2.0 Floristic diversity, status and conservation aspect of Bannerghatta National Park and buffer area
Karnataka is naturally endowed with a diversity of bioclimatic, topographic and edaphic variations resulting in rich floristic and wildlife abundance (Pascal, 1982). Bangalore district which falls under the rain shadow area and a maidan with heterogenic mosaic of moist to dry deciduous forest and grasslands supports some last areas of wild life such as in Bannerghatta National park (BNP) area. BNP covers an area of 104.3 sq. km2 harbouring rich wild life population including Elephants. The park is contiguous with Talli reserve forest in the southeast and Bilikal forest in the south. The park connects the BR Hills and the Sathyamangalam forest and is part of a wildlife corridor for elephants.
Bangalore branded once as ‘Silicon Valley of India’ has been experiencing rapid urbanisation with growth of Information Technology (IT) industries (Sudhira, et al., 2007). Unplanned urbanisation ignoring the sustianble management of natural resources has threatened the ecological integrity of Bannerghatta National Park (BNP). The park has been facing an acute environmental stress due to encroachments of animal movement paths, large scale mining (sand, granite) and also the pressure of burgeoning Bangalore city. Also, the villages in the core and buffer regions surrounding the BNP have been posing threats to BNP with various environmentally destructive activities. Bannerghatta forests is the repository of terrestrial biodiversity with the immense medicinal values and has been aiding in regulating micro climate, recharging of ground water, recreation and spiritual potential, etc. This necessitates sustainable management of national parks so that dependent communities are benefitted from ecosystem goods and services (Arnberger et al., 2013). In this regard, the current study highlights the floristic status, composition and conservation aspects of BNP with buffer region with special reference to its wild life.
2.1 Study area and Method
BNP vegetation types: Bannerghatta National Park is located in the southern elevated plateau that extends from the foot of the Western Ghats. The plateau receives less than 1000 mm annual precipitation with natural climax vegetation of dry deciduous types and are broadly divided into:
- Shorea talura-Terminalia sp-Anogiessus latifolia series tropical deciduous forest;
- Chloroxylon swietenia-Anogiessus latifolia-Albizzia sp series tropicaldry deciduous forest;
- Acacia thorn forest and
- Riverine gallery forest.
Historical vegetation of the district is in undisturbed parts such as the core areas of Chikkaragalli betta are with dense jungle of Shorea talura-Terminalia sp-Anogiessus latifolia series forest. Shorea talura tree being a member of Dipterocarpaceae (all other family members of Dipterocarpaceae occur in evergreen to semi-evergreen forest) is an endangered tree as per IUCN category. The distribution of this forest type in less disturbed areas highlights the ecological importance of the area. These forest types have disappeared in most other areas with high anthropogenic pressure and vegetation mainly consists of Chloroxylon swietenia-Anogiessus latifolia-Albizzia series. Even these are replaced by hardy Acacia chundra dominated thorn forest or scrub in areas undergoing severe degradation with rampant charcoal making, grazing and rampant fuel wood collection. Highly degraded landscapes are dominated by barren lands with sparse shrubs such as Ziziphus sp., spiny climbers Pterolobium hexapetalum, and hardy grass species (Figure 1, 2.1 and figure 2.2).
Dendrocalamus strictus (bamboo) is associated with most of the vegetation except in most degraded areas. Bamboo along with many other trees, coupled with large grass lands have been the life-line for the survival of elephants and other herbivore wild-life. Another important feature of BNP is the presence of large number of wild legumes. As the forest canopy is not dense one can find large number of grass species along with many herbaceous species. Depending upon the different habitat such as forest underneath, open grassland, granitic hilly areas, wetlands, etc., different grass and other herbaceous plant species are distributed. For instance open grasslands are dominated by Heteropogon contortus along with Apluda mutica. Likewise hilly granitic areas have large grasses such as Themeda sp., and Cymbopogon sp.
Vegetation exploration: BNP was surveyed in localities listed in Table 1 (marked in Figure 3), for floristic composition in core area (inside the park) and surrounding buffer areas (outside the park). In buffer areas surrounding the BNP, twelve 10 x 10 m quadrats were laid for accessing tree diversity, dominance and per hectare basal area. In each quadrat all trees > 30 cm were enumerated with their GBH (Girth at breast height) and height (m). In the same quadrat one 5 x 5 m shrub plot were laid and tree saplings and shrubs above 1 m were recorded. Two herb plots of 1 x 1 m were laid in each opposite ends to enumerate the seedlings. Opportunistic plant recording was also carried out in both core and buffer areas. Along with vegetation data other details regarding plant-animal interaction, human-wildlife conflicts, etc., were noted.
Table 1: Forest quadrat study localities in BNP buffer area
Sn |
Quadrat study localities |
Vegetation type |
1 |
Ginidoddi-kathrinath |
Gomala-Scrub |
2 |
Hanumanthalla |
Acacia thorn forest |
3 |
Hallimaradoddi |
Acacia thorn forest |
4 |
Shivanahalli-toklabande |
Dry deciduous forest-gomala |
5 |
Doddibetta |
Dry deciduous forest |
6 |
Elachavadi-tandya |
Acacia thorn forest |
7 |
Devarahalli-durgadkallu |
Dry deciduous-Grassland |
8 |
Guttalahunase-kanakapura |
Grassland-scrub |
9 |
Gangadarabetta-kanakapura state forest |
Dry deciduous forest |
10 |
Harekodi Eucalyptus |
Eucalptus-scrub forest |
11 |
Begihalli-Mantapa |
Dry deciduous forest |
12 |
Kvanaldoddi-devarahalli |
Dry deciduous forest |
|
|
Figure 1: Shorea talura-Terminalia sp-Anogiessus latifolia series tropical deciduous forest |
Figure 2.1: Chloroxylon swietenia-Anogiessus latifolia-Albizzia sp series tropical dry deciduous forest |
|
Figure 2.2: Acacia thorn forest |
|
|
Figure 3: Vegetation sampling locations in BNP and buffer region |
2.2 Results and Discussion
Floristic composition in BNP core area: A total of 218 plants belonging to 60 families were recorded during the survey. Among these, trees (81 sp) and herbs (88 sp) had the highest number of species, followed by shrubs (34 sp) and climber (15 sp) (Figure 4). Despite the efforts on Bangalore flora by the earlier researchers (Ramaswamy & Razi, 1973), many species such as Lannea coromandelica, Schefflera sp., Ceropegia candelabrum, Flacourtia montana, etc. have gone unrecorded. This shows that there is scope for inventorying and mapping of flora in BNP. Details of plants occurring in BNP core area and buffer area (also locality wise) are provided in Annexure 1, 2 and 3.
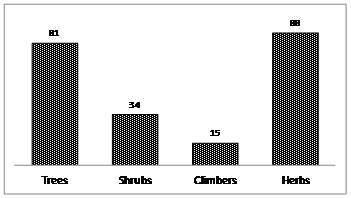 Figure 4: Habit wise number of trees, shrubs, climbers and herbs in BNP core area.
Figure 4: Habit wise number of trees, shrubs, climbers and herbs in BNP core area.
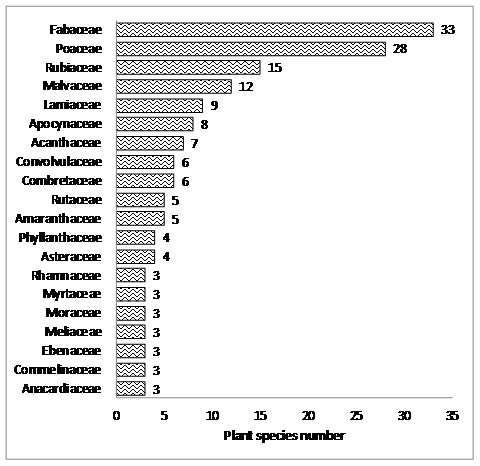 Figure 5: Family-species richness in BNP core area
Figure 5: Family-species richness in BNP core area
Species richness of Family Fabaceae (33 sp.) was highest followed by Poaceae (28 sp.) (Figure 5). This indicates the high diversity of legumes in trees, shrubs and climbers. Many wild legumes from southern plateaus are considered to be ancestors of cultivated legumes. The crops that recur and dominate Southern Deccan Neolithic archaeo-botanical samples have wild ancestors to be found in the hills of scrub woodlands of the southern Deccan region (Fuller, 2011). Family Rubiaceae (15) and Malvaceae (12) also have high species richness and along with Fabaceae and Poaceae contribute some of the major sources of food for wild life. Floristic enrichment with these native fodder plants will greatly help the BNP region which forms a crucial link for elephant movement path with inter-state corridor for wildlife.
Vegetation dynamics and dominant trees in the core area: Plant species distribution especially trees is highly dependent on conservation status including topography and other geological parameters. Most of the well conserved areas with good soil soil cover are with excellent deciduous forest cover of Shorea talura-Terminalia sp-Anogiessus latifolia series. The northern BNP areas surrounding Doddaragalli betta and Muttaraya temple area harbour these kind of forest and provide excellent fodder and canopy for wild animals. However, presence of only few large trees highlight that even these regions were subjected to disturbance atleast in earlier times. Due to rampant disturbances such as i) charcoal preparation, ii) cattle grazing, iii) illegal wood extraction and iv) other anthropogenic pressures in the rest of central and southern forest regions including Bilikal forest area, Shorea talura forest have disappeared giving way to Chloroxylon swietenia-Anogiessus latifolia-Albizzia sp., series which are hardier resisting fire and other disturbances. Large trees of Terminalia arjuna, Dalbergia lanceolaria, Ficus sp. Were seen in core areas and reverine forests. Even these regions were with stunted forests of Acacia sp and other thorny plants. Due to rampant exploitation, forests in the locailities surrounded by villages are generally Acacia thorn forest. Regeneration is poor in this region due to very high grazing pressure of large herds of cattle (Figure 6) and this has given way to thorn forest species.
Table 2: Some dominant trees of BNP core areas
Species |
Family |
Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd. |
Fabaceae |
Acacia leucophloea (Roxb.) Willd. |
Fabaceae |
Albizzia sp. |
Fabaceae |
Anogeissus latifolia (Roxb. ex DC.) Wall. ex Guill. & Perr. |
Combretaceae |
Bauhinia racemosa Lamk. |
Fabaceae |
Cassia fistula L. |
Fabaceae |
Catunaregam spinosa (Thunb.) Tirveng. |
Rubiaceae |
Chloroxylon swietenia DC. |
Rutaceae |
Cipadessa baccifera (Roth) Miq. |
Meliaceae |
Dalbergia lanceolaria L.f. |
Fabaceae |
