
38 |
Kundalahalli Lake |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Kundalahalli -05 |
30-20 |
39 |
Lingadiranahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Lingadiranahalli-2 & 4 |
5-32
4-08
T-10-00 |
40 |
Mahadevapura Lakde |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Mahadevapura -7 |
26-23 |
41 |
Malgala kere |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthapura |
Malgala - 46 |
6-26 |
42 |
Munnekolalu kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Munnekolalu-25 |
15-38 |
43 |
Narasipura-20 |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Narasipura-20 |
15-30 |
44 |
Narasipura-26 |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Narasipura-26 |
9-07 |
45 |
Nayandanahalli kere |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Nayadahalli -31 |
15-18 |
46 |
Parappana Agrahara |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Parappana Agrahara-23 |
16-11 |
47 |
Puttenahalli kere |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Puttenahalli -42 |
13-25 |
48 |
Ramagondanahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Ramagondanahalli-52 |
36-26 |
49 |
Sankey Tank |
B'lore North |
Vyalikaval |
Vyalikaval - 21 |
35-00 |
50 |
Shilavantana kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Whitefeild-41 |
19-32 |
51 |
Sigehalli |
B'lore East |
K.R Puram |
Sigehalli-32 |
31-13 |
52 |
Singasandra Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Basapura-15
Singasandra -52 |
9-34
1-08
T-11-02 |
53 |
Sowl kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Bellandur-65
Doddakanelli-68 Kaigondanahalli-36 |
23-33
7-28
30-16
T-61-37 |
54 |
Thirumenahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Thirumenahalli-63 |
7-10 |
55 |
Ulsoor |
B'lore North |
B'lore |
Ulsoor |
|
56 |
Uttarahalli kere (Mogekere) |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Uttarahalli -111 |
15-16 |
57 |
Veerasagara lake |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Veerasagara-26
Attur-25 |
'17-24
3-30
T-21-14 |
58 |
Vijanapura kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Kowdenahalli -85
Krishnarajpura-97 |
11-28
2-07
T-13-35 |
59 |
Yediyur Lake |
B'lore South |
Utharahalli |
Dasarahalli -01
Yediyur -59 |
No extent |
60 |
Yelahanka kere
(Kasaba Amanikere) |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Yelahanka-29
Kenchenahalli -15
Venkatala-39
Manchenahalli-19
Puttenahalli-49 |
53-36
30-23
199-31
7-34
18-04
T-310-08 |
Lakes with BDA
Sl. No.
|
Name of the Lake |
Taluk |
Hobli |
Name of the village Sy No. |
Extent (A-G) as per RTC |
1 |
Abbigere kere |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Abbigere-75
Singapura-95 |
26-06
21-7
T-47-13 |
2 |
Alahalli kere / Anjanapura |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Allahalli -30
Gollahalli-3 |
15-35
5-30
T-21-25 |
3 |
Amruthalli kere |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Amruthalli-115 |
24-36 |
4 |
Annappahalli/ Yelachenahalli Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Yelachenahalli-06, Govinayakanahalli-14 |
4-39
1-33
T-6-32 |
5 |
Arakere |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Arakere-34 |
37-21 |
6 |
Avalahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanaka |
Avalahalli-10
Shiganayakanahalli-64 |
11-01
2-10
T-13-11 |
7 |
B.Narayanapura |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
B.Narayanapura-109 |
15-06 |
8 |
Baiyappanahalli kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Baiyappanahalli-61 |
8-09 |
9 |
Basapura Lake-2 |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Basapura-66 |
10-29 |
10 |
Basavanapura Lake |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Basavanapura-14 |
7-34 |
11 |
Begur Lake |
Bl'lore South |
Begur |
Begur-94 |
137-24 |
12 |
Bellahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Bellahalli-68 |
18-32 |
13 |
Bellandur |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Yamaluru-62
Amanikere Bellandur Kahne-1
Ibbalur-12
Kempapura-6
Beluru-2 |
3-04
284-20
399-14
13-15
2-00
T-700-13 |
14 |
Beratena Agrahara Lake (Chowdeshwari Layout |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Beratena Agrahara (Chowdeshwari)-18 |
11-18 |
15 |
Bhattralli kere |
B'lore East |
Bidarahalli |
Bhattralli-2 |
18-10 |
16 |
Bheemanakuppe |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Bheemanakuppe-180 |
75-15 |
17 |
Bhoganalli kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Bhoganalli-21 |
12-24 |
18 |
Byrasandra |
B'lore South |
Utharahalli |
Byrasandra-56 |
15-11 |
19 |
Byrasandra kere (Chikkepet) (Melinakere) |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Byrasandra-109 |
14-19 |
20 |
Chennasandra-2 |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Banasawadi-211 |
47-38 |
21 |
Chikka Banavara |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Chikka Banavara-3, Somashettyhalli-73, Kere gullada halli-22 and Ganigarahalli-11,15 |
67-38
3-21
26-32
4-14
2-30
T-105-15 |
22 |
Chikka Bellandur kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Chikka Bellandur-9
Mullur -63 |
67-14
8-07
T-75-21 |
23 |
Chikkabasavanapura kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Basavanapura-14 |
14-07 |
24 |
Chikkabasthi |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Ramasandra-6 |
7-06 |
25 |
Chikkabettahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Chikkabettahalli-52 |
1-32 |
26 |
Chick begur Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Begur-168,
Singanadra-86 |
32-19
9-37
T-42-16 |
27 |
Chikkammanahalli Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Kammanahalli -22
Vamadevanahalli- |
5-19 |
28 |
Chikkegowdana palya Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Hemmagepura-92 |
|
29 |
Chunchanaghatta |
B'lore South |
Utharahalli |
Chunchanaghatta-70, 70/2, 70/3 |
20-31
1-0
1-0
T-22-31 |
30 |
Chowdeshwari Layout Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
|
|
31 |
Devarakere Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Bikasipura-9 |
7-15 |
32 |
Doddabidarakallu |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Doddabidarakallu-125
Nagasandra -06 |
23-21
16-36
T-40-17 |
33 |
Doddakallasandra |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Doddakallasandra-27 |
21-16 |
34 |
Doddanakundi |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram (village map)
Varthur (In RTC-Bhoomi) |
Doddanekundi -200
Kaggadasapura - 25
Vibhutipura -13 |
56-39
75-16
3-15
T-135-30 |
35 |
Dubasipalya Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Valagerehalli-43, 43/P1 |
23-35
1-0
T-24-35 |
36 |
Gangasetty kere
(Diesel shed kere (Gangadhariahnakere) (Dyavasandrakunte kere) |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
KR Pura-58
Devasandra-46 |
18-32
2-35
T-21-27 |
37 |
Gandhinagara Lake |
B'lore North |
|
|
|
38 |
Garudachar Palya Kere -1 (Achanakere) |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Mahadevapura-31 |
5-36 |
39 |
Garudachar Palya Kere -2 (Goshala) Yekkalagatta kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Mahadevapura-86 |
5-14 |
40 |
Garvebhavi Palya |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Hongasandra -41 |
18-04 |
41 |
Gattigere palya Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Somapura-27/53 |
0-37 |
42 |
Gottigere Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Gottigere-71 |
37-13 |
43 |
Gowdana Palya Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Kadirenahalli-33 |
9-30 |
44 |
Gubbalala |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Gubbalala-25
Vajarahalli- |
8-10 |
45 |
Gunjur Kere (Carmelarm) |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Gunjur-95 |
9-17 |
46 |
Gunjur Mouji kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Gunjur-301, Kachamaranhalli-74 |
59-13
4-26
T- 63-39 |
47 |
Gunjur Palya kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Gunjur-83 |
