|
Results and Discussion
A total number of 827 medicinal plant species under 544 genera and 136 families have been recorded in this study based on the published literatures. Highest number of plant species found in Eastern zone (225 spp.) followed by Northeast (207 spp.), Northern zone (150 spp.), Central zone (125 spp.) and Western zone (125 spp.), as shown in Figure 2.
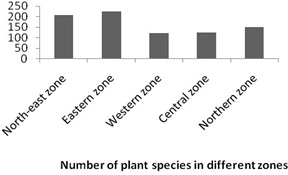
Fig.2 Number of Plant Species in Different Zones
The dominant plant form is herbs (35.91 %) as represented in Figure 3 followed by trees (30.83 %), shrubs (20.07%), climbers (12.93%) and orchid (0.24%). Different plant parts have been used for curing many ailments.
It was also observed that some medicinally important plants have more than one part with the medicinal uses. Leaves have major use (25 %), along with root (16.13 %) and stem bark (11.66%), as per Figure 4.
It appears from the study that the most dominant families are Leguminosae (89 spp.) followed by Asteraceae (45 spp.) and Rubiaceae (39 spp.), depicted in Figure 5. Ficus with 11 species, Dioscoreae and Phyllanthus with 8 species are the most dominant genera found in the study region being depicted in Figure 6. Here 590 members of plant species have more than one use for remedial measure.
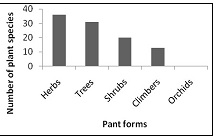
Fig.3: Plant Forms are Reported in Different Zone
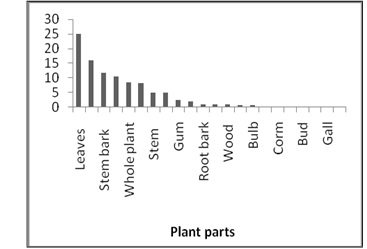
Fig.4 Plants Part used for Curing Different Diseases
It appears from the study that the most dominant families are Leguminosae (89 spp.) followed by Asteraceae (45 spp.) and Rubiaceae (39 spp.), depicted in Figure 5. Ficus with 11 species, Dioscoreae and Phyllanthus with 8 species are the most dominant genera found in the study region being depicted in Figure 6. Here 590 members of plant species have more than one use for remedial measure.Aegle marmelos has wide use in 18 locations of different region followed by Cynodon dactylon (17 locations), Azadirachta indica (16 locations), Ocimum tenuiflorum (15 locations) and many are reported from at least 2 locations shown on Figure 7. The five zones of India are inhabitants by local tribes like Kinnara, Amchi, Bodo, Bhil, Bhilala and system. The plant species which are used in Pataya, Meitei, Rawal, Gond, Bhumij, Kurmi
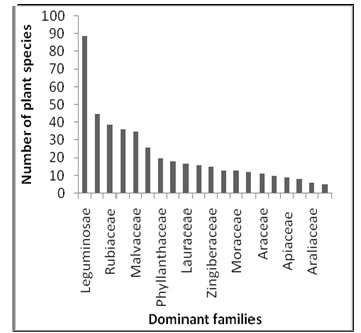
Fig.5: Dominant Families among Different Parts of India
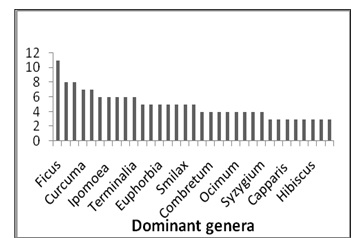
Fig.6: Dominant Genera among Different Parts of India
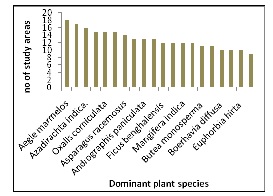
Fig.7 Species Presence in Studied Area
Among these, 157 plant species are noted for abdominal problem (diarrhoea, dysentery, dyspepsia, stomach ache, stomach problem), skin diseases with 141 plants species and respiratory problems (fever, cold, cough) with 138 species. Ninety plant species act as a drug (aphrodisiac, anthelmintic, laxative, febriguge, antiseptic). 52 plant species act as remedy for the persons bitten by animals.
