| Theme: 8. Pollution—Air, Water—Consequences and Remedial Measures | Paper 1 | Paper 2 | Paper 3 | Paper 4 |
ISOLATION OF A BACTERIAL SPECIES IN THE INSECTICIDE POLLUTED AREAS |
|||
| Presentation PDF | |||
SYNOPSIS
Bacterial species is isolated from the soil at an agricultural farm and water from a lake. Chemical analysis of the soil and water showed very high concentration of chemicals i.e., Insecticides. Cultural, microscopical and biochemical techniques showed that Bacillus formed the major biomass followed by Staphylococcus and Micrococcus . The cultural techniques involved the serial dilution of the soil and water samples followed by the plating of the sample in the culture media and also the study of cultural charachteristics. The microscopical tests included the Gram's staining of the bacteria, endospore staining and motility study. The biochemical activity of the Bacteria was confirmed by a set of tests that included IMViC, starch hydrolysis, oxidase test etc., Among the Bacillus species isolated, Bacillus stearothermophilus was found to show stress tolerance against various factors such as high temperature, high salinity and also high concentration of insecticide such as chlorpyrifos due to which this species of Bacillus was selected for further studies.
INTRODUCTION
The name Bacillus stearothermophilus is presumably intended to mean fat and heat loving. The most distinctive characters are the capacity to grow at 65°c. Bacillus strains capable of growing at temperature of 65° c and above do not belong to a single species, it is however a useful diagnostic character. Bacillus stearothermophilus occurs in soil, hot springs , desert, arctic waters, ocean sediments, foods and compost. This particular strain isolated from water and soil sample is found to grow in the presence of high percentage of insecticide, chlorpyrifos. Chlorpyrifos is one of about 100 organophosphate insecticides in the market today which is widely used. It is used to kill insect pests by disrupting their nervous system. Chlorpyrifos has an advantage over other products in that it is effective against a wide range of plant eating pests.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The samples were obtained from two different areas of Bangalore . The soil sample was collected from an agricultural farm, R.K. Farms, hosur road, Bangalore . The soil sample was collected at a depth of 15cm and transferred to a clean container (N.S.Subba Rao). The water sample was collected from the
shallow water of the lake Yellanalappa chetty lake located at Bangalore-Chennai road, (NH4) using a sterile conical flask, sealed and transported.
Culturing and isolation was done by using Hi-media. A volume of 1ml of the sample was used and successively diluted and a fixed aliquot of 1ml from each dilution was mixed with molten, cooled , culture media and plated( K.R.Aneja,) Plates were incubate for 24 hrs, cultural charachteristics of the resultant
microbial colonies were noted. Both Bacterial and fungal forms were detected from which Bacterial forms alone were selected and subcultured.(Micheal J. Pelcar, E.C.S. Chan, Noel R. Krieg,)
Gram's staining was performed by commercially available chemicals to detect the Gram's reaction of the bacterium(Harold J Benson,). Enospore staining was also performed by using the commercially available stains to detect the presence of spores and the position of spore whether terminal or center.( Harold J Benson,). The motility of the bacteria was studied by hanging drop technique (Harold J Benson,).
Biochemical tests such as Indole production test, Methyl red test, Voges-proskauer test, citrate utilization test, nitrate reduction test, urease test, catalase test, oxidase test, amylase test, sugar-fermentation test were carried out using the respective Hi-media and reagents.
Indole production test was carried out by using peptone water broth and Kovac's reagent, while Methyl red and Voges-proskauer test was conducted with glucose phosphate broth and the reagents are Methyl red and Barritt's reagent respectively
Citrate utilization test was performed by using Simmon's Citrate agar. Presence of catalase enzyme is detected by using 3% Hydrogen peroxide as the reagent, while oxidase test was conducted using oxidase reagent soaked in a filter paper followed by streaking of the culture onto the filter paper.
Nitrate reduction test is conducted by inoculating the bacteria into nitrate broth and the reagents used were naphthlamine and sulphanilamide
Amylase test was conducted using starch agar media plates that are later flooded with Gram's iodine which is used as a reagent to detect the presence of amylase in bacterial culture while the sugar fermentation tests were conducted to detect the fermentation of sugars that were taken in the desired media and also by using Durham's tube for detection of gas production by the organism. (John.G.Holt,)
The insecticide tolerance was determined by commercially available – Lethal TC- Chlorpyrifos (20%) manufactured by Insecticides, India, Ltd ®, while the salinity tolerance was detected by using different concentration of sodium chloride. Conical flasks with fixed volumes of nutrient broth were taken and the stress agents (chlorpyrifos and sodium chloride) were added to each flask in different concentrations. All the flasks were inoculated with 2% v/v inoculum from 24 hr broth culture, uninoculated broth was used as control. Flasks were placed in a shaking incubator at a temperature of 55° c for 24 hrs at 60 rpm. The culture after incubation was gently vortexed and then allowed to stand for 10min. The optical density of each inoculated broth was read at 600 nm with uninoculated broth as blank for reference by using UV-Visible spectrophotometer.
Temperature tolerance was studied using culture media onto which a 24 hrs old culture was streaked and incubated at different temperatures such as 37°c, 45° c,55° c, 60° c and 65° c and observed for growth after 24 hrs. the plates were
examined for differential growth density. The maximum growth temperature of the isolates was thus determined. Experiment was conducted in triplicates.