36-27 |
48 |
Haralakunte Lake (Somasandrakere) |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Haralakunte-51 |
16-29 |
49 |
Hoodi kere (GIDDANA KERE ) |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Hoodi-138 |
28-31 |
50 |
Hoodi kere -1 |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Hoodi-79 |
15-10 |
51 |
Horamavu Agara |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Horamavu Agra-77 |
51-34 |
52 |
Horamavu kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Horamavu-83 |
37-14 |
53 |
Hosakerehalli |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Hosakerehalli-15 |
59-26 |
54 |
Hosakere |
B'lore South |
|
|
|
55 |
Hulimavu |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Hulimavu-42
Kammanahalli -110 |
124-25
5-32
130-17 |
56 |
Ibbalur Lake |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Ibbalur-36 |
18-06 |
57 |
Jakkur & Sampigehalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Jakkur-15, 23
Yalahanka Amanikere-55
Sampigehalli-12
Agrahara-13 |
39-21,36-33
58-16
19-25
3-17
T-157-32 |
58 |
Jaraganahalli/Sarakki/Puttenahalli Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Jaraganahalli-7
Sarrakki-26
Puttenahalli - 5
Kothanuru-103
Chunchaghatta-28 |
38-14
38-0
6-10
11-21
13-07
T-107-12 |
59 |
Jimkenalli kere |
B'lore East |
Bidarahalli |
Varanasi-47 |
8-24 |
60 |
Junnsandra kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Junnasandra-32 |
24-33 |
61 |
Kadirenapalya kere |
B'lore East |
KR Puram |
Binnamangala-99 |
|
62 |
K R Puram (BEML) Bendiganahalli kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Benniganahalli-47 & 55 |
18-24, 27-14
T- 45-39 |
63 |
Kaggadasanapura |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram (village map)
Varthur (In RTC-Bhoomi) |
Byrasandra -5
Kaggadasapura-141
Bendiganahalli - 24/3 |
14-24
32-16
3-26
T-51-26 |
64 |
Kalena Agrahara Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Kalena Agrahara-43 |
7-30 |
65 |
Kalkere Rampura kere |
Anekal Taluk (B'lore East) |
Jigani
Bidarahalli |
Kalkere-162
Rampura-22 Maragondanahalli-71
Huvineane-86 |
64-25
3-04
11-35
108-07
T-187-31 |
66 |
Kalyani / Kunte ( Next to Sai Baba Temple) |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Vasanthpura-21 |
1-33 |
67 |
Kannenahalli |
B'lore North (Bng South) |
Kengeri
Yeshwanthpur |
|
|
68 |
Kelagina kere / Byrasandra |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Byrasandra-112 |
12-21 |
69 |
Kembatha halli |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Kembathahalli-3
Kathnuru-32/3 |
5-16
1-33
T-7-20 |
70 |
Kenchanapura |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Kenchanapura-10 |
17-20 |
71 |
Kengeri Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Kengeri-15, Valagerehalli-85 |
27-03
5-13
T-32-16 |
72 |
Kommaghatta |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Komaghatta-03
Ramasandra-46 |
9-04
28-01
T-37-05 |
73 |
Konankunte |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Konanakunte - 2 |
09-18 |
74 |
Konasandra |
Anekal Taluk |
Jigani |
Dyavasandra-9
Bommandahalli-18
Konasandra-17 |
21-13
7-39
3-20
T-32-32 |
75 |
Konnappana agrahara |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Naganathpura (South)81 |
5-17 |
76 |
Kothnur |
B'lore South |
Utharahalli |
Kothnur-54 |
18-09 |
77 |
Lakshmipura lake |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Lakshmipura-25 |
10-06 |
78 |
Lingadheeranahalli |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Lingadheeranahalli-13 |
5-22 |
79 |
Madavara |
B'lore North |
Dasanapura
Yeshwanthpur |
Madavara -48
Chikkabidarakallu-21
Tirumalapura-32 (from Yeshwanthpura hobli)
Doddabidarakallu -98 (From Yeshwanthpura hobli |
35-31
20-20
8-36
2-39
T-68-06 |
80 |
Mahadevapura (Bandemahadevpura kere) |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Mahadevapura-187 |
13-11 |
81 |
Mallasandra Gudde lake |
B'lore North |
Dasanapura |
Mallasandra-49, Mallasandra-50 |
11-28
5-23
T-17-11 |
82 |
Mallathahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Mallathahalli-101
Giddadakonenahalli-6 |
50-38
20-08
T-71-06 |
83 |
Manganahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Manganahalli - 43 |
6-22 |
84 |
Medi Agrahara |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Medi Agrahara-33 |
13-15 |
85 |
Meenakshi Kere |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Kammanahalli (Meenakshi)-38 |
18-37 |
86 |
Mesthripalya Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Jakkasandra- 30 |
11-21 |
87 |
Nagarabhavi |
B'lore North (Bng South) |
Yeshwanthpur |
Nagarabhavi-17 |
17-39 |
88 |
Nagareshwara-Nagenahalli Lake |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Nagareshwara-Nagenahalli -10 |
11-08 |
89 |
Nellagaderanahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Nallagaderanahalli - 62 |
19-22 |
90 |
Nalluralli tank |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Nalluralli-4
Pantandur Agrahara-85 |
20-34
27-05
T-47-39 |
91 |
Narasappanahalli |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Karivabanahalli-40
Nelagadiranahalli - 90
Nelagadiranahalli -89
Doddabidarakallu - 24 |
27-13
19-05
5-26
1-20
T-53-24 |
92 |
Nyanappanahalli Lake |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Begur-344 |
6-07 |
93 |
Panathur kere -38 |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Panathur - 38 |
27-17 |
94 |
Panathur kere -48 |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Panathur - 48 |
6-30 |
95 |
Pattandur Agrahara |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Pattandur Agrahara-124 |
16-35 |
96 |
Pattandur Agrahara |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Pattandur Agrahara-54 |
12-37 |
97 |
Pattanagere Kenchenhalli |
B'lore South |
|
Kenchenahalli-33
Pattanagere-43 |
3-39
0-31
T-4-30 |
98 |
Rachenahalli |
B'lore North
B'lore East |
Yelahanka
K.R Puram |
Dasarahalli-61 (Bng East- KR Puram)
Jakkur - 82 (Bng North-Yelahanka)
Rachenahalli - 69 (Bng East-KR Puram) |
73-23
39-07
18-16
T-131-06 |
99 |
Ramsandra (Hirekere) |
B'lore South
B'lore North |
Kengeri
Yeshwanthpur |
Ramasandra-159
Kenchanpura-36/*
Kenchenapura - 36/¥ÉÊQ
Kannahalli-37 (Bng north-Yeshwanthpura) |
66-20
56-05
5-0
12-29
T-140-14 |
100 |
Sadaramangala kere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Sadaramangala-61, Kodigehalli-8 |
51-04
1-17
T-52-21 |
101 |
Shivanahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
shivanahalli-48 Allalasandra-38, 48 |
14-30
3-22
0-27
T-18-39 |
102 |
Siddapura kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Siddapura -18 |
27-38 |
103 |
Singapura Kere |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Singapura-102 |
66-18 |
104 |
Singasandra |
B'lore South |
Beguru |
Singasandra -99, 100 |
10-14
0-34
T-11-08 |
105 |
Sitaram Palya |
B'lore East |
K R Puram |
Sonnenahalli (Seetharmapalya)-33 |
23-37 |
106 |
Sompura |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Sompura - 11 |
17-38 |
107 |
Srigandadakaval (near Rajivgandhi nagar) |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Srigandakavalu-15 |
6-33 |
108 |
Srinivasapura Kere |
B'lore North |
Yelahanaka |
Srinivasapura-2 |
3-14 |
109 |
Subbarayanakere |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Gottigere-12 |
5-10 |
110 |
Subedeharanakere |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Begur-48 |
6-05 |
111 |
Subramanyapura Lake |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Uttarahalli-64 |
18-06 |
112 |
Sulekere (Soolikere) |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Maragondanahalli Krishnasagara |
|
113 |
Swarnakunte gudda kere |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Chandrashekarpura-1 |
09-05 |
114 |
Talaghattapura (Gowdarakere) |
B'lore South |
Uttarahalli |
Talaghattapura -73 |
19-16 |
115 |
