
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
NAME
v.net.path - Finds shortest path on vector network.KEYWORDS
vector, network, shortest pathSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- -t
- Use turntable
- -g
- Use geodesic calculation for longitude-latitude locations
- -s
- Write output as original input segments, not each path as one line.
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input vector map
- Or data source for direct OGR access
- output=name [required]
- Name for output vector map
- arc_layer=string [required]
- Arc layer
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 1
- arc_type=string[,string,...] [required]
- Arc type
- Input feature type
- Options: line, boundary
- Default: line,boundary
- node_layer=string [required]
- Node layer
- Vector features can have category values in different layers. This number determines which layer to use. When used with direct OGR access this is the layer name.
- Default: 2
- file=name
- Name of file containing start and end points. If not given, read from stdin
- arc_column=string
- Arc forward/both direction(s) cost column (number)
- arc_backward_column=string
- Arc backward direction cost column (number)
- node_column=string
- Node cost column (number)
- dmax=float
- Maximum distance to the network
- If start/end are given as coordinates. If start/end point is outside this threshold, the path is not found and error message is printed. To speed up the process, keep this value as low as possible.
- Default: 1000
- turn_layer=string
- Layer with turntable
- Relevant only with -t flag
- Default: 3
- turn_cat_layer=string
- Layer with unique categories used in turntable
- Relevant only with -t flag
- Default: 4
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
v.net.path determines least costly, e.g. shortest or fastest path(s) on a vector network.Costs may be either line lengths, or attributes saved in a database table. These attribute values are taken as costs of whole segments, not as costs to traverse a length unit (e.g. meter) of the segment. For example, if the speed limit is 100 km / h, the cost to traverse a 10 km long road segment must be calculated as
length / speed = 10 km / (100 km/h) = 0.1 h.
The input vector needs to be prepared with v.net operation=connect in order to connect points representing center nodes to the network.
Nodes and arcs can be closed using cost = -1.
Least cost paths are written to the output vector map with an attached attribute table.
Nodes can be
- piped into the program from file or from stdin, or
- defined in the graphical user interface ("enter values interactively").
id start_point_category end_point_category
or
id start_point_x start_point_y end_point_x end_point_y
Points specified by category must be exactly on network nodes, and the input vector map needs to be prepared with v.net operation=connect.
When specifying coordinates, the next network node to a given coordinate pair is used.
The attribute table will contain the following attributes:
- cat - path unique category assigned by module
- id - path id (read from input)
- fcat - from point category
- tcat - to point category
- sp - result status:
- 0 - OK, path found
- 1 - node is not reachable
- 2 - point of given category does not exist
- cost - travelling costs (on the network, not to/from network)
- fdist - the distance from first point to the network
- tdist - the distance from the network to second point
Application of flag -t enables a turntable support. This flag requires additional parameters turn_layer and turn_cat_layer that are otherwise ignored. The turntable allows to model e.g. traffic code, where some turns may be prohibited. This means that the input layer is expanded by turntable with costs of every possible turn on any possible node (intersection) in both directions. Turntable can be created by the v.net module. For more information about turns in the vector network analyses see wiki page.
NOTES
Nodes and arcs can be closed using cost = -1.If the cost columns arc_column, arc_backward_column and node_column are not specified, the length of network segments is measured and zero costs are assumed for nodes.
When using attributes, the length of segments is not used. To get accurate results, the line length must be taken into account when assigning costs as attributes. For example, to get the fastest path, the columns 'max_speed' and 'length' are required. The correct fastest path can then be found by specifying arc_column=length/max_speed. If not yet existing, the column containing the line length ("length") has to added to the attributes table using v.to.db.