The results of the above studies are represented in tables and figures.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1: cultural characteristics of water microflora
| Plate dilution | Size | Shape | Margin | Elevation | Pigmentation | Opacity | Texture | Gram's nature |
| 10 -1 | Pin point | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | Smooth | - rods |
| Medium | Circular | Entire | Raised | Pinkish | Translucent | Smooth | + rods | |
| Medium | Circular | Entire | Convex | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods | |
| Large | Irregular | Serrate | Raised | White | Opaque | smooth | + rods | |
| Small | Circular | Wavy | Umbonate | White | Translucent | smooth | + rods | |
| 10 -2 | Pinpoint | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods |
| Small | Circular | Wavy | Umbonate | White | Translucent | Smooth | + rods | |
| Large | Circular | Entire | Convex | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods | |
| 10 -3 | Pinpoint | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | smooth | - rods |
| Large | Circular | Entire | Convex | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods |

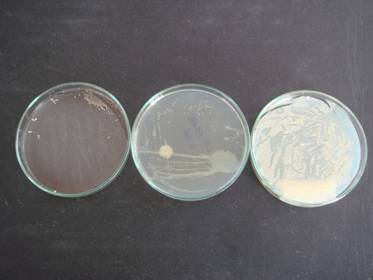
FIGURE:1 Bacterial colonies of water microflora
Table 2: cultural characteristics of soil microflora
| Plate dilution | Size | Shape | Margin | Elevation | Pigmentation | Opacity | Texture | Gram's nature |
| 10 -1 | Small | Circular | Wavy | Umbonate | White | Translucent | smooth | + rods |
| Medium | Circular | Entire | Raised | Pinkish | Translucent | Smooth | + rods | |
| Medium | Circular | Entire | Convex | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods | |
| Large | Irregular | Serrate | Raised | White | Opaque | smooth | + rods | |
| Large | Circular | Entire | Convex | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods | |
| 10 -2 | Pinpoint | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | Smooth | + rods |
| Small | Circular | Wavy | Umbonate | White | Translucent | Smooth | + rods | |
| Pinpoint | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | smooth | - rods | |
| 10 -3 | Large | Circular | Entire | Convex | Off white | Opaque | Smooth | + rods |
| Pin point | Circular | Irregular | Raised | White | Opaque | Smooth | - rods |
Table 3: Morphological charachteristics of the isolate
| Gram's reaction | Gram positive |
| Morphology | Rods |
| Motility | Motile |
| Endospore | terminal |
Based on the results of the table:3, the genera of the isolate is concluded as Bacillus
Table 4: Biochemical tests
| Test | Result |
| Indole | + |
| Methyl red | +++ |
| Voges-proskauer | - |
| pH in VP medium <6 | + |
| Citrate utilization | - |
| Nitrate reduction | + |
| Urease test | - |
| Sugar fermentation –Glucose | ++ |
| Lactose | - |
| Mannitol | - |
| Catalase test | +++ |
| Oxidase test | ++ |
| Amylase | +++ |
Based on the results of the table:4, the isolate is concluded as Bacillus stearothermophilus
Table 5: Studies on temperature tolerance profile of the isolate
| Temperature | Incubation period(Hrs) | Growth on agar | Degree of growth | Growth on broth | Degree of growth |
| 37 0 c | 24 | + | 3+ | + | 3+ |
| 45 0 c | 24 | + | 3+ | + | 3+ |
| 55 0 c | 24 | + | 3+ | + | 3+ |
| 60 0 c | 24 | + | 3+ | + | 3+ |
| 65 0 c | 24 | - | - | - | - |
+ refers to presence of growth; - refers to absence of growth ; 3+ refers to high degree of growth |
|||||





FIGURE:2 BACTERIAL COLONIES AT VARYING TEMPARATURES
Table 6: Results of turbidometric studies on stress tolerance profile
| Stress agent | Concentration | Incubation temperature | O.D. at 660nm |
| Sodium chloride | 2% | 55 0 c | 0.05( + 0.01) |
| 6% | 55 0 c | 0.09( + 0.03) | |
| 8% | 55 0 c | 0.01( + 0.02) | |
| 10% | 55 0 c | 0.01( + 0.02) | |
| chlorpyrifos | 0.001% | 55 0 c | 0.03( + 0.03) |
| 0.005% | 55 0 c | 0.05( + 0.02) | |
| control | 2%v/v | 37 0 c | 0.05( + 0.01) |
| 2%v/v | 55 0 c | 0.09( + 0.03) | |
Figures in the parenthesis represent the standard deviation. |
|||
BIBLIIOGRAPHY
BIODATA OF THE AUTHORS
• Dr. D.N.Saraswathi Raman is currently working as Professor in St.Joseph's college since 1986. She started the research as JRF and SRF (CSIR) and continued with Post doctoral fellowship (DST). She is currently involved in research related to biotechnology, molecular biology, biochemistry and physiology. In addition to PG teaching, she is involved in guiding students for M.Phil and Ph.D of various universities.
• Ms. Savitha.K is working as Lecturer in Biotechnology in Don Bosco College from August 2002 till date. She has done her Post graduation in Microbiology and presently pursuing Ph.D degree in Biotechnology under the guidance of Dr. D.N.Saraswathi Raman.