Ullal |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Ullal-93 |
24-12 |
116 |
Vaderahalli |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Vaderahalli-32 |
9-34 |
117 |
Varahasandra Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Hemigepura-4, Varahasandra-24 |
4-11
13-09
T-17-20 |
118 |
Varthur |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Varthur-319 |
445-14 |
119 |
Vasanthapura (Janardhanakere) |
B'lore South |
Utharahalli |
Vasanthpura-28 |
7-10 |
120 |
Venkateshpura |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Ventateshpura-12
Sampigehalli-37 |
6-35
11-29
T-18-24 |
121 |
Vibhuthipura kere |
B'lore East |
Varthur |
Vibhuthipura-175 |
45-18 |
122 |
Vishwa nidam lake |
B'lore North |
Yeshwanthpur |
Herohalli-50 |
4-30 |
123 |
Yellenhalli Lake (Elenahalli) |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Yellenhalli-55 |
4-39 |
Lakes under Lake Development Authority (LDA)
Sl.No |
Name of the Lake |
Taluk |
Hobli |
Name of the village Sy No. |
Extent (A-G) as per RTC |
1 |
Agaram Lake |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Agara-11
Venkojiraokhane-11 |
5-39
136-30
T-142-29 |
2 |
Hebbal Lake |
B'lore North |
Kasaba |
Hebbla-38
Kodigehalli-37 |
92-26
99-33
T-192-19 |
3 |
Nagavara Lake |
B'lore North |
Kasaba |
Nagawara-58
Vishwanatanagenahalli - 12,13 |
56-17
12-35
6-01
T-75-13 |
4 |
Vengaiahnakere |
B'lore East |
K.R. Puram |
Krishnarajapura-9
Sannathammanahalli-46 |
38-12
26-23
T-64-35 |
Lakes - Karnataka Forest Department
Sl.No
|
Name of the Lake |
Taluk |
Hobli |
Name of the village Sy No. |
Extent (A-G) as per RTC |
1 |
Hennur (K.R.Puram Range) |
B'lore North |
Kasaba |
Hennur - 53
Nagawara - 13 |
58-30
14-11
T-73-01 |
2 |
J.B.Kaval Tank (Bangalore Range) |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Jyarakabande Kavalu-P1-36 |
44-21
2-04 |
3 |
Madiwala (K.R.Puram Range) |
B'lore South |
Begur |
Madivala- 7
Kodichikkanahalli-23
Belekannahalli-64
Rupena Agrahara-11 |
166-39
80-09
21-35
6-10
T-275-13 |
4 |
Mylsandra (Kaggalipura Range) Gumaiahanakere (Mylasandra 1)
Mylasandra 2 |
B'lore South |
Kengeri |
Mylasandra-37
Kasaba Kengeri-58
Mylasandra - 27
Kasaba Kengeri-66 |
6-24
6-02
T-12-26
10-14
5-28
T-16-02 |
5 |
Puttenahalli (Yelahanka Range) |
B'lore North |
Yelahanka |
Puttenehalli - 36
Attur - 49 |
29-14
7-26
T-37-00 |
Lakes - Minor Irrigation Department
Sl.No
|
Name of the Lake |
Taluk |
Hobli |
Name of the village Sy No. |
Extent (A-G) as per RTC |
1 |
Agara kere |
Bangalore South |
Kengeri |
Agara - 103
Agara -102
Agara - 104 |
13-11
0-08
0-06
T-13-25 |
2 |
Alluru kere |
Bangalore North |
Dasanapura |
Aluru-132
Vaderahalli - 8
Mathahalli - 25
Narasipura - 41 |
39-38
27-23
5-32
1-21
T-75-34 |
3 |
Bhimanakuppe kere |
Bangalore South |
Kengeri |
Bheemanakuppe-180 |
75-15 |
4 |
Bidara Amanikere |
Anekal |
|
|
|
5 |
Bidarahalli kere |
Bangalore East |
Bidrahalli |
Bidarahalli-8
Byappanahalli - 21 |
15-10
81-16
T-96-26 |
6 |
Chikkanahalli |
Bangalore East |
|
|
|
7 |
Doddagubbi kere |
Bangalore East |
Bidarahalli |
Doddagubbi-38
NadagowdaGollahalli-39
Chikkagubbi-9 |
105-18
16-37
1-32
T-124-07 |
8 |
Ghattahalli Bommankere |
Anekal |
Sarjapura |
Gattahalli-62
Rayasandra - 33 |
51-17
21-22
T-72-39 |
9 |
Hoskuru kere (Huskur Lake) |
Anekal |
Sarjapura |
Huskur - 163
Harohalli - 51
Avalahalli - 50 |
91-10
23-0
---
T-114-10 |
10 |
Hulimangala Doddakere |
Anekal |
Jigani |
Hulimangala - 22 |
67-07 |
11 |
Kodatikere |
Bangalore East |
Varthru |
Kodati-8
Solikunte - 52 |
40-32
37-09
T-78-01 |
12 |
Margondanahalli kere |
Bangalore South |
Kengeri |
Margondanahalli -45 |
5-33 |
13 |
Rampura kere |
Bangalore East |
|
|
|
14 |
Sakalavara Bujangadasana kere |
Anekal |
Jigani |
Sakalavara - 93 |
23-34 |
15 |
Singanayakana halli kere |
Bangalore North |
|
|
|
16 |
Singena Agrahara kere |
Anekal |
Sarjapura |
Singena Agrahara-94
Narayanaghatta - 128
Gottammanahalli - 13 |
95-39
19-32
8-04
T-123-35 |
17 |
Vaderahalli kere |
Bangalore South |
Kengeri |
B.M.Kaval P1 -136 |
21-07 |
18 |
Yellemallappa Shetty kere |
Bangalore East |
K.R. Puram |
Avalahalli -57
Avalahalli -12
Heerandahalli - 95
Heerandahalli -96
Kurudu Sonnenahalli -2
Medahalli -63
Veerenahalli -29 |
13-26
17-26
170-16
33-24
31-2
91-35
132-06
T-490-15 |
Source: https://www.karnataka.gov.in/ldakarnataka/documents/Listof-210Lake-BDA,BBMP,LDA, KFD, MILIst.xlsx
The anthropogenic activities particularly, indiscriminate disposal of industrial effluents and sewage wastes, dumping of building debris have altered the physical, chemical as well as biological integrity of the ecosystem. This has resulted in the ecological degradation, which is evident from the current ecosystem valuation of wetlands. Global valuation of coastal wetland ecosystem shows a total of 14,785/ha US$ annual economic value. Valuation of relatively pristine wetland in Bangalore shows the value of Rs. 10,435/ha/day while the polluted wetland shows the value of Rs.20/ha/day (Ramachandra et al., 2005). In contrast to this, Varthur, a sewage fed wetland has a value of Rs.118.9/ha/day (Ramachandra et al., 2011). The pollutants and subsequent contamination of the wetland has telling effects such as disappearance of native species, dominance of invasive exotic species (such as African catfish, water hyacinth, etc.), in addition to profuse breeding of disease vectors and pathogens. Water quality analyses revealed of high phosphates (4.22-5.76 ppm) levels in addition to the enhanced BOD (119-140 ppm) and decreased DO (0-1.06 ppm). The amplified decline of ecosystem goods and services with degradation of water quality necessitates the implementation of sustainable management strategies to recover the lost wetland benefits.
Conservation and Management of Wetlands:
In recent years, there has been concern over the continuous degradation of wetlands due to unplanned developmental activities (Ramachandra, 2002). Urban wetlands are seriously threatened by encroachment of drainage through landfilling, pollution (due to discharge of domestic and industrial effluents, solid wastes dumping), hydrological alterations (water withdrawal and inflow changes), and over-exploitation of their natural resources. This results in loss of biodiversity of the wetland and loss of goods and services provided by wetlands (Ramachandra, 2009). The mitigation of frequent floods and the associated loss of human life and properties entail the restoration of interconnectivity among wetlands, restoration of wetlands (removal of encroachments), conservation and sustainable management of wetlands (Ramachandra et al., 2012).
Despite good environmental legislations, loss of ecologically sensitive wetlands is due to the uncoordinated pattern of urban growth happening in Bangalore. Principal reason is lack of good governance and decentralized administration evident from lack of coordination among many Para-state agencies, which has led to unsustainable use of the land and other resources. Failure to deal with water as a finite resource is leading to the unnecessary destruction of lakes and marshes that provide us with water. This failure in turn is threatening all options for the survival and security of plants, animals, humans, etc. There is an urgent need for:
- Restoring and conserving the actual source of water - the water cycle and the natural ecosystems that support it - are the basis for sustainable water management
- Reducing the environmental degradation that is preventing us from reaching goals of good public health, food security, and better livelihoods world-wide
- Improving the human quality of life that can be achieved in ways while maintaining and enhancing environmental quality
- Reducing greenhouse gases to avoid the deleterious effects of climate change is an integral part of protecting freshwater resources and ecosystems.