EXAMPLE
Shortest (red) and fastest (blue) path between two digitized nodes (Spearfish):
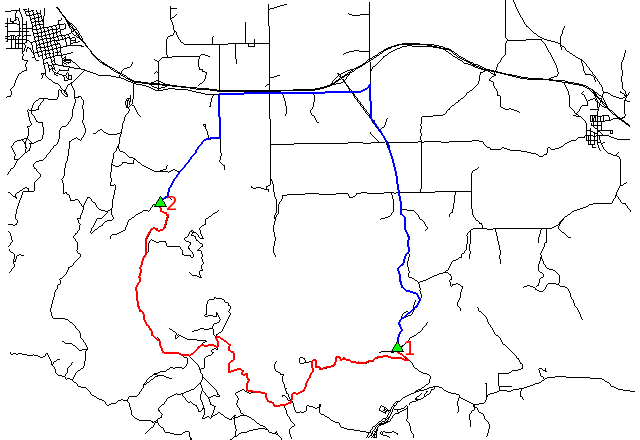
# Spearfish
echo "1|601955.1|4916944.9|start
2|594385.6|4921565.2|end" | v.in.ascii in=- cat=1 x=2 y=3 out=startend col="cat integer, \
east double precision, north double precision, label varchar(6)"
v.db.select startend
g.copy vect=roads,myroads
# create lines map connecting points to network
v.net myroads points=startend out=myroads_net op=connect thresh=500 arc_layer=1 node_layer=2
# set up costs
# create unique categories for each road in layer 3
v.category in=myroads_net out=myroads_net_time opt=add cat=1 layer=3 type=line
# add new table for layer 3
v.db.addtable myroads_net_time layer=3 col="cat integer,label varchar(43),length double precision,speed double precision,cost double precision,bcost double precision"
# copy road type to layer 3
v.to.db myroads_net_time layer=3 qlayer=1 opt=query qcolumn=label columns=label
# upload road length in miles
v.to.db myroads_net_time layer=3 type=line option=length col=length unit=miles
# set speed limits in miles / hour
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="5.0"
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="75.0" where="label='interstate'"
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="75.0" where="label='primary highway, hard surface'"
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="50.0" where="label='secondary highway, hard surface'"
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="25.0" where="label='light-duty road, improved surface'"
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=speed val="5.0" where="label='unimproved road'"
# define traveling costs as traveling time in minutes:
# set forward costs
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=cost val="length / speed * 60"
# set backward costs
v.db.update myroads_net_time layer=3 col=bcost val="length / speed * 60"
# ... the 'start' and 'end' nodes have category number 1 and 2
# Shortest path: ID as first number, then cat1 and cat2
echo "1 1 2" | v.net.path myroads_net_time arc_layer=3 node_layer=2 out=mypath
# Fastest path: ID as first number, then cat1 and cat2
echo "1 1 2" | v.net.path myroads_net_time arc_layer=3 node_layer=2 arc_column=cost arc_backward_column=bcost out=mypath_time
g.region vector=myroads_net d.mon x0 d.vect myroads_net # show shortest path d.vect mypath col=red width=2 # show fastest path d.vect mypath_time col=blue width=2 # start and end point d.vect myroads_net icon=basic/triangle fcol=green size=12 layer=2 d.font font=Vera d.vect startend disp=cat type=point lsize=14 layer=2
SEE ALSO
d.path, v.net, v.net.alloc, v.net.iso, v.net.salesman, v.net.steiner, v.to.dbAUTHORS
Radim Blazek, ITC-Irst, Trento, ItalyDocumentation: Markus Neteler, Markus Metz
TURNS SUPPORT
The turns support was implemnented as part of GRASS GIS turns cost project at Czech Technical University in Prague, Czech Republic.
Implementation: Stepan Turek
Documentation: Lukas Bocan, Eliska Kyzlikova, Viera Bejdova
Mentor: Martin Landa
SOURCE CODE
Available at: v.net.path source code (history)
Latest change: Thu Oct 1 17:35:27 2020 in commit: 744fcaefa6aa37121e72a9530e90b48fa07bef3a
Note: This document is for an older version of GRASS GIS that will be discontinued soon. You should upgrade, and read the current manual page.
Main index | Vector index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 7.8.8dev Reference Manual