Dendrocalamus strictus Nees |
Poaceae |
Diospyros melanoxylon Roxb. |
Ebenaceae |
Ficus benghalensis L. |
Moraceae |
Ficus amplissima Sm. |
Moraceae |
Givotia moluccana (L.) Sreem |
Euphorbiaceae |
Lagerstroemia parviflora Roxb. |
Lythraceae |
Naringi crenulata (Roxb.) Nicolson |
Rutaceae |
Premna tomentosa Willd. |
Lamiaceae |
Psydrax umbellata (Wight) Bridson |
Rubiaceae |
Semecarpus anacardium L.f. |
Anacardiaceae |
Shorea roxburghii G. Don |
Dipterocarpaceae |
Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels |
Myrtaceae |
Tamarindus indica L. |
Fabaceae |
Terminalia arjuna (Roxb. ex DC.) Wight & Arn. |
Combretaceae |
Terminalia paniculata Roth |
Combretaceae |
Vitex altissima L.f. |
Lamiaceae |
Wrightia arborea (Dennst.) Mabb. |
Apocynaceae |
Wrightia tinctoria (Roxb.) R. Br. |
Apocynaceae |
|
Figure 6: Glimpse of cattle pressure in BNP forest area |
Vegetation type in the buffer regions of BNP: Much of the buffer area vegetation is of Chloroxylon swietenia-Anogiessus latifolia-Albizzia sp series type in moderately disturbed areas to Acacia thorny scrub forest in highly degraded areas. Most of the forest vegetation in buffer has been more or less entirely wiped out for agricultural and other man made land uses, excspt in reserve forests, village lots (Karab lands), common grazing lands (Gomala) and other private areas. The region had continuous tropical deciduous forest and now this vegetation is restricted to BNP and protected areas. Forest in these village common lands is sparse and mostly of thorny scrub. Annexures 2 and 3 provide the details of plants in buffer area.
Floristic composition, diversity and basal area in buffer area: Total number of plant species in buffer region was 136 species fbelonging to 46 families. Most of the forest trees encountered were in village wood lots and gomalas with very few in agricultural landscapes. Trees encountered in agicultural landscapes were mostly non-forest trees - Azadirachta indica, Mangifera indica, Melia dubia, Artocarpus integrifolia etc. A total of 40 trees were encountered with 26 shrub species (Figure 7).
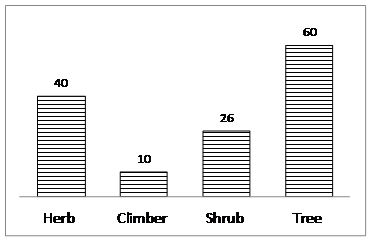 Figure 7: Habit wise number of trees, shrubs, climbers and herbs in BNP buffer area.
Figure 7: Habit wise number of trees, shrubs, climbers and herbs in BNP buffer area.
Family Fabaceae (25 sp.) had the highest number of species (Figure 8) followed by Poaceae (13 sp.) and Rubiaceae (11 sp.). Family Fabaceae has the highest number of species in buffer and this indicates that substantial amount of diversity found in core area is retained in these forest fragments of buffer regions. However much of these are under private ownerships and are on fast decline.
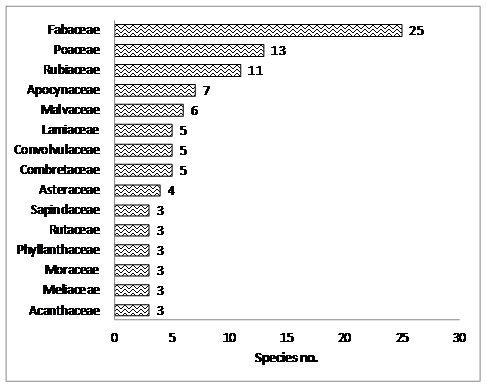 Figure 8: Family-species richness in BNP buffer area.
Figure 8: Family-species richness in BNP buffer area.
Tree heights in buffer forest area were stunted with highest being the Eucalyptus mixed forest in Harekodi in north BNP (Figure 9). Most other forested areas had tree heights less than 9 m. In many locations of buffer areas, Tamarind trees were dominant as in Devaralli-durgadakallu area with forest trees more or less absent. Forest tree species were more in reserve forests of Guttalahunase Kanakapura state forest. In the same area the gomalas were totally degraded without any forest trees. This forest also faces rampant fuel wood collection and illegal tree felling. Many gomalas like Ginidoddi-Kathrinatha had the lowest tree heights.
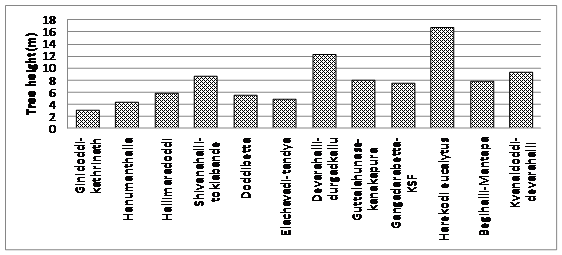 Figure 9: Tree height in different buffer study localities.
Figure 9: Tree height in different buffer study localities.
Species diversity was also very low in buffer area due to high fragmentation disturbances. Ginidoddi-Kathrinath and Guttalahunase gomalas were devoid of trees with zero Shannon value. Slightly protected areas such as Doddibetta (1.48), Devarahalli-Durgadakallu (0.69) and in Begehalli-Mantapa area (private owner ship area) have slightly higher Shannon diversity (Figure 10).
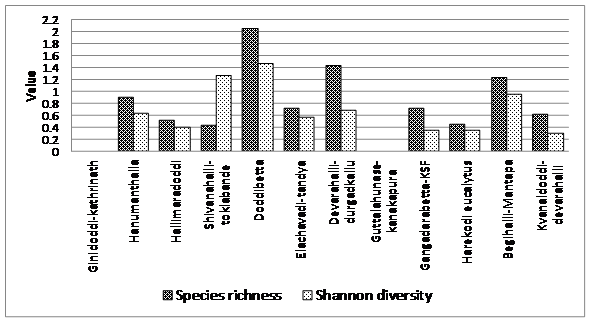 Figure 10: Species richness and Shannon diversity in different buffer study areas.
Figure 10: Species richness and Shannon diversity in different buffer study areas.
Basal area was higher than 30 sq.m2/ha in four localities with one being a Eucalyptus mixed scrub forest (Figure 11). Among the sampled localities, Devarahalli-Durgadakallu basal area was mostly contributed by Tamarind, and Albizzia amara, while in Shivanahalli-Toklabande and Kvanaldoddi-devrahalli had more forest species contributing to the basal area. Most other localities had very low basal areas indicating the high degradation of vegetation patches.
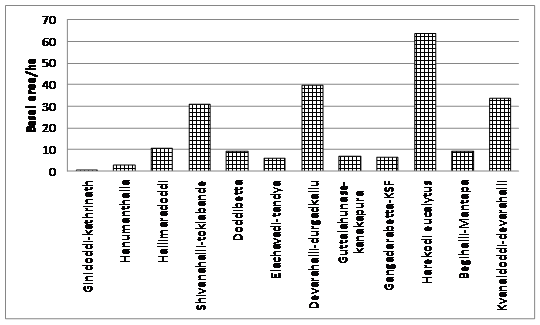 Figure 11: Per hectare basal area in different buffer study regions.
Figure 11: Per hectare basal area in different buffer study regions.
Table 12: Most abundant trees in buffer area.
|
Most abundant tree species in buffer area |
Sl. No. |
Scientific name |
Family |
1 |
Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd. |
Fabaceae |
2 |
Albizia amara Boiv. |
Fabaceae |
3 |
Albizia odoratissima (L.f.) Benth. |
Fabaceae |
4 |
Anogeissus latifolia (Roxb. ex DC.) Wall. ex Guill. & Perr. |
Combretaceae |
5 |
Azadirachta indica A. Juss. |
Meliaceae |
6 |
Cassia fistula L. |
Fabaceae |
7 |
Cassine glauca (Rottb.) Kuntze |
Celastraceae |
8 |
Diospyros melanoxylon Roxb. |
Ebenaceae |
9 |
Eucalyptus sp |
Myrtaceae |
10 |
Lagerstroemia parviflora Roxb. |
Lythraceae |
11 |
Melia dubia Cav. |
Meliaceae |
12 |
Naringi crenulata (Roxb.) Nicolson |
Rutaceae |
13 |
Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre |
Fabaceae |
14 |
Premna tomentosa Willd. |
Lamiaceae |
15 |
Semecarpus anacardium L.f. |
Anacardiaceae |
16 |
Tamarindus indica L. |
Fabaceae |
17 |
Terminalia arjuna (Roxb. ex DC.) Wight & Arn. |
Combretaceae |
18 |
Terminalia elliptica Willd. |
Combretaceae |
19 |
Vitex altissima L.f. |
Lamiaceae |
20 |
Wrightia tinctoria (Roxb.) R. Br. |
Apocynaceae |
Biodiversity in fragmented buffer areas: Human-dominated agricultural landscapes in the tropics contain a high biodiversity, though mostly consisting of a group of abundant, pantropical, cultivated, weedy or anthropic species. The presence of fragments of original forest will significantly enhance the diversity of the landscape and increase the likelihood of the survival of the indigenous biota, or at least a portion of it (Turner & Corlett, 1996). Most of the forest exists outside BNP in small isolated patches and in some what bigger area as state forests. Elephants and other wild animals were seen using these fragmented forests outside the BNP also. For instance, Gangadharabetta-Kanakaputa state forest with dry deciduous forest, Begihalli-Mantapa with Acacia-Bamboo forest, Shivanahalli-Toklabande dry deciduous forest, Elachavadi-Tandya with Acacia scrub jungle etc., are proven elephant habitats providing food, shelter and corridors (but fall outside BNP). Many smaller wood lots though may not support elephant population still harbour lot of smaller wild mammals and birds otherwise found in core areas. These regions are highly interspersed with agricultural and human habitat lands are forest patches are being illegally converted to other land uses. This is perhaps the single most destructive causes as large extent of forests, woodlands, wetlands, and savannas outside the reserve forest which are administered by the revenue department has been continuously converted in to farm lands through encroachments and land grants (Figure 13). These forest fragments with repositories of biodiversity among the agriculture dominated landscapes are to be conserved to ensure the exchange of ecological services from forest ecosystem to agrarian ecosystems. Hence these areas have to be mapped and inventories biodiversity for earmarking for conservation. Protection of these areas can be achieved by formation of village wise active VFC’s who can monitor the sustainable utilization and conservation of these fragments. Highly degraded fragments instead of being converted to other land uses can be brought back under suitable afforestation programmes. This will not only restores the ecosystem functions including support of wild fauna.
Medicinal plant resources in BNP area: Many cultures that have survived close to the nature, depending on its products for their needs. These people had a deep understanding of the properties of their local plants and this knowledge is in wane in recent population apart from the ecline of these endangered plant species (IUCN, 1993). This hold equally true to BNP areas as the present study showed nearly 63 % of the total plants with 138 plants were medicinally important from both the core and buffer areas. This shows the high medicinal plant diversity harboured by BNP area. Due to rapid urbanisation and landscape changes, habitat of large number of medicinal plants is on decline and also the local peoples who had excellent knowledge of medicinal plants are now on wane. The valuable knowledge they had on various human and cattle ailments and medicinal plants is not even recorded. Many species such as Cissampelos pariera, Decalepis hamiltonii, Cardiospermum helicabum, Gloriosa superba, Cassia fistula, Wrightia sp., Holarrhena pubescens, Aegle marmelos, Shorea roxburghii, Phyllanthus emblica etc., are highly valued medicinal plants with many of them are rare or endangered and traded in high volumes. This necessitates mapping, inventorying and conservation of medicinal plants in the BNP and buffer areas. List of medicinal plants is provided in Annexure 1.
 |
 |
Figure 13: Large area of gomalas with Acacia forest and elephant corridors now under private owner ship in BNP buffer area. |
Figure 14: Elephants breaking the BNP boundary electric fence to move out into buffer areas. |
Elephants and their conservation status in BNP-A need for more practical management plans.