- Maintaining intergeneration Equity
A comprehensive approach to water resource management is needed to address the myriad water quality problems that exist today from non-point and point sources as well as from catchment degradation. Watershed-based planning and resource management is a strategy for more effective protection and restoration of aquatic ecosystems and for protection of human health. The watershed approach emphasizes all aspects of water quality, including chemical water quality (e.g., toxins and conventional pollutants), physical water quality (e.g., temperature, flow, and circulation), habitat quality (e.g., stream channel morphology, substrate composition, riparian zone characteristics, catchment land cover), and biological health and biodiversity (e.g., species abundance, diversity, and range). The suggestions to implement in lakes in order to maintain its healthy ecosystem include:
- Good governance (too many para-state agencies and lack of co-ordination) - Single agency with the statutory and financial autonomy to be the custodian of natural resources (ownership, regular maintenance) and action against polluters (encroachers as well as those let untreated sewage and effluents, dumping of solid wastes).
- De-congest Bangalore: Growth in Bangalore has surpassed the threshold evident from stress on supportive capacity (insufficient water, clean air and water, electricity, traffic bottlenecks, etc.) and assimilative capacity (polluted water and sediments in water bodies, enhanced GHG – Greenhouse gases, etc.). No new projects shall be sanctioned and the emphasis would be on increasing green cover and restoration of lakes.
- Disband BDA – creation of Bangalore Development Agency has given impetus to inefficient governance evident from Bangalore, the garden city turning into ‘dead city’ during the functional life of BDA.
- Digitation of land records (especially common lands – lakes, open spaces, parks, etc.) and availability of this geo-referenced data with query option (Spatial Decision Support System) to public.
- Comprehensive development plan (CDP) for the city has to be developed through consultative process involving all stakeholders and should not be outsourced to outside agencies / consultants (from other countries).
- Removal of encroachment near to lakes after the survey based on reliable cadastral maps;
- Effective judicial system for speedy disposal of conflicts related to encroachment;
- Apply principles of ‘polluter pays’ principle to agencies responsible for contamination of Bangalore surface and ground water (Agency: BWSSB, industries);
- Action against regulatory agency (KSPCB) for dereliction of statutory duties and other responsibilities by allowing sustained contamination of water, land and air;
- Restriction of the entry of untreated sewage into lakes;
- To make land grabbing cognizable non-bailable offence;
- Letting off only treated sewage into the lake through constructed wetlands and shallow algae ponds (as in Jakkur lake);
- Regular removal of macrophytes in the lakes;
- Implementation of ‘polluter pays’ principle as per water act 1974;
- Plant native species of macrophytes in open spaces of lake catchment area;
- Stop solid wastes (municipal and demolition debris) dumping into lakes; treatment and management of solid waste shall be as per MSW Rules 2000, GoI.
- Ensure proper fencing of lakes
- Restrictions on the diversion of lake for any other purposes;
- Complete ban on construction activities in the valley zones;
- Monitoring of lakes through network of schools and colleges;
- Mandatory environment education at all levels (schools and colleges including professional courses).
Wetlands in Bangalore are to be restored considering:
Activities around lakes |
Norms to protect and conserve Wetlands |
Encroachment of lake bed and loss of interconnectivity among
lakes |
The Hon’ble Supreme Court in Civil appeal number 1132/2011 at SLP (C) 3109/2011 on January 28,2011 has expressed concern regarding encroachment of common property resources, more particularly lakes (and raja kaluves) and it has directed the state governments for removal of encroachments on all community lands.
Eviction of encroachment: Need to be evicted as per Karnataka Public Premises (eviction of unauthorised occupants) 1974 and the Karnataka Land Revenue Act, 1964 |
Buildings in the buffer zone of lakes |
In case of water bodies, a 30.0 m buffer of ‘no development zone’ is to be maintained around the lake (as per revenue records)
- As per BDA, RMP 2015 (Regional Master Plan, 2015)
- Section 17 of KTCP (Karnataka Town and Country Planning) Act, 1961 and sec 32 of BDA Act, 1976
- Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules 2010, Government of India; Wetlands Regulatory Framework, 2008.
|
Construction activities in the valley zone (SEZ by Karnataka Industrial Areas Development Board (KIADB)) in the valley zone |
This is contrary to sustainable development as the natural resources (lake, wetlands) get affected, eventually leading to the degradation/extinction of lakes. This reflects the ignorance of the administrative machinery on the importance of ecosystems and the need to protect valley zones considering ecological function and these regions are ‘NO DEVELOPMENT ZONES’ as per CDP 2005, 2015 |
Alterations in topography |
Flooding of regions would lead to loss of property and human life and, spread of diseases. |
Increase in deforestation in catchment area |
Removing vegetation in the catchment area increases soil erosion and which in turn increases siltation and decreases transpiration |
Documentation of biodiversity |
- The biodiversity of every water body should form part of the School, College, People’s Biodiversity Registers (SBR, CBR, PBR).
- The local Biodiversity Management Committees (BMC) should be given necessary financial support and scientific assistance in documentation of diversity.
- The presence of endemic, rare, endangered or threatened species and economically important ones should be highlighted
- A locally implementable conservation plan has to be prepared for such species
|
Implementation of sanitation facilities |
- The lakes are polluted with sewage, coliform bacteria and various other pathogens
- Preserving the purity of waters and safeguarding the biodiversity and productivity, dumping of waste has to be prohibited
- All the settlements alongside the water body should be provided with sanitation facilities so as not to impinge in anyway the pristine quality of water
|
Violation of regulatory and prohibitory activities as per Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010;
Regulatory wetland framework, 2008 |
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA) Notification, 2009.
Wetlands (Conservation and Management) rules 2010, Government of India; Regulatory wetland framework, 2008
Regulated activity
- Withdrawal of water/impoundment/diversion/interruption of sources
- Harvesting (including grazing) of living/non-living resources (may be permitted to the level that the basic nature and character of the biotic community is not adversely affected)
- Treated effluent discharges – industrial/ domestic/agro-chemical.
- Plying of motorized boats
- Dredging (need for dredging may be considered, on merit on case to case basis, only in cases of wetlands impacted by siltation)
- Constructions of permanent nature within 50 m of periphery except boat jetties
- Activity that interferes with the normal run-off and related ecological processes – up to 200 m
Prohibited activity
- Conversion of wetland to non-wetland use
- Reclamation of wetlands
- Solid waste dumping and discharge of untreated effluents
|
Damage of fencing, solid waste dumping and encroachment problems in Varthur lake series
|
High Court of Karnataka (WP No. 817/2008) had passed an order which include:
- Protecting lakes across Karnataka,
- Prohibits dumping of garbage and sewage in Lakes
- Lake area to be surveyed and fenced and declare a no development zone around lakes
- Encroachments to be removed
- Forest department to plant trees in consultation with experts in lake surroundings and in the watershed region
- Member Secretary of state legal services authority to monitor implementation of the above in coordination with Revenue and Forest Departments
- Also setting up district lake protection committees
|
Polluter Pays principle |
National Environment Policy, 2006
The principal objectives of NEP includes :
- Protection and conservation of critical ecological systems and resources, and invaluable natural and man-made heritage
- Ensuring judicious use of environmental resources to meet the needs and aspirations of the present and future generations
- It emphasizes the “Polluter Pays” principle, which states the polluter should, in principle, bear the cost of pollution, with due regard to the public interest
|
Prevention of pollution of lake |
National Water Policy, 2002
Water is a scarce and precious national resource and requires conservation and management.
Watershed management through extensive soil conservation, catchment-area treatment, preservation of forests and increasing the forest cover and the construction of check-dams should be promoted.
The water resources should be conserved by retention practices such as rain water harvesting and prevention of pollution. |
Discharge of untreated sewage into lakes |
The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986
- Lays down standards for the quality of environment in its various aspects
- Laying down standards for discharge of environmental pollutants from various sources and no persons shall discharge any pollutant in excess of such standards
- Restriction of areas in which industries, operations or processes shall not be carried out or carried out subject to certain safeguards
|
The water pollution, prevention and its control measures were not looked upon |
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974
- It is based on the “Polluter pays” principle.
The Pollution Control Boards performs the following functions :
- Advice the government on any matter concerning the prevention and control of water pollution.
- Encourage, conduct and participate in investigations and research relating to problems of water pollution and prevention, control or abatement of water pollution.
- Inspects sewage and effluents as well as the efficiency of the sewage treatment plants.
- Lay down or modifiy existing effluent standards for the sewage.
- Lay down standards of treatment of effluent and sewage to be discharged into any particular stream.
