2. Materials and methods |
The study area, Kolar is located in Karnataka state, India. It lies in the plain regions (semi arid agro-climatic zone) extending over an area of 8238 sq. km. between 77°21’ to 78°35’ E and 12°46’ to 13°58’ N (shown in figure 2). For administrative purposes, it is divided into 11 taluks (or administrative boundaries /blocks/units). The distribution of rainfall is during southwest and northeast monsoon seasons. The average population density of the district is about 2.09 persons/hectare. The district forms part of northern extremity of the Bangalore plateau. The area is often subjected to recurring drought. The rainfall is both scanty and erratic in nature. The district is devoid of significant perennial surface water resources leading to limited ground water potential. The terrain has a high runoff due to less vegetation cover contributing to erosion of top productive soil layer leading to poor crop yield. Out of about 280 thousand hectares of land under cultivation, 35% is under well and tank irrigation (Ramachandra et al., 2005).
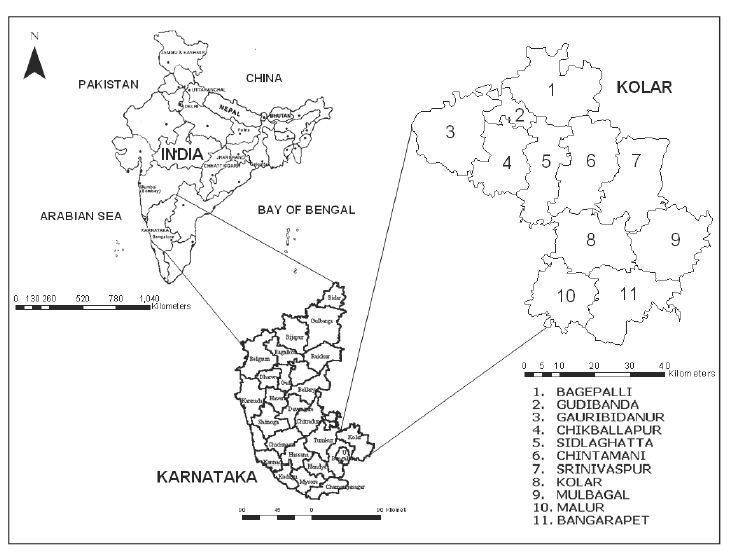
Figure 2: Study area – Kolar district, Karnataka State, India.
MODIS data were downloaded from the Earth Observing System Data Gateway (http://edcimswww.cr.usgs.gov/pub/imswelcome/). These data sets are known as “MOD 09 Surface Reflectance 8-day L3 global” product with spatial resolutions 250 m (band 1 and band 2) and 500 m (band 1 to band 7). The MODIS Surface-Reflectance Product (MOD 09) is computed from the MODIS Level 1B land bands 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 7 (centered at 648 nm, 858 nm, 470 nm, 555 nm, 1240 nm, 1640 nm, and 2130 nm, respectively). The product is an estimate of the surface spectral reflectance for each band as it would have been measured at ground level if there were no atmospheric scattering or absorption (http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/dataproducts.php? MOD_NUMBER=09). Each MODIS Level-1B data product (Guenther et al., 1998), contains the radiometrically corrected, fully calibrated and geolocated radiances at-aperture for all 36 MODIS spectral bands at 1 km resolution (http://daac.gsfc.nasa.gov/MODIS/Aqua/product_descriptions_modis.shtml#rad_geo). These data are broken into granules approximately 5-min long and stored in Hierarchical Data Format (HDF). Bands 1 to 36 MODIS data “MOD 02 Level-1B Calibrated Geolocation, Data Set” were downloaded from EOS Data Gateway (http://edcimswww.cr.usgs.gov/pub/imswelcome/). The Level 1B data set contains calibrated and geolocated at-aperture radiances for 36 bands generated from MODIS Level 1A sensor counts (MOD 01). The radiances are in W/(m2 µm sr). In addition, Earth BRDF may be determined for the solar reflective bands (1-19, 26) through knowledge of the solar irradiance (e.g., determined from MODIS solar-diffuser data and from the target-illumination geometry). Additional data are provided, including quality flags, error estimates, and calibration data (http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/data/dataprod/ dataproducts.php? MOD_NUMBER=02). The Indian Remote Sensing (IRS) Satellites-1C/1D LISS 3 (Linear Imaging Self-Scanning Sensor 3) MSS (Multi Spectral Scanner) having 3 bands (G, R and NIR) data with a spatial resolution 23.5 m were procured from NRSA, Hyderabad. The main sources of primary data are from field (using GPS), the Survey of India (SOI) toposheets of 1:50,000, 1:250,000 scale and the secondary data were collected from the government agencies (Directorate of census operations, Agriculture department, Forest department and Horticulture department) etc.
The methods adopted in the analysis involved :