Asian Elephant (Elephas maximus) is categorized as an endangered species in IUCN list 2009, struggling for their survival due to habitat loss, forest fragmentation and disturbances in movement paths. Elephants are bulkfeeders and therefore have lower densities in areas with low plant biomass (Parker and Graham, 1989; Olff et al., 2002). In areas with high amounts of plant biomass, like rainforests, a relatively large part of the vegetation is inaccessible for elephants, which could result in lower elephant densities (Olff et al., 2002). Plant biomass is not the only important factor determining elephant distribution and density. Various studies have documented variation in elephant densities in different vegetation types, explained by differences in forage biomass, forage quality, shade, water availability, or plant species composition (Harris et al., 2008). Elephants have large home ranges and need extensive areas (Shannon et al., 2010). Habitat fragmentation leads to the reduction of the total habitat area, and the isolation and breaking up of habitat into smaller patches. Habitat fragmentation is therefore expected to negatively correlate with elephant distribution (Leimgruber et al., 2003). The conservation status of an area and protection efforts are positively correlated with wildlife population trends (Bruner et al., 2001; Caro and Scholte, 2007). However, protection not only depends on the existence of reserves but also on the policy of a country or region, the level of corruption, and the capacity of a country successfully to implement such a policy (Smith et al., 2003). Elephant densities strongly correlate with conservation policy, literacy rate, corruption and economic welfare, and associated vital parameters such as the availability of food and water. Hence, conservation strategies should be organized in a socioeconomic context. The successful conservation of large animal species depends more on human education, greater literacy and good governance, than merely setting aside areas for conservation (Willem et al, 2013).
Practical Management Action plans
- Habitat factors are important in determining the nature and extent of crop raiding by elephants; thus the reduction of natural habitat or its fragmentation may leave elephants with little choice but to seek a part of their forage needs from cultivated fields (Sukumar 1985b, 1989). Hence BNP core forest areas have to be enriched with elephant and other wild herbivores preferred fodder plants and fruiting trees (Table 4).
- Electric fence, although an effective and successful protective measure, require high maintenance and people who involved need some technical expertise. Local people involvement is very important to maintain the fence. In some places the fence was broken by elephants, therefore proper maintenance is required (Figure 14).
- A double barrier such as elephant proof trench-rubble wall, elephant proof trench-solar powered electric fence or rubble wall-solar powered electric fence have been suggested for preventing elephant straying to human habitations in the conflict zone.
- Elephant habitat utilization are not confined to forest alone, it also uses the buffer zone between forest and agricultural lands. Apart from the use of these lands for food, the animals come to these lands for drinking water purposes during lean season of summer. If we seal the boundaries of forest with solar fence or EPTs, it is inevitable on part of the wildlife manager to create water resources inside the forest to cater to the needs drinking water during summer. These measures include construction of percolation ponds, check dams, water troughs supplying water through solar powered pumps, etc.
- With the rapid shrinkage of habitat, the elephants and other larger animals are being forced into smaller and smaller areas. Consequently leading very high densities of elephant population. Hence corridors with other protected areas have to substantially improved to effectively increase the elephants foraging area.
- In BNP many bottleneck corridors has to be widened substantially (Some bottlenecks are less than 500m!) for smooth passage of elephants and other wildlife within BNP. Importantly BNP corridors with other protected areas have to be smoother such as with Cauvery wildlife sanctuary and Tamilnadu protected areas, without any human interferences. For planning this corridors both present and past elephant migration routes has to be considered.
- Creation of VFC’s village wise for strengthening, management and sustainable utilization of remaining wilderness outside the park, both for the benefit of local peoples and wildlife. Improving degraded forests to acheive higher biomass forests (with native species) to atleast 30 m2/ha would be an ideal objective.
- Conflict could also be reduced by promoting the cultivation of crops that are unpalatable to elephants, and improvement in grain storage systems.
- Adequate and timely compensation for damage to crops and property could also help to foster more positive attitudes towards elephant conservation.
- Village panchayat wise creation of fodder farms to reduce the cattle grazing pressure inside BNP and sourrounding buffer areas.
- As every village has rich cattle population, village wise creation of community biogas plants would highly reduce the fuel wood collection from BNP and buffer areas. Along with this creation of fuel cum fodder plantations, solar water heaters such as in Ungra-Hosalli-Biogas system.
- Creation of medicinal plants park to create both awareness and in-situ conservation of rare medicinal plants.
Table 4: Elephants fodder plants in BNP
Sl.No. |
Species name |
Family |
Habit |
Preference |
Parts eaten |
1 |
Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Twig, Bark |
2 |
Acacia leucophloea (Roxb.) Willd. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf |
3 |
Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf, Twig |
4 |
Asparagus racemosus Willd. |
Asparagaceae |
Climber |
High |
Leaf, Root |
5 |
Bambusa bambos (L.) Voss |
Poaceae |
Bamboo |
High |
Leaf, Twig, Bark |
6 |
Bauhinia racemosa Lamk. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf |
7 |
Butea monosperma (Lam.) Taub. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Tree |
8 |
Careya arborea Roxb. |
Lecythidaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Fruit, Bark |
9 |
Cassia fistula L. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
Low |
Leaf, Twig |
10 |
Crytococcum sp |
Poaceae |
Herb |
High |
Leaf |
11 |
Cymbopogon flexuosus (Nees ex Steud.) W. Watson |
Poaceae |
Herb |
Low |
Leaf |
12 |
Dendrocalamus strictus Nees |
Poaceae |
Bamboo |
High |
Leaf, Twig |
13 |
Diospyros melanoxylon Roxb. |
Ebenaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Fruit, Root |
14 |
Ficus benghalensis L. |
Moraceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Bark |
15 |
Flacourtia indica (Burm. F.) Merr. |
Salicaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Twig, Bark |
16 |
Gmelina arborea Roxb. |
Lamiaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Bark |
17 |
Grewia tiliifolia Vahl |
Malvaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Twig |
18 |
Helicteres isora L. |
Malvaceae |
Shrub |
High |
Leaf, Young twig |
19 |
Heteropogon contortus (L.) P. Beauv. ex Roem. & Schult. |
Poaceae |
Herb |
High |
Leaf |
20 |
Holarrhena pubescens (Buch.-Ham.) Wall. ex G. Don |
Apocynaceae |
Tree |
Low |
Twig |
21 |
Ichnocarpus frutescens (L.) W.T. Aiton |
Apocynaceae |
Climber |
Low |
Entire plant |
22 |
Lagerstroemia parviflora Roxb. |
Lythraceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Bark, Twig |
23 |
Madhuca indica J.F. Gmel. |
Sapotaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Flower, Fruit |
24 |
Mangifera indica L. |
Anacardiaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Fruit |
25 |
Mitragyna parvifolia (Roxb.) Korth. |
Rubiaceae |
Tree |
Low |
Bark |
26 |
Naringi crenulata (Roxb.) Nicolson |
Rutaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf, Twig |
27 |
Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf |
28 |
Schleichera oleosa (Lour.) Merr. |
Sapindaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf, Twig |
29 |
Semecarpus anacardium L.f. |
Anacardiaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Bark |
30 |
Smilax zeylanica L. |
Smilacaceae |
Climber |
Low |
Leaf |
31 |
Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels |
Myrtaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf, Twig, Bark |
32 |
Tamarindus indica L. |
Fabaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Fruit |
33 |
Tectona grandis L.f. |
Lamiaceae |
Tree |
Low |
Bark |
34 |
Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb. |
Combretaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf |
35 |
Terminalia chebula Retz. |
Combretaceae |
Tree |
Medium |
Leaf |
36 |
Terminalia elliptica Willd. |
Combretaceae |
Tree |
High |
Leaf, Bark |
37 |
Themeda triandra Forssk. |
Poaceae |
Herb |
High |
Leaf |
38 |
Ziziphus oenoplia (L.) Mill. |
Rhamnaceae |
Shrub |
Medium |
Leaf |
Plate 1: BNP Forest types
A: Tropical deciduous forest with Shoreatalura-Terminalia sp-Anogiessuslatifolia series, B: Tropical dry deciduous forest with Chloroxylonswietenia-Anogiessuslatifolia-Albizziasp series, C: Acacia thorn forest, D: Bilikalgudda-dry deciduous forest
Plate 2: Plant diversity in BNP
A: Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd, B: Acacia caesia (L.) Willd, C:Morindasp.. yellow bark,D: ArgyreiacuneataKer.-Gawl, E:Tribulusterrestris L.,F:Shorearoxburghii G. Don
Plate 3: Plant diversity in BNP
A:Ceropegia candelabrum L.,B: Cipadessabaccifera(Roth) Miq.,C:GrewiavillosaWilld., D:Diplocyclospalmatus (L.) C. Jeffrey,E:Givotiamoluccana (L.) Sreem, F:GmelinaarboreaRoxb.
Plate 4: Plants of BNP
A: Canthiumdicoccum (Gaertn.) T. & B., B: Ichnocarpusfrutescens (L.) W.T. Aiton,C:LepidagathiscristataWilld., D: Naringicrenulata (Roxb.) Nicolson,E: PremnatomentosaWilld.F:Rotalafimbriata Wt.
Plate 5: Plants of BNP
A:SemecarpusanacardiumL.f. B: Wrightiatinctoria (Roxb.) R. Br.C: Wrightiaarborea (Dennst.) Mabb.D:Andrographisserpyllifolia Wt.E: ByttneriaherbaceaRoxb.F:Dioscorea sp.
Plate 6: Forest disturbances in BNP
A:Large scale cattle grazing inside core area, B: Highly degraded gomala after the sand filtration, C: Gomala encroachment, D: Illegal sand filtering in gomala
Plate 7: Field work study team and interactions
Plate 8: Field work study team and interactions
3.0 Flora of Bannerghatta National Park