- Notify certain industries to stop, restrict or modify their procedures if the present procedure is deteriorating the water quality of streams.
|
Pathetic water scenario and insufficient drinking water in Bangalore |
The depletion of ground water and drying up off lakes has affected the water availability to meet the current population. At the 4% population growth rate of Bangalore over the past 50 years, the current population of Bangalore is 8.5 million (2011). Water supply from Hesaraghatta has dried, Thippagondanahalli is drying up, the only reliable water supply to Bangalore is from Cauvery with a gross of 1,410 million liters a day (MLD). There is no way of increasing the drawal from Cauvery as the allocation by the Cauvery Water Disputes Tribunal for the entire urban and rural population in Cauvery Basin in Karnataka is only 8.75 TMC ft (one thousand million cubic – TMC ft equals 78 MLD), Bangalore city is already drawing more water-1,400 MLD equals 18 TMC—than the allocation for the entire rural and urban population in Cauvery basin |
The restoration and conservation strategies has to be implemented for maintaining the ecological health of aquatic ecosystems, aquatic biodiversity in the region, inter-connectivity among lakes, preserve its physical integrity (shorelines, banks and bottom configurations) and water quality to support healthy riparian, aquatic and wetland ecosystems. The regular monitoring of waterbodies and public awareness will help in developing appropriate conservation and management strategies (Ramachandra, 2005).
Ecological and Environmental Implications:
- Land use change: Conversion of watershed area especially valley regions of the lake to paved surfaces would alter the hydrological regime.
- Loss of Drainage Network:Removal of drain (Rajakaluve) and reducing the width of the drain would flood the surrounding residential as the interconnectivities among lakes are lost and there are no mechanisms for the excessive storm water to drain and thus the water stagnates flooding in the surroundings.
- Alteration in landscape topography: This activity alters the integrity of the region affecting the lake catchment. This would also have serious implications on the storm water flow in the catchment.
- The dumping of construction waste along the lakebed and lake has altered the natural topography thus rendering the storm water runoff to take a new course that might get into the existing residential areas. Such alteration of topography would not be geologically stable apart from causing soil erosion and lead to siltation in the lake.
- Loss of Shoreline: The loss of shoreline along the lakebed results in the habitat destruction for most of the shoreline birds that wade in this region. Some of the shoreline wading birds like the Stilts, Sandpipers; etc will be devoid of their habitat forcing them to move out such disturbed habitats. It was also apparent from the field investigations that with the illogical land filling and dumping taking place in the Bellandur lakebed, the shoreline are gobbled up by these activities.
- Loss of livelihood: Local people are dependent on the wetlands for fodder, fish etc. estimate shows that wetlands provide goods and services worth Rs 10500 per hectare per day (Ramachandra et al., 2005). Contamination of lake brings down goods and services value to Rs 20 per hectare per day.
Decision makers need to learn from the similar historical blunder of plundering ecosystems as in the case of Black Swan event (http://blackswanevents.org/?page_id=26) of evacuating half of the city in 10 years due to water scarcity, contaminated water, etc. or abandoning of Fatehpur Sikhri and fading out of AdilShahi’s Bijapur, or ecological disaster at Easter Island or Vijayanagara empire
It is the responsibility of Bangalore citizens (to ensure intergeneration equity, sustenance of natural resources and to prevent human-made disasters such as floods, etc.) to stall the irrational conversion of land in the name of development and restrict the decision makers taking the system (ecosystem including humans) for granted as in the case of wetlands by KIADB, BDA, BBMP and many such para-state agencies.
Recommendations for Conservation and Sustainable Management of Wetlands
- Carrying capacity studies for all macro cities: Unplanned concentrated urbanisation in many cities has telling impacts on local ecology and biodiversity, evident from decline of water bodies, vegetation, enhanced pollution levels (land, water and air), traffic bottlenecks, lack of appropriate infrastructure, etc. There is a need to adopt holistic approaches in regional planning considering all components (ecology, economic, social aspects). In this regard, we recommend carrying capacity studies before implementing any major projects in rapidly urbanizing macro cities such as Greater Bangalore, etc. Focus should be on
- Good governance (too many para-state agencies and lack of co-ordination) - Single agency with the statutory and financial autonomy to be the custodian of natural resources (ownership, regular maintenance) and action against polluters (encroachers as well as those let untreated sewage and effluents, dumping of solid wastes).
- De-congest Bangalore: Growth in Bangalore has surpassed the threshold evident from stress on supportive capacity (insufficient water, clean air and water, electricity, traffic bottlenecks, etc.) and assimilative capacity (polluted water and sediments in water bodies, enhanced GHG – Greenhouse gases, etc.)
- Disband BDA – creation of Bangalore Development Agency has given impetus to inefficient governance evident from Bangalore, the garden city turning into ‘dead city’ during the functional life of BDA.
- Digitation of land records (especially common lands – lakes, open spaces, parks, etc.) and availability of this geo-referenced data with query option (Spatial Decision Support System) to public.
- Demarcation of the boundary of water bodies:
- The existing regulations pertaining to boundary demarcations within different states need to be reviewed according to updated norms and based on geomorphology and other scientific aspects pertaining to individual water bodies.
- Maximum Water Level mark should form the boundary line of the water body.
- In addition, a specified width, based on historical records/ survey records etc. may be considered for marking a buffer zone around the water body. In case such records are not available, the buffer zones may be marked afresh considering the flood plain level and also maximum water levels.
- The width of the buffer zone should be set considering the geomorphology of the water body, the original legal boundaries, etc.
- The buffer zone should be treated as inviolable in the long term interests of the water body and its biodiversity.
- Declare and maintain floodplains and valley zones of lakes as no activity regions
- Remove all encroachments – free flood plains, valley zones, storm water drains, etc. of encroachments of any kind.
- Ban conversion of lake, lake bed for any other purposes.
- Urban wetlands, mostly lakes to be regulated from any type of encroachments.
- Regulate the activity which interferes with the normal run-off and related ecological processes – in the buffer zone (200 m from lake boundary / flood plains is to be considered as buffer zone)
- Mapping of water-bodies: The mapping of water bodies should also include smaller wetlands, particularly streams, springs etc. The neglect of these hydrological systems could cause considerable impoverishment of water flow in the river systems as well as turn out to be threats to rare kinds of biodiversity. The waters of many of these streams are being diverted for private uses. This causes diminished water flow especially in the during the summer months. A judicious water sharing mechanism has to be worked out at the local level taking into account also the broader national interest as well as conservation of dependent biodiversity. The mapping of these smaller water-bodies, along with their catchments needs to be conducted involving also the local Biodiversity Management Committees. The jurisdictional agreements on the water usage and watershed protection need to be arrived at on a case to case basis involving all the stakeholders.
- Spatial Extent of Water bodies,
- Spatial extent of its catchment (watershed/basin),
- Demarcate Flood plains,
- Demarcate buffer zone – with a list of regulated activities,
- Land cover in the catchment,
- Ensure at least 33% of land cover is covered with natural vegetation (to ensure the lake perennial),
- Identify the natural areas in the catchment,
- Biodiversity inventory – capture entire food chain,
- The jurisdictional agreements on the water usage and watershed protection need to be arrived at on a case to case basis involving all the stakeholders,
- Develop a comprehensive database (spatial with attribute information) and available to public,
- Development of Spatial Decision Support System to aid decision makers,
- Identify and demarcate the region around the lake where all activities are to be prohibited (Flood plain)
- The biodiversity of every water body should form part of the Biodiversity Registers (BR),
- The local Biodiversity Management Committees (BMC) should be given necessary financial support and scientific assistance in documentation of diversity,
- The presence of endemic, rare, endangered or threatened species and economically important ones should be highlighted,
- A locally implementable conservation plan has to be prepared for such species.
- Holistic and Integrated Approaches – Conservation and Management: Integration of the activities with the common jurisdiction boundaries of Government para-state Agencies for effective implementation of activities related to management, restoration, sustainable utilization and conservation. This necessitates:
- Common Jurisdictional boundary for all para-state agencies
- To minimise the confusion of ownership – assign the ownership of all natural resources (lakes, forests, etc.) to a single agency – Lake Protection and Management Authority (or Karnataka Forest Department). This agency shall be responsible for protection, development and sustainable management of water bodies).
- Custodian (single para-state agency) shall manage natural resources - let that agency have autonomous status with all regulatory powers to protect, develop and manage water bodies.
- All wetlands to be considered as common property resources and hence custodians should carefully deal with these ensuring security.
- Management and maintenance of lakes to be decentralized involving stakeholders, local bodies, institutions and community participation without any commercialization or commoditization of lakes.
