
NAME
r.resamp.interp - Resamples raster map to a finer grid using interpolation.KEYWORDS
raster, resample, interpolation, nearest neighbor, bilinear, bicubic, lanczos, parallelSYNOPSIS
Flags:
- --overwrite
- Allow output files to overwrite existing files
- --help
- Print usage summary
- --verbose
- Verbose module output
- --quiet
- Quiet module output
- --ui
- Force launching GUI dialog
Parameters:
- input=name [required]
- Name of input raster map
- output=name [required]
- Name for output raster map
- method=string
- Sampling interpolation method
- Options: nearest, bilinear, bicubic, lanczos
- Default: bilinear
- nearest: Nearest-neighbor interpolation
- bilinear: Bilinear interpolation
- bicubic: Bicubic interpolation
- nprocs=integer
- Number of threads for parallel computing
- Default: 1
- memory=memory in MB
- Maximum memory to be used (in MB)
- Cache size for raster rows
- Default: 300
Table of contents
DESCRIPTION
r.resamp.interp resamples an input raster map by interpolating between the neighboring cells via a selectable resampling algorithm. All cells present in the neighborhood of the input raster cell must be non-null to generate a non-null cell in the output raster map. A choice of four interpolation methods is available; each uses the weighted values of a different number of adjacent cells in the input map to determine the value of each cell in the output map as follows:- nearest neighbour (1 cell)
- bilinear (4 cells)
- bicubic (16 cells)
- lanczos (25 cells)
This module is intended for reinterpolation of continuous data to a different resolution rather than for interpolation from scattered data (use the v.surf.* modules for that purpose).
NOTES
Resampling modules (r.resample, r.resamp.stats, r.resamp.interp, r.resamp.rst) resample the map to match the current region settings.
Note that for bilinear, bicubic and lanczos interpolation, cells of the output raster that cannot be bounded by the appropriate number of input cell centers are set to NULL (NULL propagation). This could occur due to the input cells being outside the current region, being NULL or MASKed.
For longitude-latitude locations, the interpolation algorithm is based on degree fractions, not on the absolute distances between cell centers. Any attempt to implement the latter would violate the integrity of the interpolation method.
PERFORMANCE
By specifying the number of parallel processes with nprocs option, r.resamp.interp can run significantly faster, see benchmarks below.
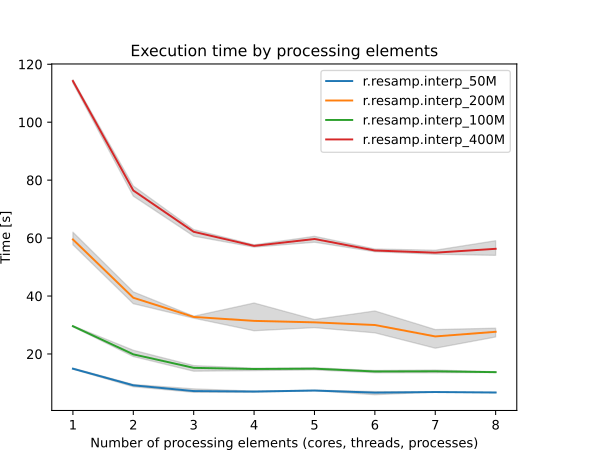
Figure: Benchmark shows execution time for different number of cells. See benchmark scripts in source code.
To reduce the memory requirements to minimum, set option memory to zero. To take advantage of the parallelization, GRASS GIS needs to compiled with OpenMP enabled.
EXAMPLE
Resample elevation raster map to a higher resolution (from 500m to 250m; North Carolina sample dataset):
g.region raster=elev_state_500m -p
g.region res=250 -ap
r.resamp.interp input=elev_state_500m output=elev_state_250m \
method=bilinear
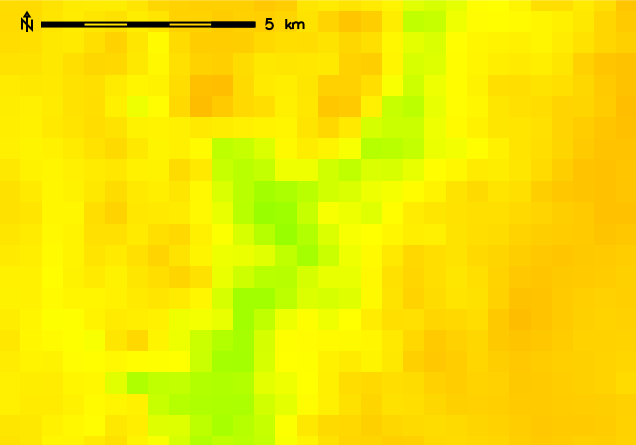
Original 500m resolution elevation map
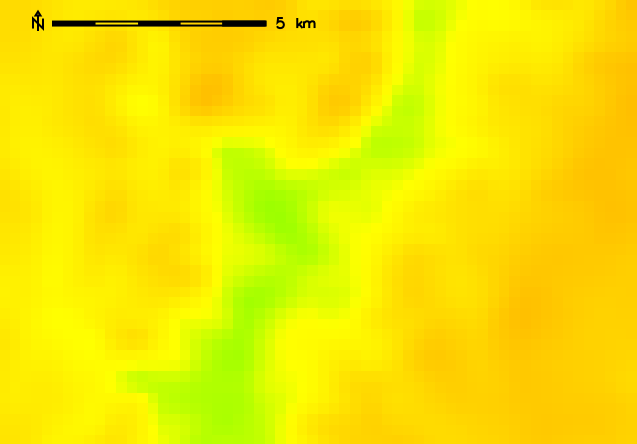
Resampled (bilinear) 250m resolution elevation map
SEE ALSO
g.region, r.resample, r.resamp.filter, r.resamp.rst, r.resamp.statsOverview: Interpolation and Resampling in GRASS GIS
AUTHOR
Glynn ClementsSOURCE CODE
Available at: r.resamp.interp source code (history)
Latest change: Thursday Jan 26 14:10:26 2023 in commit: cdd84c130cea04b204479e2efdc75c742efc4843
Main index | Raster index | Topics index | Keywords index | Graphical index | Full index
© 2003-2023 GRASS Development Team, GRASS GIS 8.3.dev Reference Manual