|
Acacia caesia (L.) Willd.
Vernacular name: Kaduseege
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A prickly climbing shrub up to 10 m. Leaves 20-25 cm long, pinnae 5-8 pairs, oblong, truncate at base, apiculate at apex. Heads terminal, panicled. Pods to 13*2.2 cm, oblong, flat, acuminate at both ends, marginate2.
Flowering and fruit: October-December |
Acacia chundra (Rottler) Willd.
Vernacular name: Kempu jail
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Moderate-sized tree. Leaves alternate and pinnately compound with glands present on the rachis. Flowers are small, pale yellow in terminal spikes. Spike 6-8 cm long, pod stalked, flat, glabrous, subacute, 3-4 seeded1,2.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: May- October |

|

Source-2
|
Acacia farnesiana (L.) Willd.
Vernacular name: Kasturi jail
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Small tree. Leaves 5 cm long, petiole gland near the middle. Heads 1.3 cm across, orange. Pod subcylindrical, dehiscent, 6 cm long, 1 cm thick. 4-6 seeded1,2,3.
Native: America; Flowering and fruit: November - February |
Acacia leucophloea (Roxb.) Willd.
Vernacular name: Thapala
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Trees upto 20 m high, bark yellow to yellowish-brown, rough. Leaves bipinnate, alternate, and stipulate, apex subacute, margin ciliate, glabrous. Flowers yellow or yellowish-white. Fruit pod 6-15*0.8-1cm flat, strap-shaped. Seeds 5-12, ovate, 5-683-4 mm1,2.
Flowering and fruit: February-March |

|

Source-2
|
Acacia sinuata (Lour.) Merr.
Vernacular name: Seege kai
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Climbing shrubs. Branches light brown-pubescent. Leaves 9 cm long, petiole gland below the middle. Heads 1 cm across, calyx red, finely 5-lobed, glabrous. Pod 15*2.5 cm, fleshy, wrinkled when dry. 10-14 seeds1,2,3.
Native: Tropical Asia; Flowering and fruit: March – July |
Achyranthes aspera L.
Vernacular name: Uttarani
Family: Amaranthaceae
Description: An erect herb. Leaves are thick, elliptic or obovate, entire and obtuse. Flowers are greenish-white, small, numerous, stiffly deflexed against the rachis. Fruit is a utricle1,2,3.
Native: Southeastern Asia; Flowering and fruit: September - April |

|

|
Aerva lanata (L.) Juss.
Vernacular name: Bili hindi gida
Family: Amaranthaceae
Description: An erect or prostrate herb. Leaves alternate, elliptic to obovate or acute, entire with cottony hair beneath. Flowers are tiny, white and are crowded in compact axillary spikes1,2,5.
Native: Afrotropics; Flowering and fruit: October - April |
Aeschynomene sp
Family: Fabaceae |
|