- Integrated aquatic ecosystem management needs to be implemented to ensure sustainability, which requires proper study, sound understanding and effective management of water systems and their internal relations.
- The aquatic systems should be managed as part of the broader environment and in relation to socio-economic demands and potentials, acknowledging the political and cultural context.
- Wetlands lying within the protected area of National Parks and Wildlife Sanctuaries shall be regulated under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. Wetlands lying within the notified forest areas shall be regulated by the Indian Forest Act, 1927 and the Forest Conservation Act, 1980; and the relevant provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986. The Wetlands outside protected or notified forest areas shall be regulated by the relevant provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
- Immediate implementation of the regulatory framework for conservation of wetlands.
- Socio-economic studies with land use planning in and around the lakes can help in providing ecological basis for improving the quality of lakes.
- Prohibit activities such as conversion of wetlands for non-wetland purposes, dumping of solid wastes, direct discharge of untreated sewage, hunting of wild fauna, reclamation of wetlands.
- Maintain Catchment Integrity to ensure lakes are perennial and maintain at least 33% land cover should be under natural Vegetation.
- Plant native species of vegetation in each lake catchment.
- Create new water bodies considering the topography of each locality.
- Establish laboratory facility to monitor physical, chemical and biological integrity of lakes.
- Maintain physical integrity - Free storm water drains of any encroachments. Establish interconnectivity among water bodies to minimise flooding in certain pockets. The process of urbanization and neglect caused disruption of linkages between water bodies such as ancient lake systems of many cities. Wherever such disruptions have taken place alternative arrangements should be provided to establish the lost linkages.
- Encroachment of lake beds by unauthorized /authorized agencies must be immediately stopped. Evict all unauthorized occupation in the lake beds as well as valley zones.
- Any clearances of riparian vegetation (along side lakes) and buffer zone vegetation (around lakes) have to be prohibited
- Penalise polluters dumping solid waste in the lake bed.
- Implement polluter pays principle for polluters letting liquid waste in to the lake either directly or through storm water drains.
- Lake privatized recently to be taken over and handed over to locals immediately thus restoring the traditional access to these lakes by the stakeholders.
- Restore surviving lakes in urban areas strengthening their catchment area and allowing sloping shorelines for fulfilling their ecological function.
- Alteration of topography in lake / river catchments should be banned.
- Appropriate cropping pattern, water harvesting, urban development, water usage, and waste generation data shall be utilized and projected for design period for arriving at preventive, curative and maintenance of aquatic ecosystem restoration action plan (AERAP).
- Desilting of lakes for removal of toxic sediment, to control nuisance macrophytes; further silting in the catchment should be checked by suitable afforestation of catchment areas and the provision of silt traps in the storm water drains.
- Maintaining the sediment regime under which the aquatic ecosystems evolve including maintenance, conservation of spatial and temporal connectivity within and between watersheds.
- Conversion of land around the lakes particularly in the valley zones and storm water drains for any kind of development must be totally banned.
- Flora in the catchment area should be preserved & additional afforestation programmes undertaken.
- Check the overgrowth of aquatic weeds like Eichhornia, Azolla, Alternanthera etc. through manual operations.
- Aquatic plants greatly aid in retarding the eutrophication of aquatic bodies; they are the sinks for nutrients & thereby play a significant role in absorption & release of heavy metals. They also serve as food and nesting material for many wetland birds. Therefore, knowledge of the ecological role of aquatic species is necessary for lake preservation.
- Adopt biomanipulation (Silver carp and Catla– surface phytoplankton feeders, Rohu – Column zooplankton feeder Gambusia and Guppies – larvivorous fishes for mosquito control), aeration, and shoreline restoration (with the native vegetation) in the management of lakes.
- Environmental awareness programmes can greatly help in the protection of the water bodies.
- Government Agencies, Academies, Institutions and NGO’s must co-ordinate grass-root level implementation of policies and activities related to conservation of lakes and wetlands (both Inland and Coastal), their sustainable utilization, restoration and development including human health. There is also a need for management and conservation of aquatic biota including their health aspects. Traditional knowledge and practices have to be explored as remedial measures. Cost-intensive restoration measures should be the last resort after evaluating all the cost-effective measures of conservation and management of the wetlands.
- A Committee be constituted consisting of Experts, Representatives of Stakeholders (researchers, industrialists, agriculturists, fishermen, etc.) and Line Agencies, in addition to the existing Committee(s), if any, in order to evolve policies and strategies for reclamation, development, sustainable utilization and restoration of the wetlands and socio-economic development of the local people.
- At regional level, Lake Protection and Management Authority (LPMA) with autonomy, corpus funds from plan allocations of state and center and responsibility and accountability for avoiding excessive cost and time over runs. LPMA shall have stakeholders-representatives from central and state and local body authorities, NGO’s and eminent people and experts shall be constituted
- Generous funds shall be made available for such developmental works through the Committee, as mentioned above. Local stakeholders be suggested to generate modest funds for immediate developmental needs in the aquatic systems in their localities.
- Provisions should be made for adoption of lakes and wetlands by the NGO’s and Self-help groups for their conservation, management, sustainable utilization and restoration.
- Aquatic ecosystem restoration works taken up by any agency, Govt. or NGO’s should have 10% of restoration costs (per annum) spent or set off for creating awareness , research and monitoring compulsorily in future.
- Public education and outreach should be components of aquatic ecosystem restoration. Lake associations and citizen monitoring groups have proved helpful in educating the general public. Effort should be made to ensure that such groups have accurate information about the causes of lake degradation and various restoration methods.
- Documentation of biodiversity: The biodiversity of every water body should form part of the School, College, People’s Biodiversity Registers (SBR, CBR, PBR). The local Biodiversity Management Committees (BMC) should be given necessary financial support and scientific assistance in documentation of diversity. The presence of endemic, rare, endangered or threatened species and economically important ones should be highlighted. A locally implementable conservation plan has to be prepared for such species.
- All kinds of introduction of Exotic species and Quarantine measures be done in consultation with the concerned Authorities and the data bank
- There is an urgent need for creating a `Data Bank’ through inventorisation and mapping of the aquatic biota.
- Identify water bodies of biodiversity importance and declare them as wetland conservation reserves (WCR)
- Preparation of management plans for individual water bodies: Most large water bodies have unique individual characteristics. Therefore it is necessary to prepare separate management plans for individual water bodies.
- Greater role and participation of women in management and sustainable utilization of resources of aquatic ecosystems.
- Impact of pesticide or fertilizers on wetlands in the catchment areas to be checked.
- Regulate illegal sand and clay mining around the wetlands.
- Implementation of sanitation facilities: It was noted with grave concern that the water bodies in most of India are badly polluted with sewage, coliform bacteria and various other pathogens. This involves:
- Preserving the purity of waters and safeguarding the biodiversity and productivity, dumping of waste has to be prohibited;
- In addition to this, all the settlements alongside the water body should be provided with sanitation facilities so as not to impinge in anyway the pristine quality of water.
- Management of polluted lakes: This programme needs priority attention. This involves:
- Implementation of bioremediation method for detoxification of polluted water bodies.
- The highly and irremediably polluted water bodies to be restored on priority to prevent health hazards.
- Based on the concept of polluter pays, a mechanism be evolved to set up efficient effluent treatment plants [ETP], individual or collective, to reduce the pollution load. Polluting industries be levied Environmental Cess, which can be utilised for conservation measures by the competent authorities. A `waste audit’ must be made compulsory for all the industries and other agencies.
- Restoration of lakes: The goals for restoration of aquatic ecosystems need to be realistic and should be based on the concept of expected conditions for individual eco-regions. Further development of project selection and evaluation technology based on eco-region definitions and description should be encouraged and supported by the national and state government agencies.
- Ecosystem approach in aquatic ecosystem restoration endeavor considering catchment land use plan as of pre-project status and optimal land use plan shall first be prepared for short term (10 to 30 years) and long term (>30) periods keeping in view developmental pressure over time span.
- Research and development is needed in several areas of applied limnology, and this programme should take an experimental approach which emphasizes manipulation of whole ecosystems.
- Appropriate technologies for point and non-point sources of pollution and in situ measures for lake restoration shall be compatible to local ethos and site condition as well as objectives of Aquatic Ecosystem Restoration Action Plan (AERAP).
- Traditional knowledge and practices have to be explored as remedial measures. Cost-intensive restoration measures should be the last resort after evaluating all the cost-effective measures of conservation and management of ecosystems.
