Greenhouse gases. Approximate values.
GWP - Global Warming Potential - describes the relative importance of different greenhouse gases in comparison to CO2. The GWP is described as CO2-equivalents. (Measuring the GWP of greenhouse gases, IUCC; UNEP, Geneva)
In addition to this natural carbon cycle, Carbon dioxide is emitted through the burning of fossil fuels: coal, oil and oil-products such as petrol and gas. Putrefying organic materials and the burning of wood, paper and other organic matter also emit CO2. In stationary combustion, gas, heating oils and kerosene are forms of energy sources emitting CO2. These emissions fluctuate with temperature variations. The colder the weather, the more heating is needed. If sufficient hydroelectricity is not available, the burning of fossil fuels will increase.
Water vapour and CO2 are the major natural greenhouse gases of the atmosphere. Water vapour is the most important green house gas. However, this gas will not be treated further here, as water vapour is not anthropogenic; human activities have little
or no impact on the amount in the atmosphere.
The CO2-concentration in the atmosphere has increased from 280 parts per million by volume (ppmv) to 358 ppmv or 0.036 per cent CO2 in 1994. This gives a general increase of over 27 per cent since preindustrial times. With an increase of CO2, it is likely that the storing capacity of energy in the atmosphere will be affected.
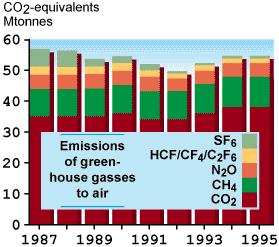
Of the total global man-made emissions of CO2 , Norway released approximately 41 million tonnes, or approximately 0.2 per cent in 1996. Per capita this is rather high, just above 9 tonnes of CO2. Global average is approximately 3.9 tonnes per capita. In 1989 the CO2 emissions per capita in Norway were 8,3 tonnes, which is the Norwegian aim for the year 2000.
Burning of wood is not considered as contributing to the greenhouse effect, since the energy released is assumed to be balanced by new tree growth.
The global yearly increase of CO2 in the atmosphere is now appr. 0.5 per cent.
The CH4 in the atmosphere has increased 145 per cent since preindustrial times.This increase has been linked to the rapid world population growth resulting in demands for energy, food, water, shelter and other basic needs.
Norwegian emissions of methane were approximately 471,000 tonnes in 1996. The emissions increased by 10 per cent from 1989 to 1996.
Norwegian emissions mainly come from livestock (21%) and decomposition of waste in landfills .-Emissions from landfills account for almost 70 per cent. The number of landfills is now decreasing, and at some landfills, the methane gas is now collected.In spite of this, methane emissions increase due to increasing depositions of organic waste.
Methane has a GWP of 21 times that of CO2.