|
Alangium salvifolium (L.f.) Wang.
Vernacular name: Ankule mara
Family: Cornaceae
Description: A small deciduous tree or shrub. Leaves narrowly elliptic or ovate or obtuse. Flowers greenish-white, pubescent outside. Fruit ellipsoid, crowned with vestiges of calyx1,2,6.
Native: Tropical Asia; Flowering and fruit: February – May & April – July |
Albizia amara Boiv.
Vernacular name: Ghujjalu
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A large deciduous tree upto 13 m high, bark thin, surface grey, rough. Leaves bipinnate, alternate, stipulate, stipules minute, with a gland near the base on the upper side, yellow tomentose. Flowers bisexual, white, heads solitary, densely pubescent, glabrous except the bearded apex. Fruit a pod 10-24* 2.5-4 cm, flat, greyish-brown, veiny, straight or wavy along margin. Seeds 6-13, compressed, ovate-orbicular1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: June-January |

|

|
Albizia lebbeck (L.) Benth.
Vernacular name: Bage
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Deciduous trees up to 25 m high. Leaves bipinnate, alternate, stipules, stipules small, free, lateral, cauduous, slender, grooved above, with a gland at its base. Glabrous, pulvinate. Flowers bisexual, greenish-white, in subglobose heads, solitary or 2-4 together in axillary corymbose racemes. Fruit a pod, flat, oblong, compressed, straw coloured, base and apex obtuse, dull dark brown, flattened1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: March-December |
Albizia odoratissima (L.f.) Benth.
Vernacular name: Bilwara
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Deciduous tree upto 30 m high, bark 10-15 mm thick, initially tawny pubescent, finally glabrous. Leaves bipinnate, alternate, stipulate, stipule free, lateral, caducous. Flowers bisexual, white, in globose heads forming terminal panicles. Fruit a pod flat, strap-shaped, with parallel margin or often some portion constricted, rounded to rostrate at apex. Seeds 6-12, oblong, orbicular, compressed1,2,4.
Flowering and fruit: April-January |

Source-2
|
|
Albizia sp
Family: Fabaceae |
Allmania nodiflora (L.) R. Br. ex Wight
Family: Amaranthaceae
Description: Diffused herb. Leaves 6*2 cm, broadly elliptic, base narrowed and petiole-like, drying olive green. Flowers in terminal and axillary globose, congested cyme. Achenes 3*2mm, ellipsoid with a long beak, black1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July-October |

|

|
Alternanthera pungens H. B. & K.
Vernacular name: Mullu honagonne
Family: Amaranthaceae
Description: A spreading herb. Leaves opposite, simple, stalked, entire, spathulate. Flowers are small, inconspicuous, head-like inflorescence1,2,3.
Native: Neotrpoics
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |
Andrographis serpyllifolia Wt.
Vernacular name: Kaasinasarada gida
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: A prostrate herb. Leaves are orbicular and glabrous. Flowers are subsessile, mostly solitary with small bracts. Fruit is a capsule1,2,3.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: June - September |

|

|
Annona squamosa L.
Vernacular name: Seethaphala
Family: Annonaceae
Description: Shrub or small trees, somewhat bushy. Leaves simple, alternate, ovate, oblong-lanceolate to oblong –elliptic, margin entire, apex obtuse to acute, coriaceous, membranous. Flowers bisexual, subcapitate, pedicels slender, minutely pubescent about 1-3 cm long. Carpels many, subglobose or ovoid, subconnate, minutely pubescent. Ripe carpels, broadly globose pr ovoid in fruit, fragrant. Seeds many, black with dark brown patches, slightly flattened, arillate1,2,3.
Flowering: April-July ; Fruiting: July-August |
Anogeissus latifolia (Roxb. ex DC.) Wall. ex Guill. & Perr.
Vernacular name: Dindiga, Dindlu
Family: Combretaceae
Description: Deciduous trees up to 18 m high, bark 10-12 mm thick, surface grey or yellowish-grey, smooth, lenticellate, drooping. Leaves simple, opposite to alternate, estipulate, suborbicular or oblong –obovate, base obtuse. Flowers bisexual, pale green or yellow, in axillary aggregated globose heads. Fruit a drupe, greenish-yellow, compressed, puberulous, circular, wings 2, margin entire or slightly undulate beaked. Seeds one, obovate1,2,5.
Flowering: June-September; Fruiting: December-March |

Source-2
|

|
Apluda mutica L.
Vernacular name: Grass
Family: Poaceae
Description: Annual or perennial herbs. Culms 40-140 cm high. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate or linear-lanceolate, base attenuate, apex setaceous. Spikelet’s 3- per raceme, 1 sessile, 2 pedicelled. Sessile spikelets 3 -7 mm long, awned. Pedicelled spikelet 3-6*1-1.5 mm oblong-lanceolate. Lower glume 3-6*1-1.5 mm, lanceolate, chartaceous. Florets more or less similar to those of sessile spikelet, upper lemma entire, unawned1,2,3,5. |
Argyreia cuneata Ker.-Gawl.
Vernacular name: Kad Dasala
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: Silky shrubs. Leaves obovate-lanceolate, emarginate or obtuse and apiculate, broadly cuneate at base, glabrous above. Corolla funnel-shaped, bright red. Berry leathery, yellow-brown1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: August – January |

|

Source-2
|
Aristida setacea Retz.
Vernacular name: Parke hullu
Family: Poaceae
Description: A coarse perennial. Leaves linear, convolute, sheaths long, flumes linear-lanceolate. Lemma awn smooth1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Myanmar
Flowering and fruit: May - December |
Asparagus racemosus Willd.
Vernacular name: Sathavari
Family: Asparagaceae
Description: Woody perennial climbers. Cladodes from the axils of scale. Leaves in clusters of 2-6, linear-falcate, slightly triquetrous, base narrow, apex acute. Flowers bisexual, 5-6 mm across, bracts triangular. Berry 4- 6 mm diameter globose, purple on ripening. Seeds 2-5, globose1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July-August |

|

Source-2
|
Atalantia racemosa Wt. & Arn.
Vernacular name: Kadu-kanchi
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Shrubs or small tree up to 4 m tall. Leaves simple, alternate, spiral, elliptic to elliptic –ovate, apex emarginated, base acute to rounded, margin entire, coriaceous, glandular punctate. Inflorescence axillary short cymes, flowers white, stamens connate. Berry globose. Seeds 41,2,5.
Native: Western India, Sri Lanka; Flowering and fruit: April - May |
Azadirachta indica A. Juss.
Vernacular name: Bevu
Family: Meliaceae
Description: Evergreen trees up to 20 m, bark greyish-brown, vertically striated. Leaves imparipinnate, alternate, estipulate, rachis 14-30 cm long, glabrous. Flowers bisexual, white, in axillary panicles. 5 sepals, 5 petals. Fruit a drupe, oblong –ovoid, greenish-yellow, seed one, surrounded by a sweet pulp1,2,3.
Flowering: February-April, Fruiting: June-August |

|
|
Bambusa sp
Family: Poaceae |
Barleria buxifolia L.
Vernacular name: Gubbee mullu
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: A spinescent herb. Leaves simple, opposite, entire and ovoate with a sharp pointed. The petals are fused and the corolla is tubular and funnel-shaped. Fruit is an oblong capsule containing few compressed seeds1,2,5.
Native: Indian Archipelago; Flowering and fruit: July – February |

|

|
Barleria prattensis sant.
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: Woody, erect herbs. Leaves ovate, acute-acuminate, cunceate, glabrous, usually drying black1,2,5.
Flowering and fruit: September - October |
Bauhinia racemosa Lamk.
Family: Fabaceae
Vernacular name: Kanchuvala, Achiga
Description: A tree with leaf-lobes joined in the middle. Flowers are small (1 cm.), inconspicuous with narrow petals. Bark is grey and rugged with longitudinal fissures1,2,5.
Native: Tropics of both hemispheres
Flowering and fruit: March |

|

|
Blepharis maderaspatensis (L.) Roth
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: A prostrate native herb. Leaves simple, 4-whorled in opposite pairs, roughly elliptic with margins showing fine saw-like teeth. Flowers in axillary clusters of 2 or 31,2,5.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, T. Africa
Flowering and fruit: November - February |
Boswellia serrata Roxb. ex Colebr.
Common name: Indian Olibanum tree
Family: Burseraceae
Native: India
Description: A large sized deciduous tree. Leaves unipinnate and crowded at the branch end. Flowers are small, white and occur in fascicled racemes. Fruit is 3 lobed drupe2,3.
Flowering and fruit: February – May |

|

|
Bridelia retusa (L.) A. Juss
Common name: Mullu jogala
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Description: Medium sized deciduous tree up to 18 m. leaves are simple, elliptic-oblong, brown pubescent on the lower surface. Flowers are borne in clusters on an elongated spike. Fruit is a 1 seeded pyrene1,2,5.
Native: South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: March-September |
Bryophyllum pinnatum (Lam.) Oken
Vernacular name: Kadubasale
Family: Crassulaceae
Description: Branches terete. Leaves simple or pinnately 2-5-lobed, elliptic-oblong, crenate-serrate, obtuse, rounded or narrowed at base. Flowers yellow, pendulous1,2,5.
Native: Tropics
Flowering and fruit: December - February |
 Source-2 Source-2
|