- Public needs to be better informed about the rational, goal and methods of ecosystem conservation and restoration. In addition, the need was realized for scientist and researchers with the broad training needed for aquatic ecosystem restoration, management and conservation.
- Improved techniques for littoral zone and aquatic microphytes management need to be developed. Research should go beyond the removal of nuisance microphytes to address the restoration of native species that are essential for waterfowl and fish habitat.
- Basic research is necessary to improve the understanding of fundamental limnological processes in littoral zones and the interactions between littoral and pelagic zones of lakes.
- Bio manipulation (food web management) has great potential for low-cost and long-term management of lakes, and research in this emerging field must be stimulated.
- Innovative and low-cost approaches to contaminant clean up in lakes need to be developed.
- The relations between loadings of stress-causing substances and responses of lakes need to be understood more precisely. Research should be undertaken to improve predictions of trophic state and nutrient loading relationships.
- Improved assessment programmes are needed to determine the severity and extent of damage in lakes and wetlands and a change in status over time. Innovative basic research is required to improve the science of assessment and monitoring.
- There is a great need for cost effective, reliable indicators of ecosystems function, including those that would reflect long-term change and response to stress.
- Research on indicators should include traditional community and ecosystem measurements, paleoecological trend assessments and remote sensing.
- Effective assessment and monitoring programme would involve network of local schools, colleges and universities.
- Valuation of goods and services : Goods and services provided by the individual water bodies and the respective species to be documented, evaluated through participatory approach and be made part of the Biodiversity Registers (PBR: People’s Biodiversity Registers, SBR: School Biodiversity Registers). If in any case the traditional fishing rights of the local fishermen are adversely affected by lake conservation or by declaring it as a bird sanctuary, etc. they should be adequately compensated.
- Ecological values of lands and water within the catchment / watershed shall be internalised into economic analysis and not taken for granted. Pressure groups shall play as watchdogs in preventing industrial and toxic and persistent pollutants by agencies and polluters.
- Regulation of boating: Operation of motorized boats should not be permitted within lakes of less than 50 ha. In larger lakes the number of such boats should be limited to restricted area and carrying capacity of the water body. In any case boating during the periods of breeding and congregations of birds should be banned.
- Protection of riparian and buffer zone vegetation: Any clearances of riparian vegetation (along side rivers) and buffer zone vegetation (around lakes) have to be prohibited.
- Restoration of linkages between water bodies: The process of urbanization and neglect caused disruption of linkages between water bodies such as ancient lake systems of many cities. Wherever such disruptions have taken place alternative arrangements should be provided to establish the lost linkages.
- Rainwater harvesting: Intensive and comprehensive implementation of rain water harvesting techniques can reduce taxation of water bodies and also minimize electricity requirements. The country needs in principle a holistic rainwater harvesting policy aimed at directing water literally from “roof-tops to lakes” after catering to the domestic needs.
- Environment Education: It was felt among the participants that public needs to be better informed about the rational, goal and methods of ecosystem conservation and restoration. In addition, the need was realized for scientist and researchers with the broad training needed for aquatic ecosystem restoration, management and conservation. Public education and outreach should include all components of ecosystem restoration. Lake associations and citizen monitoring groups have proved helpful in educating the general public. Effort should be made to ensure that such groups have accurate information about the causes of lake degradation and various restoration methods. Funding is needed for both undergraduate and graduate programmes in ecosystem conservation and restorations. Training programmes should cross traditional disciplinary boundaries such as those between basic and applied ecology: water quality management and fisheries or wildlife management: among lakes, streams, rivers, coastal and wetland ecology. In this regard the brainstorming session proposes:
- Environmental education program should be more proactive, field oriented and experiential (with real time examples) for effective learning.
- Environmental education should be made mandatory at all levels – schools, colleges, universities, professional courses, teachers and teacher educators at the teachers’ training institutes (C P Ed, B P Ed, B Ed, D Ed)
- Adopt Inter-disciplinary Approach: Aquatic ecosystem conservation and management requires collaborated research involving natural, social, and inter-disciplinary study aimed at understanding various components, such as monitoring of water quality, socio-economic dependency, biodiversity and other activities, as an indispensable tool for formulating long term conservation strategies. This requires multidisciplinary-trained professionals who can spread the understanding of ecosystem’s importance at local schools, colleges, and research institutions by initiating educational programmes aimed at rising the levels of public awareness of aquatic ecosystems’ restoration, goals and methods. Actively participating schools and colleges in the vicinity of the water bodies may value the opportunity to provide hands-on environmental education, which could entail setting up of laboratory facilities at the site. Regular monitoring of water bodies (with permanent laboratory facilities) would provide vital inputs for conservation and management.
Wetland Protection Laws and Government Initiatives
The primary responsibility for the management of these ecosystems is in the hands of the Ministry of Environment and Forests. Although some wetlands are protected after the formulation of the Wildlife Protection Act, the others are in grave danger of extinction. Effective coordination between the different ministries, energy, industry, fisheries revenue, agriculture, transport and water resources, is essential for the protection of these ecosystems. Thus, wetlands were not delineated under any specific administrative jurisdiction. Recently the Ministry of Environment and Forests of the Government of India issued Notification 2010 Regulatory Framework for Wetlands Conservation (Wetland Conservation Rules). Wetlands in India are protected by an array of laws given below:
- The Indian Fisheries Act - 1857
- The Indian Forest Act - 1927
- Wildlife (Protection) Act - 1972
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act - 1974
- Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Cess Act - 1977
- Forest (Conservation) Act - 1980
- The Environment (Protection) Act - 1986
- Wildlife (Protection) Amendment Act - 1991
- National Conservation Strategy and Policy Statement on Environment and Development – 1992
- Environment Impact Assessment Notification, 2009
- Wetlands Regulatory Framework, 2008
- Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules 2010, Government of India
In addition to the above laws, India is a signatory to the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands and the Convention of Biological Diversity. According to these formulations India is expected to conserve the ecological character of these ecosystems along with the biodiversity of the flora and fauna associated with these ecosystems. Despite these, there is no significant development towards sustaining these ecosystems due to the lack of awareness of the values of these ecosystems among the policymakers and implementation agencies. The effective management of these wetlands requires a thorough appraisal of the existing laws, institutions and practices. The involvement of various people from different sectors is essential in the sustainable management of these wetlands.
Apart from government regulation, development of better monitoring methods is needed to increase the knowledge of the physical and biological characteristics of each wetland resources, and to gain, from this knowledge, a better understanding of wetland dynamics and their controlling processes. Discussions based on accurate knowledge and increased awareness of wetland issues can then begin to develop management strategies (to protect, restore and/or mitigate) that account for the function and value of all wetland resources in the face of natural and socioeconomic factors, while continuing to satisfy critical resource needs of the human population.
The Legal framework for the conservation and management of Wetland Ecosystems is provided by the following National and International Legal instruments:
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972: This act provides for the protection of wild animals, birds and plants. For the purpose of this act, the state government constitutes the Wildlife Advisory board, which performs the following functions: It advices the state government:
- In the selection of areas to be declared as Sanctuaries, National Parks and Closed Areas.
- In the formulation of policy of protection and conservation of wildlife and specified plants.
- In relation to the measures to be taken for harmonizing the needs of the tribals and forest dwellers with the protection and conservation of wildlife.
This Act imposes prohibition on hunting of wild animals, their young ones as well as their eggs except with prior permission of the Chief Wildlife Warden. This acts prohibits the picking, uprooting, destroying, damaging, possessing of any plant in a protected area, except with prior permission of the Chief Wildlife Warden. The State government may declare any area; which it considers to have adequate ecological, faunal, geomorphological, natural or zoological significance for the purpose of protecting, propagating or developing wildlife or its environment; to be included in a sanctuary or a National Park. No person shall, destroy, exploit or remove any wildlife from a National Park and Sanctuary or destroy or damage the habitat or deprive any wild animal or plant its habitat within such National Park and Sanctuary. The State government may also declare any area closed to hunting for a designated period of time if it feels the ecosystem of that area is disturbed by hunting.
Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: for the prevention and control of water pollution and the maintaining or restoring of wholesomeness of water. To carry out the purposes of this act, the Central and the State government constitutes the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Board (SPCB) respectively. The main functions of the pollution control boards include:
- Advice the government on any matter concerning the prevention and control of water pollution.
