IDENTIFICATION CHARACTERS OF UTTARA KANNADA EDIBLE BIVALVES
Anadara granosa (Linnaeus)
Shell orbucularly-ovate, equivalve, side slightly angulated. Sclupture radiately ribbed; ribs upto 20, tuberculate and crenulated Source: (Dey, 2006).
Meretrix casta (Chemnitz)
Meretrix casta does not show colour patterns. Shell ovate to oblong with or without two obscure and often imperfect radial bands. Anterior cardinal tooth in left valve entire. Hinge elongate and strong. Pallial sinus shallow. Length of shell is usually less than 50 mm. Posterior margin of the shell when more angular and pointed are considered as a varietal form as M. casta var. ovum (Hanley) (Hornell 1917). Source: (Nayar and Mahadevan, 1974; Rao et al., 1989)
Meretrix meretrix (Linnaeus)
Shell large, heavy, thick, ventricose, umbo pointed, elevated and slightly anterior in position; anterior margin rounded, ventral margin convex, posterior margin angulated; valves trigono suborbicular; anterior adductor scar elongately ovate, posterior adductor scar broader posteriorly and pointed anteriorly; pallial sinus very shallow. Posterior lateral teeth in the left valve and corresponding depression in the right valve are finely denticulate or striate. Anterior cardinal tooth of left valve distinctly notched. It is highly variable in colour; length (anterio-posterior axis) 60-75 mm. Source: (Nayar and Mahadevan, 1974; Rao et al., 1989; Apte, 1998; Dey, 2006)
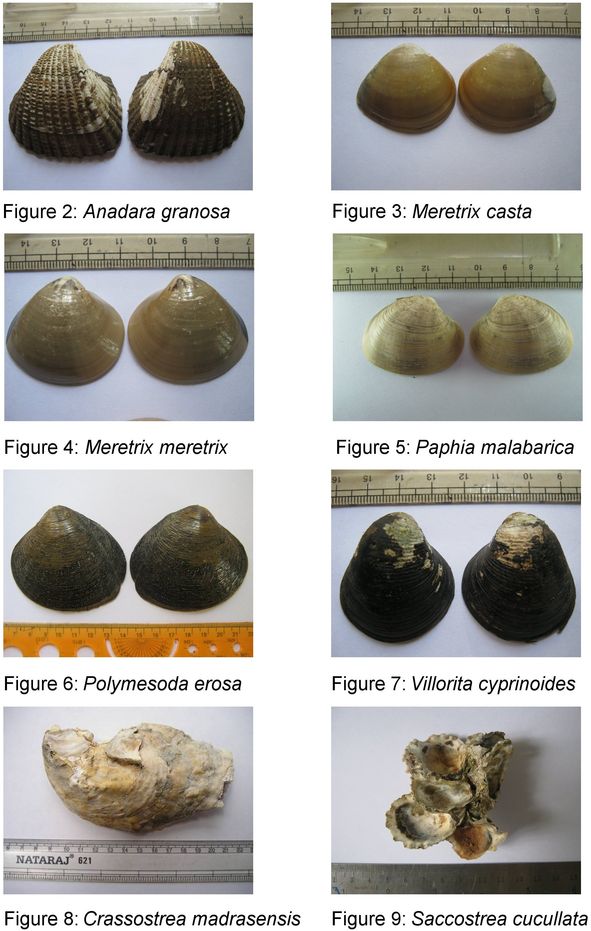
Paphia malabarica (Chemnitz)
Shell large, thick, heavy, sculptured with strong close set ridges. Length of the shell about one and one third times as long as high. Pallial sinus 'U' shaped and very deep. Lunule short and broader. Hinge bears three short but strong cardinal teeth. The tooth in front of the cardinals in the left valve and the hollow in the right is rudimentary. Pale yellowish brown colour.
Source: (Rao et al., 1989; Apte, 1998)
Polymesoda erosa (Solander)
Shell large, solid, inequilateral, subtrigonal or orbicular with concentric striae on the outer surface, periostracum thin and yellow or thick and brown or dark green or black. Slight, distinct and characteristic flexure extending from the umbo to the mid-posterior margin of the shell. The hinge tooth are strong, larger and antero-lateral tooth located closer to the anterior cardinal tooth.
Source: (Morton, 1984; Rao, 1989; Ingole et al., 1994)
Villorita cyprinoides (Gray)
Shell fairly large, trigonal, cordate and very oblique, anterior margin short, regularly curved above, almost straight in the middle, then with a rapid curve and meeting the ventral boarder, the latter curving upwards and meeting the posterior margin, the posterior margin nearly straight, much larger than the anterior, with thick concentric ridges, umbones prominent, near the anterior side, recurved, a large, thick external ligament posteriorly, inflated in the umbonal as well as in the middle regions and greatly compressed ventrally. Shell thick with concentric ridges prominent with anterior portion, umbones striated. Periostracum greenish brown, dark brown or black.
Source: (Rao, 1989; Rao et al., 1989)
Crassostrea madrasensis (Preston)
Shell straight, shape irregular, covered by numerous foliaceous laminae, left valve deep, right one slightly concave, hinge narrow and elongated, adductor scar sub-central, reniform and dark purple in colour, inner surface of valves white, glosssy and smooth, purplish black colouration on the inner margin of the valves . Source: (Rao, 1974)
Saccostrea cucullata(Born, 1778)
Variable in shape, inequivalve, irregularly circular to oval, left valve more thick, deep and large than right valve sometimes cup like, sometimes flat; outer margin with a series of sharp folds, which interlock with each other; sculpture of oppressed lamellae, some becoming spiny, other worn,smooth; muscle scars kidney shaped. Nodular chomata usually present around all margins. Colour whitish or greenish white, marked with deep purple towards the margins, muscle scars darker than surrounding shell area. Source: (Dey, 2006)