|
Butea monosperma (Lam.) Taub.
Common name: Flame of the Forest
Family: Fabaceae
Description: moderate sized deciduous tree up to 8 m high. Leaves alternate, 3-foliate, pulvinate, brown silky pubescent when young. Inflorescence a raceme. Fruit a pod, flat, thickened on the sutures, leathery, oblong. Seed solitary, compressed, obovate1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: February |
Byttneria herbacea Roxb.
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Creeping, unarmed herbs. Leaves ovate, acute at apex, cordate or rounded at base, dentate, glabrescent. Sepals linear-lanceolate, recurved. Capsule 0.7 cm across1,2,4.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: August - January |

|

Source-2
|
Cajanus scarabaeoides (L.) Thouars
Vernacular name: Kaduthogari
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Pubescent shrubs. Leaflets elliptic to elliptic-oblong, acute to obtuse, grey-pubescent beneath. Raceme slender. Pod covered with golden spreading hairs, 4-6-seeded1,2,3.
Native: Indomalesia, China; Flowering and fruit: November-February |
Calotropis gigantea (L.) R. Br.
Common name: Giant Milk- weed
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Perennial shrub with milky latex. Leaves simple in opposite pairs. Flowers showy. Fruits is a pair of follicles with innumerable seeds having white long silky hairs at the end1,2.
Native : Tropical Asia, Tropical Africa; Flowering and fruit: Throughtout the year |

|

|
Canthium coromandelicum (Burm.f.) Alston
Vernacular name: Kaaki
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: A shrub. Leaves ovate to elliptic, acute or acuminate at apex, stipules triangular with a long subulate point. Flowers small, greenish-yellow. Drupes obcordate1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: March - April |
Capparis zeylanica L.
Vernacular name: Thottalu balli
Family: Capparaceae
Description: A climbing shrub. Leaves are rough in texture, broadly lanceolate with short. Flowers are extra-axillary with 4 greenish-white petals. Fruits are ovoid berries, bright scarlet with many seeds1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowers: All Seasons |

|

|
Cardiospermum halicacabum L.
Vernacular name: Bekkinabude gida
Family: Sapindaceae
Description: A small annual climbing herb. Leaves alternate, broad, segmented with toothed margin. Flowers are small in axillary umbels on a coiled wiry. Fruit is 3 angled and inflated1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: December - February |
Careya arborea Roxb.
Common name: Kaval
Family: Lecythidaceae
Description: Deciduous trees up to 12 m high. Leaves simple, alternate, estipulate, clustered at the tips of branchlets. Flowers bisexual, greenish-white, in terminal spikes. Fruit a berry, 5-7.5 cm globose1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Afganisthan, Myanmar, Malaysia; Flowering and fruit: February-July |

|

|
Cassia fistula L.
Common name: Indian laburnum
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Tree up to 5 m high. Leaves alternate, pinnate, leaflets up to 8 pairs, ovate-oblong, inflorescence a lax raceme, and drooping up to 50 cm long. Fruit a pod, pendulous, black, cylindrical1.2,3,4.
Native:India, China, Southeast Asia
Flowering and fruit: March – May; September |
Cassine glauca (Rottb.) Kuntze
Vernacular name: Mookrike
Family: Celastraceae
Description: Medium to large size evergreen tree. Leaves are simple, ovate to ovate-elliptic with entire or crenate margin. Inflorescence is axillary dichotomously branched cyme. Flowers are white with a green disk and yellow anthers. Fruits is a drupe1,2,3.
Native: Indo-Malayan; Flowering and fruit: August - February |

Source-2
|

|
Catunaregam spinosa (Thunb.) Tirveng.
Vernacular name: Mangeri
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves elliptic-obovate, subacute. Flowers 1-few-fascicled, 5-merous. Corolla pale yellow. Berry ellipsoid, 4 cm across1,2,3.
Native: Paleotropics; Flowering and fruit: Year long |
Celosia argentea L.
Vernacular name: Anne soppu
Description: A tall annual herb. Leaves are simple, alternate and elongated. Flowers tiny and crowded in terminal cone-shaped spikate inflorescence1,2,4.
Native: Tropical AsiaFlowering and fruit: September - October |

|

|
Ceropegia candelabrum L.
Vernacular name: Bitharige
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Rhizome tuberous. Leaves usually elliptic, glabrous, and slightly apiculate. Corolla swollen at base, follicles to 10 cm, narrowly attenuate1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka; Flowering and fruit: July - January |
Chamaecrista mimosoides (L.) Greene
Common name: Feather-leaved Cassia,
Family : Fabaceae
Description: Delicate herb. Leaves 6-10 cm long, with gland at tip of petiole. Flowers solitary, small. Pod flat, pubescent, and dehiscent to 3.5 * 0.3 cm1,2,3.
Native: India, Old World Tropics; Flowering and fruit: September – February |
 Source-2 Source-2
|
|
Chloris sp
Family: Poaceae |
Chloroxylon swietenia DC.
Vernacular name: Huragalu mara, Masivala mara
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Moderate-sized deciduous tree. Leaves are pinnate with 10-20 pairs, often clustered towards the apex. Inflorescence is a panicle, flower are pedicelled with sepals and petals 5 each. Fruit is a loculicidal capsule1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: February- July |

|

|
Eupatorium odoratum L.
Family: Asteraceae
Description: An erect undershrub. Leaves opposite and palmately veined. Corolla white to purple. Florets bisexual. Pappus hairs are one seriate1,2,3.
Native: South America
Flowering and fruit: November - April |
Chrysopogon aciculatus (Retz.) Trin.
Family: Poaceae
Description: Rhizome subterrancan, creping. Leaves mostly basal, rounded at tip, glabrous. Callus pungent, as long as spikelet1,2,3.
Native: Tropical Asia
Flowering and fruit: August - October |

|
Cipadessa baccifera (Roth) Miq.
Vernacular name: Sidigolli
Family: Meliaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaf rachis to 27 cm long, leaflets 9-13, elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate, acuminate. Sepals sparsely pubescent. Seeds not winged, exarillate1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: Year long |

|

Source-2
|
Cissampelos pareira
Vernacular name: Padvali
Family: Menispermaceae
Description: Climbing herbs. Leaves broadly ovate to suborbicular, rounded to acute at apex with apiculate tip. Flowers greenish-white. Drupe scarlet, pubescent1,2,3.
Native: Tropics; Flowering and fruit: July - October |
Clausena anisata (Willd.) Hook.f. ex Benth.
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Small tree. Leaves compound, usually imparipinnate, cluster at twig ends. Leaflets generally increase in size towards apex. Inflorescence axillary racemes, white flower. Berry globose1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: March-June |

|

|
Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels
Vernacular name: Dhagadiballi
Family: Menispermaceae
Description: Climbing shrub. Leaf blade 15-6*0.5-2.5 cm, ovate, obtuse or mucronate at apex, rounded or truncate at base, clustered pistillate flowers. Drupe reddish-black1,2,4.
Native: Tropical Africa and India; Flowering and fruit: August – March |
Commelina canescens
Family: Theaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves elliptic-oblong, apex acuminate, base acute, serrate. Flowers axillary, solitary to 3 cm across, white. Capsule to 2mm across, woody, subglobose1,2,3,4.
Flowering and fruit: June-January |

|
|
Corchorus sp
Family: Malvaceae |
Crotalaria sp
Family: Fabaceae |
|

|
Crotalaria vestita Baker
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Erect herb. Leaves oblong, obtuse. Raceme few-flowered. Calyx villous. Corolla equaling or included in calyx. Pod exserted, glabrous, many-seeded1,2,3,5.
Native: Tropics
Flowering and fruit: November - February |
Crytococcum sp
Family: Poaceae |
|

|
Curculigo orchioides Gaertn.
Vernacular name: Nela taale
Family: Hypoxidaceae
Description: Perennial herb. Leaves strap-like with parallel veins. Flowers solitary, attractive and borne on a long stalk that arises from base. Fruit is a three-lobed capsule1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: June - August |
Cyanotis sp
Family: Commelinaceae |
|

Source-7
|
Cymbopogon coloratus (Nees) Stapf
Vernacular name: Nimber hullu
Family: Poaceae
Description: Perennial grass. Culms upto 2 m tall. Leaf sheaths 5-15 cm, basal tomentose, upper globrous. Panicle dense, upto 8 cm. Sessile spikelet, lower glume, coriaceous, oblong. Lemmas hyaline, epaleated1,2,3,4.
Flowering and fruit: August -October |
Cymbopogon flexuosus (Nees ex Steud.) W. Watson
Family: Poaceae
Description: Blade lanceolate, glaucous. Sheath hairy. Inflorescence congested with raceme pairs in masses1,2,3,4.
Native: Indomalaysia
Flowering and fruit: September |