- Encourage, conduct and participate in investigations and research relating to problems of water pollution and prevention, control or abatement of water pollution.
- Lay down or modify standards on various parameters for the release of effluents into streams.
- Collect and examine effluent samples as well as examine the various treatment procedures undertaken by the industries releasing the effluent.
- Examine the quality of streams.
- Notify certain industries to stop, restrict or modify their procedures if it feels that the present procedure is deteriorating the water quality of streams.
- Establish or recognize laboratories to perform its functions including the analysis of stream water quality and trade effluents.
Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980: Without the permission of the Central government, no State government or any other authority can:
- Declare that any reserved forest shall cease to be reserved.
- Issue permit for use of forest land for non-forest purpose.
- Assign any forest land or portion thereof by way of lease or otherwise to any private person, authority, corporation, agency or any other organization, not owned, managed or controlled by government.
- Clear off natural trees from a forest land for the purpose of reafforestation.
The Biological Diversity Act, 2002: India is a signatory to the United Nations Convention on Biological Resources, 1992 and in accordance with that convention, brought into force The Biological Diversity Act, 2002. This act prohibits biodiversity related activities as well as transfer of the results of research pertaining to biodiversity to certain persons. It also necessitates the approval of National Biodiversity Authority before applying for Intellectual Property Rights on products pertaining to biological diversity. This act emphasizes the establishment of National Biodiversity Authority to carry out various functions pertaining to the Act, viz guidelines for approving collection, research and patents pertaining to biological diversity. It also notifies the central government on threatened species. The central government to develop plans, programmes and strategies for the conservation, management and sustainable use of the biodiversity. Where the Central Government has reason to believe that any area rich in biological diversity, biological resources and their habitats is being threatened by overuse, abuse or neglect, it shall issue directives to the concerned State Government to take immediate ameliorative measures.
Convention on Wetlands of International Importance, especially as Waterfowl habitats, (Ramsar) 1971: To stem the progressive destruction of the wetlands, Ramsar convention was signed. Waterfowls are birds ecologically dependent on the wetlands. The various points agreed under Ramsar convention includes:
- Each contracting party should nominate at least one wetland having significant value in terms of ecology, botany, zoology, limnology or hydrology to be included in the List of Wetlands of International Importance (Ramsar sites) and precisely describe its boundaries.
- The contracting parties will have right to add further wetland sites to the list, expand the boundaries of the existing sites and also to delete or minimize the boundaries of the existing sites.
- Each contracting party shall strive for the conservation, management and restoration of the wetlands in the list.
- Establishment of nature reserves in the area of wetlands thereby protecting it as well as the biological diversity it supports.
- Restriction of boundaries or deletion of a wetland listed as Ramsar sites should be immediately compensated by the creation of additional nature reserves for the protection of waterfowls and other species habiting that wetland.
International convention for the protection of Birds, 1950: To abate the ever dwindling number of certain bird species (particularly the migratory ones) as well as the other birds, this convention was made. This is an amendment to the “International Convention for the Protection of Birds useful to Agriculture, 1902”. The objectives of this convention include:
- Protection to all birds, their young ones and their eggs especially in their breeding season.
- Prohibit hunting, killing, mass capture or captivating birds, except those causing intense damage to crops or other components of the ecosystem, such so that the above said components is in the danger of extinction.
- Adopt measures to prohibit industries and other processes causing contamination of air and water that has adverse effects on the survival of birds.
- Adopt measures to prohibit the destruction of suitable breeding grounds and the bird habitat and also encourage the creation of suitable land and water habitat for the birds.
Bonn Convention on Conservation of Migratory Species, 1979: According to the Bonn Convention on Conservation of Migratory Species, the participating parties:
- Should promote, co-operate in and support research relating to migratory species.
- Shall endeavour to provide immediate protection for migratory species which are endangered.
- Shall strive to conserve and restore those habitats of the endangered species in an effort to eliminate the chances of extinction of that species.
- Shall prohibit or minimize those activities or obstacles that seriously impede or prevent the migration of the species.
Convention on Biological Diversity, 1992: The main objectives of this convention are the conservation of biological diversity, the sustainable use of its components and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources. In accordance with this convention, each contracting party shall –
- Identify places supporting immense biological diversity.
- Monitor through sampling or other means the components of biological diversity identified and strive for the conservation of those components requiring urgent attention.
- Develop new or adapt existing strategies, plans and programmes for the conservation and sustainable use of biological diversity.
- Identify activities which have or may have significant adverse impact on the sustainability of the biodiversity in an area.
- It prescribes conservation of biological diversity by either In situ conservation mechanisms or Ex situ conservation mechanisms or both.
In situ conservation: Each contracting parties shall declare a region harbouring immense biological diversity as a protected area and develop various plans and strategies for the establishment, conservation and management of these protected areas and also strive to conserve biodiversity beyond these protected areas.
- Promote environmentally sound and sustainable development in the areas adjacent to the protected areas so as to further enhance the development and protection of these protected areas.
- Promote the protection of ecosystems, prevent the introduction of alien species likely to have an adverse effect on the existing ecosystem and also rehabilitate & restore degraded ecosystems.
- Enforce legislative measures for the protection of threatened species and population.
Ex situ conservation : Each contracting party shall establish facilities for ex situ conservation and for research on plants, animals and micro-organisms, especially the threatened species, augment their number and take steps for their reintroduction in their own natural habitat.
Relative merits and scope of the respective Indian laws with respect to the wetlands protection and conservation is given in Table 2.
Table 2: Sections applicable to Wetlands in the various environmental laws
No. |
Act |
Relevant Sections |
1 |
The Wildlife (Conservation) Act, 1972 |
Prohibits hunting of wild animals, their young ones as well as their eggs
Prohibits the picking, uprooting, destroying, damaging, possessing of any plant in a protected area
Can declare any area with high ecological significance as a national park, sanctuary or a closed area. |
2 |
The Biological Diversity Act, 2002 |
Prior approval needed from National Biodiversity Authority for collection of biological materials occurring in India as well as for its commercial utilization.
Panchayath to document biodiversity and maintain biodiversity registers |
3 |
Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980 |
Without the permission of the Central government, no State government or any other authority can :
- Declare that any reserved forest shall cease to be reserved.
- Issue permit for use of forest land for non-forest purpose.
- Assign any forest land by way of lease or otherwise to any private person, authority, corporation, agency or any other organization, not owned, managed or controlled by government.
- Clear off natural trees from a forest land for the purpose of re-afforestation.
|
4 |
Water (Control and Prevention of Pollution) Act, 1974 |
It is based on the “Polluter pays” principle.
The Pollution Control Boards performs the following functions :
- Inspects sewage and effluents as well as the efficiency of the sewage treatment plants.
- Lay down or modifies existing effluent standards for the sewage.
- Lay down standards of treatment of effluent and sewage to be discharged into any particular stream.
- Notify certain industries to stop, restrict or modify their procedures if the present procedure is deteriorating the water quality of streams.
|
5 |
Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules, 2010 |
Prohibited Activities
- Conversion of wetland to non-wetland use
- Reclamation of wetlands
- Solid waste dumping and discharge of untreated effluents.
Regulated activities
- Withdrawal of water, diversion or interruption of sources
- Treated effluent discharges – industrial/domestic/agro-chemical.
- Plying of motorized boats
- Dredging
- Constructions of permanent nature within 50 m
- Activity which interferes with the normal run-off and related ecological processes – up to 200 m
|
6 |
National Environment Policy, 2006 |
The principal objectives of NEP includes :
- Protection and conservation of critical ecological systems and resources, and invaluable natural and man made heritage.
- Ensuring judicious use of environmental resources to meet the needs and aspirations of the present and future generations.
- It emphasizes the “Polluter Pays” principle, which states the polluter should, in principle, bear the cost of pollution, with due regard to the public interest.
|
8 |
The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 |
Lays down standards for the quality of environment in its various aspects.
Laying down standards for discharge of environmental pollutants from various sources and no persons shall discharge any pollutant in excess of such standards.
Restrictions of areas in which industries, operations or processes shall not be carried out or carried out subject to certain safeguards. |
9 |
National Water Policy, 2002 |
Water is a scarce and precious national resource and requires to be conserved and management.
Watershed management through extensive soil conservation, catchment-area treatment, preservation of forests and increasing the forest cover and the construction of check-dams should be promoted.
The water resources should be conserved by retention practices such as rain water harvesting and prevention of pollution. |
| |



