Active Chlorine Content
that portion of total chlorine (or of a chlorine compound) which exerts a germicidal effect when added to raw water, also called free available chlorine
Alkalinity
in hydrology the ability of water to neutralize acid, due primarily to the presence of bicarbonate, carbonate and hydroxide (expressed as an equivalent amount of calcium carbonate, like hardness)
Carbon Hardness
is determined by the content of hydrogen-carbonate in water (HCO3-ions, usually bonded to a calcium or magnesium ion). It is governed by the equilibrium:
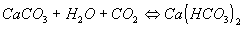
If the equilibrium is disturbed due to the escape of CO2 (e.g., through heating), calcium precipitates. Excess CO2 has a corrosive effect on pipes made of metal or concrete. It therefore must be removed (e.g. by means of aeration). The ideal state is that of the equilibrium of the water (pH of 7), i.e., when there is just enough CO2 in the water to keep the calcium hydrocarbonates in solution.
Colloids
Electrically charged particles (mostly negative) which adsorb particles of opposite charge on their surface (formation of an electric double layer). They don't agglomerate because of the repelling force of similarly charged particles. They don't settle to the bottom on account of their low specific gravity.
E. Coli
Escherichia coli, serve as indicator organisms. Their presence indicates fecal contamination. Water samples in disinfected jars must be analyzed for E. coli within a few hours. Two standard methods of sorting are available. They are based on the fact that germs multiply in a specific culture medium and at a certain temperature. The germs are then counted. The Membrane Filter (MF) procedure (number of germs in 100ml) and the Multiple Tube Method (MPindex/100ml).
Filter Resistance
is equal to the head difference between inflow and outflow (head loss), increases as the voids in the filter medium get clogged by retained particles.
Filtration Rate, v
also called filtration velocity or flow velocity, amount of water (m³) that passes through a filter area of 1 m² in 1 hour (m³/m² · h = m/h).
Flow Rate, Q
amount of water passing a plant per hour or per day (usually expressed in m³/d, m³/h or a/h), also called capacity of a plant
MF
Membrane Filter Technique (see E. coin)
MPN
Most probable number (see E. coli)
Percent Volume
measure of concentration for solutions: 1 Vol % = 1 g of dissolved substance per 100 ml of solution
Percent Weight
Measure of concentration for mixtures solid/liquid or liquid/solid: 1% weight = 1 g of substance per 100 g of mixture.
pH Value
pH is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen-ion concentration. Pure neutral water has equal concentration of H+ and OH-ions; 1 1iter contains 10^(-7) g, i.e., water at:
pH = 7 is neutral
pH= 0 to 7 is acid
pH = 7 to 14 is basic
Almost all water with pH < 7 has a corrosive effect on metals, caused by excessive CO2 (see carbon hardness).
ppm
parts per million: measure for the concentration of a substance in a mixture (e.g., 1 g per kg, 1 ml per m³ )
Turbidity
caused by suspended matter present in water. It is measured by the interference with fine suspended particles of light penetrating the solution. Units: 1 NTU (Nephelometric Turbidity Unit) = 1 FTU (Formazin Turbidity Unit) ~ 1 mg SiO2/a
Uniformity Coefficient, UC
measures the ratio of d60 over d10 of a sieve analysis
Unit Measures for Impurities of Water (diameter)
coarse impurities
> 1 m m (10-6 m)
colloids
1 nm -1 m m
small dispersed particles (ions, molecules)
< 1 nm (10-9 m)
viruses
1 nm (to 1 m m)
bacteria
10 nm -1 m m
1 A = 0.1 nm = 10-10 m
(1 Angstroem)