Source-2
|

|
Cymbopogon nardus (L.) Rendle
Family: Poaceae
Description: A tall perennial. Blade lanceolate, acuminate, glaucous. Lower glume not grooved not slotted. Panicle often turning purplish under dry conditions1,2,3,4.
Native: South India, Sri Lanka |
Cymbopogon sp
Family: Poaceae |
|

|
Dactyloctenium aegyptium (L.) Willd.
Vernacular name: Konana tale hullu
Family: Poaceae
Description: An annual grass. Culms erect or prostrate. Leaves linear-acuminate, glaucous, ligule short and membranous. Spikes digitately radiating1,2,3,5. |
Dalbergia lanceolaria L.f.
Vernacular name: Bili beete
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A deciduous tree up to 25 m high with pubescence on younger partions. Leaves are once pinnate, leaflets 13-15, obovate, membranous. Corolla white. Pod is narrow at both ends, 1.5 cm wide1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: August - September |

Source-2
|

|
Dalbergia latifolia Roxb.
Vernacular name: Beete mara
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A large erect deciduous tree. Leaves are compound with 7-9 leaflets with broad at the free end. Flowers are small, white and appear on an axillary panicle. The fruit is 1-4 seeded rather flattened pod1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: May - September |
Dendrocalamus strictus Nees
Family: Poaceae
Description: Clum sheath, triangular, with brown shining hairs on the back. Blade narrow, small, deciduous, sheath glabrous with narrow ligule1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Burma |

Source-2
|
|
Desmodium sp
Family: Fabaceae |
Dicliptera paniculata (Forssk.) I. Darbysh. Apud I. Darbysh. & Vollesen
Vernacular name: Cheebi gida
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: Subshrub. Leaves ovate and acuminate, hairy. Flowers in cymes. Calyx lobes linear, hairy. Corolla is pink, hairy outside. Fruit is a capsule1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Myanmar, Vietnam, Tropical Africa
Flowering and fruit: October - January |

Source-2
|
|
Digitaria sp
Family: Poaceae |
Dioscorea oppositifolia L.
Family: Dioscoreaceae
Description: Stem twining. Leaves opposite and alternate, very variable in shape. Male spike brownish pubescent. Capsule stipitate, pendulous, broader than long1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: August -January |

|

|
Dioscorea pentaphylla L.
Family: Dioscoreaceae
Description: Climber. Leaves 3-5-foliate, leaflets digitate, ovate-elliptic, oblique at base. Male spikes in axillary or terminal panicles. Capsule longer than broad. Seeds winged only at base1,2,3,5.
Flowering and fruit: August – November |
Diospyros chloroxylon Roxb.
Vernacular name: Nensi
Family: Ebenaceae
Description: Shrubs or tree. Leaf blade elliptic-oblong or obovate, usually obtuse, grey-pubescent when young. Inflorescence of short axillary cymes in male. Flowers 4-merous, sessile or subsessile. Berry globose, 1 cm across. Seeds 2-3, smooth1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Fruits: October - November |

Source-2
|

|
Diospyros melanoxylon Roxb.
Vernacular name: Tumari
Family: Ebenaceae
Description: Deciduous tree with branchlets fulvous-tomentose. Leaves simple, elliptic or oblong. Male flowers in short cymes, females solitary. Corolla white1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: Late March |
Diospyros montana Roxb.
Vernacular name: Balagunike
Family: Ebenaceae
Description: tree. Leaf blade elliptic-oblong or obovate, obtusely acute or acuminate at apex, rounded or subcordate at base. Male flowers in cymes, pubescent, female solitary flowers 4-merous. Corolla greenish-white, glabrescent, urceolate. Berry globose, glabrous1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: March - April |

|

|
Diplocyclos palmatus (L.) C. Jeffrey
Vernacular name: Shivalingi
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Description: A climbing herb. Leaves are simple, alternate with semilunar-margined lobes. Flowers arise in axillary fascicles, unisexual with a shallow bell-shaped hairy corolla. Fruit is fleshy1,2,3.
Native: India, South-east Asia, Tropical Africa
Flowering and fruit: August - September |
Drosera burmannii Vahl
Family: Droseraceae
Description: Acaulescent herbs. Stipulate leaves. Scape terminal, circinate. Flowers white, 5 petals, obovate1,2,3.
Native: West Africa to North E Australia |

|

Source-8
|
Echinochloa colonum (L.) Link.
Family: Poaceae
Description: Annuals. Leaves linear-lanceolate, rounded or shallowly cordate at base, apex acuminate. Lower glume 1-2*1-1.5 mm, ovate, acuminate, chartaceous1,2,3.
Flowering and fruiting: Throughout the year |
Eleusine aegyptiaca (L.) Desf.
Family: Poaceae
Description: culms 30-60 cm long, creeping or geniculately ascending. Leaves linear, rounded or shallowly cordate at base, acuminate, margins at base ciliate. Spikes 2-6 digitate, spikelets sessile1,2,3,5.
Native of South America, naturalised in Paleotropics
Flowering and fruiting: Throughout the year |

Source -9
|

Source -10
|
Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn.
Vernacular name: Madhulika
Family: Poaceae
Description: Annual herb. Culms tufted, erect, slender, compressed, glabrous. Inflorescence a terminal branched flowered. Lemma lanceolate, acute. Palae slightly shorter than the lemma, keeled, narrowly, winged. Grain oblong, globose1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July - September |
Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC.
Family: Asteraceae
Description: Annual herb. Leaves simple, auriculate at base, obovate with toothed margin. Flower heads small. Cypsela are slender, ribbed, brown with white coma1,2,3,5.
Native: Old World Tropics
Flowering and fruit: September - December |
 Source-2 Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Eragrostiella bifaria (Vahl) Bor
Family: Poaceae
Description: Perennial culms tufted. Spikelets straw coloured, laterally compressed, linear to ovate-oblong. Caryopsis globose1,2,4,5.
Native: South America
Flowering and fruit: July – June |
Eragrostis unioloides (Retz.) Nees ex Steud.
Family: Poaceae
Description: Tufted annuals with spreading panicle. Spikelets white to pink or reddish-purple, ovate, acute, sometimes oblong1,2,4,5.
Native: Indomalaysia
Flowering and fruit: July-October |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Erythrina suberosa Roxb.
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A moderate size deciduous tree with small prickles on the bark. Leaves are three leaflets and crowded at branch ends. Flowers are bright red in fascicles. Pod is long, tapering at both ends1,2,3,5.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: February - May |
Erythroxylum monogynumRoxb.
Family: Erythroxylaceae
Description: Small tree. Leaves alternate, sometimes fascicled, obovate and glaucous beneath. Flowers are solitary or in fascicles. Fruit is a drupe with single seed and bright red when ripe1,2,3,4.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |

|
|
Eucalyptus sp
Family: Myrtaceae |
Evolvulus alsinoides (L.) L.
Vernacular name: Vishnu kranthi
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: A small herb. Leaves ovate-elliptic, alternate and silky hairy. Flowers are small and solitary. Fruit is capsule globose1,2,3,5.
Native: Tropical Africa, Asia
Flowering and fruit: July – November |

|
 Source-2 Source-2
|
Ficus amplissima Sm.
Vernacular name: Bilibasuri mara
Family: Moraceae
Description: A large spreading tree. Petiole 3 cm long, leaf blade ovate, slightly acuminate at the apex. Figs occur in axillary pairs, sessile, bracts small and scaly1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |
Ficus drupacea Thunb.
Vernacular name: Bili golimara
Family: Moraceae
Description: Large tree with spreading crown. Leaves are shiny on the upper surface. Figs occur in pairs in the leaf axils1,2,3,4.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: January - March |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Ficus microcarpa L.f.
Vernacular name: Kiru goli
Family: Moraceae
Description: Tree with few aerial roots. Leaf blade elliptic-obovate, obtuse or abruptly acuminate at apex. Figs in axillary pairs, sessile, glabrous to 1 cm across1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka |
Fimbristylis barbata (Rottb.) Bth.
Family: Cyperaceae
Habit: Herb. Leaves narrow, linear, acute, glabrous, sheath pilose. Inflorescence a terminal, subglobose, spiked head. Glumes laterally compressed, lanceolate or cymbiform, glabrous or minutely hispid. Fruit a nut, broadly obovoid, trigonous, smooth, straw-coloured1,2,3,5.
Flowering and fruity: July - November |