It was also reported that the plant species have medicinal benefits for animals. The ethnoveterinary medicine used from 12 plants against 9 disease (galactagogue, ulcer, wounds, eye disease, urination, loose evacuation, stomach ache, typhoid fever and for removing parasites from their skin.). Stem bark and seeds are most used plants parts for veterinary medicine than root, whole plants, leaves and fruits. The route of administration for animals is oral by using plant parts in the form of decoction, externally as a paste and powder. The ethno medicine for humans are used mostly paste followed by juice, powder, decoction as shown in Figure 8.
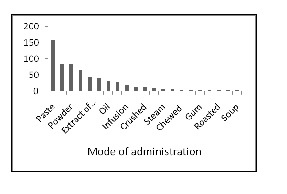
Fig.8 Route of Administration used in Health Care System
Fidelity Level
Table 1 lists the FL values which highlight the most important medicinal species among the five zones of India. Fidelity Level (FL) of plants has been calculated based on most dominant plant and showed the corresponding plant against a particular ailment. Higher values of Fidelity Level (%) indicate the most preferred dominant plant species for each particular ailment category. The analysis showed that the highest FL value found in 3 plant species among the five study region for different diseases are Gymmema sylvestre (diabetes, 100%) followed by Biden pilosa (tooth problem, 100%) and Valernia jantamansi (stomach ache, 100%). The least FL values for Oxalis corniculata (23%) which indicates less preferred plant species in regards to constancy.
| Disease |
Dominant plants |
Fidelity level |
| Diarrhoea |
Aegle marmelos |
37.5% |
| Cold |
Cold Ocimum sanctum |
Cold Ocimum sanctum 41.17% |
| Wounds & cuts |
Tridax procumbens |
78% |
| Skin problem |
Azadirachta indica |
70% |
| Malaria |
Andrographis paniculata |
50% |
| Diabetes |
Gymmema sylvestre |
100% |
| Tooth problem |
Bidens pilosa |
100% |
| Piles |
Piles Oxalis corniculata |
Piles Oxalis corniculata 23.07% |
| Stomach ache |
Stomach ache Valernia jantamansi |
Stomach ache Valernia jantamansi 100% |
| Asthma |
Emblica offcinales |
25% |
Table 1: Dominant Plant Species for a Particular Diseases and their Fidelity Level.
Informant Consensus Factor (ICF)
ICF is considered to know the traditional values of plants among the five zones of India to treat certain ailment categories (Table 2). From the study literature, out of the 489 sacred groves, 829 species with medicinal values, treating 33 different ailments. In our study, for the sake of simplicity out of 33 different ailments only 10 ailments are categorized. It is clear from the study that the ICF values varied from 0.04 to 0.64. Cold has the highest ICF value 0.64 with 40 use-reports for 15 plant species followed by diarrhoea have 0.24 with 76 use-reports for 58 plant species, wounds and cuts have 0.24 with 103 use-reports for 78 plant species.
The high ICF value for cold possibly showed that this ailment is common in the study area. High ICF values also helps searching for bioactive compounds and subsequently considered as more preferred traditionally to treat ailments. The low ICF value is for asthma due to lack of less constancy about the ailments.
Threats
These small patches have multiple disturbance factors like anthropogenic pressure, pollution, urbanization, soil erosion, logging, agriculture conversion of forest into land and road construction, invasion, over grazing, encroachment, developing industries, shifting social and cultural perspectives which put these medicinal plant resources under threat category. Out of 829 medicinal plant species, herbs species have 3 spp. endangered, 1 spp. critically endangered, 27 spp. under least concern, where tree species, have 1 spp. near threatened, 2 spp. vulnerable, 18 spp. least concern, shrub have 8 spp. least concern, climber have 1 spp. vulnerable and 2 spp. least concern and even orchid also 1 spp. under least concern.
| Disease |
No of Plant Species |
Used Report |
ICF |
| Diarrhoea |
58 |
76 |
0.24 |
| Cold |
15 |
40 |
0.64 |
| Wounds and cuts |
78 |
103 |
0.24 |
| Skin problem |
141 |
185 |
0.23 |
| Malaria |
23 |
29 |
0.21 |
| Diabetes |
39 |
49 |
0.2 |
| Tooth problem |
42 |
54 |
0.12 |
| Piles |
45 |
52 |
0.07 |
| Stomach ache |
17 |
20 |
0.15 |
| Asthma |
30 |
34 |
0.04 |
Table 2 Category of Different Diseases and their Informant Consensus Factor (ICF). |