Source-11
|

Source-2
|
Flacourtia indica (Burm. F.) Merr.
Vernacular name: Miradi
Family: Salicaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves obovate with serrate or entire margin. Flowers small, dioecious, greenish-yellow. Fruit a globose berry1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Southeast Asia
Flowering and fruit: September - March |
Flacourtia montana J. Graham
Vernacular name: Kakkade hannu
Family: Salicaceae
Description: A large tree. Leaves elliptic, oblong, acuminate, rounded at base, crenate pubescent on midrib. Flowers unisexual. Berry fleshy1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: April-June |

|

Source-2
|
Flueggea leucopyrus Willd.
Vernacular name: Bilishooli gida
Family: Phyllanthaceae
Description: A large shrub. Leaves simple, alternate and ovate. Flowers are unisexual, small, fragrant. Fruit is small, globose, smooth and white in colour1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: June - September |
Garuga pinnata Roxb.
Vernacular name: Goddana mara
Family: Burseraceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves grow closely crowded at the ends of branches. Pinnately compound with terminal leaflet at tip. Flowers in panicles are 1-1.2 cm long, bell shaped. Fruits resemble small grapes. Fruits are edible1,2,3.
Native: Asia; Flowering and fruit: November - March |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Givotia moluccana (L.) Sreem
Vernacular name: Butti mara
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Description: Moderate sized tree. Leaves are simple, broadly ovate or orbicular, coarsely dentate. Flowers are unisexual and dieocious. Fruit is a drupe1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: March - May |
Gloriosa superba L.
Vernacular name: Kolikuttuma
Family: Colchicaceae
Description: Climbing to 4-6 m. Leaves oblong to ovate-lanceolate. Pedicels 6-8 cm, reflexed at the tip. Stigma introse. Capsule green, smooth oblong1,2,3,4.
Native: Paleotropics; Flowering and fruit: August - October |

|

|
Gmelina arborea Roxb.
Vernacular name: Gambhari, Kasmari
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Large deciduous tree. Leaves are long-stalked, broadly heart-shaped and are arranged in opposite pairs. Flowers arise in branching clusters towards the end of twigs, trumpet-shaped. Fruit is ovoid, 2-3 cm. long and yellow when ripe1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: April - May |
Grewia nervosa (Lour.) Panigrahi
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Erect shrubs. Leaves elliptic-oblong or ovate-lanceolate, base rounded or cordate. Flowers in axillary and terminal panicles. Fruit drupe 6-10 mm across1,2,3,4.
Flowering and fruit: August – April |

|
|
Grewia sp
Family: Malvaceae |
Grewia villosa Willd.
Vernacular name: Battigargale
Family: Malvaceae
Description: shrubs. Leaf blade rounded, acute, subcordate at base. Peduncle extra-axillary, shorter than petiole. Drupe globose, crustaceous, pilose1,2,3,5.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: July - October |

|

Source-2
|
Haldina cordifolia (Roxb.) Ridsdale
Vernacular name: Anavu
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves simple, orbicular to cordate, with an acuminate tip. Flowers are small and yellow and aggregated in heads. Fruit capsule1,2,3.
Native; India, Sri Lanka, China; Flowering and fruit: March - June |
|
Helicteres isora L.
Vernacular name: Kempukaaveri
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Woody shrub. Leaves simple, elliptic-obovate, obliquely cordate at base. Flowers are cyme axillary. Sepals are brown, hairy and 2 lipped. Fruit is spirally twisted1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Bhutan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, China, Malaysia, Java, Australia
Flowering and fruit: September - February |

|

|
Heteropogon contortus (L.) P. Beauv. ex Roem. & Schult.
Vernacular name: Gandu bin
Family: Poaceae
Description: Annual or perennial grass with strongly-tufted stems. Leaf blades are lanceolate. Inflorescence is a solitary spike-like silky-hairy raceme with minute flowers1,2,3.
Native: California; Flowering and fruit: July - November |
Holarrhena pubescens (Buch.-Ham.) Wall. ex G. Don
Vernacular name: Kudha
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Small tree. Flowers white fragrant. Fruit in long paired follicles white dotted1,2,3,4.
Native India-Malay Peninsula
Flowering and fruit: March - June |

|

|
Holoptelea integrifolia (Roxb.) Planch.
Vernacular name: Rahu beejada mara
Family: Cannabaceae
Description: Large deciduous tree. Leaves are simple, entire with lateral and membranous stipules. Flowers are small, unisexual and borne in fascicles. Fruit is winged1,2,3,5.
Native: India and South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: October - February |
Hymenodictyon orixense (Roxb.) Mabb.
Vernacular name: Dossa toppemara
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves broadly ovate, acuminate at apex, narrowed into the petiole at base, membranous. Flowers white, in dense cylindrical leafy bracteates. Fruit capsule ovoid, 2 cm long1,2,3,4.
Native: Indian sub-continent; Flowering and fruit: May - November |

Source-2
|

|
Ichnocarpus frutescens (L.) W.T. Aiton
Vernacular name: Gauri balli
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: An evergreen woody twiner with milky sap. Leaves elliptic-oblong or lance shaped. Flowers are borne in many flowered clusters. Fruit is a follicle, solitary or paired1,2,3,4.
Native: Tropical Asia; Flowering and fruit: August - December |
Impatiens sp
Family: Balsaminaceae |
|
|
Indigofera sp
Family: Fabaceae |
Indigofera tinctoria L.
Vernacular name: Neela gida olle neele
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaf rachis to 8 cm long, rarely subopposite, obtuse, apiculate. Raceme to 4 cm long. Pod linear, slightly curved, sparsely hairy1,2,3.
Native: Tropics |

|

Source-2
|
Iphigenia indica (L.) A. Gray ex Kunth
Family: Colchicaceae
Description: Herb. Leave dense, linear-lanceolate, acuminate, and sessile. Perianth segments linear, subulate, chocolate. Capsule oblong or sub globose1,2,3.
Native: Indomalaysia
Flowering and fruit: August – January |
Ipomoea grandifolia (Dammer) O' Donell
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: Climber. Leaves broadly ovate to orbicular in outline, entire or 3-lobed, glabrous. Flowers in pedunculate, subumbellate cyme. Capsules 5-6 mm long, subglobose, bristly hairy1,2,3.
Native: Tropical America
Flowering and fruit: September - November |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Ipomoea nil (L.) Roth
Vernacular name: Gouribeeja
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: Climbing shrub. Leaf ovate, cordate, palmately 3 lobed. Cyme umbellate, few flowered. Corolla campanulate, blue or pink. Capsule 3 subglobose1,2,3.
Native: Tropics; Flowering and fruit: September - December |
Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker Gawl
Vernacular name: Godlajadi
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: Slender climber. Leaf entire-angled, ovate, acuminate, cordate, glabrous or pubescent. Corolla funnel-shaped, sparsely pubescent. Fruit capsule ellipsoid, apiculate1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka; Flowering and fruit: August - April |
 Source-2 Source-2
|
|
Ischaemum sp
Family: Poaceae |
Ixora notoniana Wall.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Shola tree. Leaf stalk stout, entire, more or less elliptic, firm. Flowers are in hemispherical clusters massed into broadly rounded. Fruit black nearly round, of two cells1,2,3.
Native: India |

Source-12
|
|
Jasminum sp
Family: Oleaceae |
Jatropha gossypifolia L.
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Description: Shrubs. Leaves spiral, deeply lobed, orbicular-cordate, margin with gland-tipped hairs. Flowers red with yellow centre, unisexual in axillary and terminal monoecious corymbose cyme. Fruit capsule, 3 lobed1,2,3.
Native of South America; Flowering and fruit: July-September |

|

|
Justicia simplex
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: herb. Leaves linear, simple, opposite. Flowers about 0.5 cm, clustered in terminal hairy spikes. Fruit is few-seeded capsule1,2,3.
Native: India, Nepal, Sri Lanka, Pakistan
Flowering and fruit: July- September |
Kyllinga pumila Michx.
Vernacular name: Mustaka
Family: Cyperaceae
Description: Small, tufted herb. Leaves long-pointed. Head rounded-pyramidal, greenish or yellowish-white with 3 spreading bracts. Glumes thin, unwinged1,2,3.
Native: Paleotropics and into subtropics
Flowering and fruit: August - October |

Source-13
|

|
Lagerstroemia parviflora Roxb.
Vernacular name: Chennangi mara
Family: Lythraceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves subsessile, elliptic-oblong, glaucous beneath. Capsule ellipsoid, appressed by calyx tube1,2,3.
Native: Western India, Myanmar
Flowering and fruit : May-February |
Lannea coromandelica (Houtt.) Merr.
Vernacular name: Ajjashringi
Family: Anacardiaceae
Description: Tree upto 25 m high. Leaves imparipinnate, alternate, clustered at the end of branchlets. Flowers unisexual, yellowish-green. Fruit a drupe, ovoid, red. Seed compresed1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka |

Source-2
|

Source-14
|
Lantana tiliaefolia Cham.
Family: Verbenaceae
Description: Prickly straggling shrub. Leaves opposite, simple, ovate or ovate-oblong, serrulate, acute. Inflorescence in terminal and axillary umbellate. Fruit a fleshy drupe, dark-pink, edible1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: February – August |
Lepidagathis cristata Willd.
Vernacular name: Nari goodi
Family: Acanthaceae
Description: Creeping herb. Leaves linear-oblong, glabrous. Spikes capitate, mostly crowded on lower nodes. Corolla white, hairy1,2,3.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |

|

|
Leucas aspera (Willd.) Spr.
Vernacular name: Thumbe gida
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Erect herb upto 40 cm tall. Leaves linear-lanceolate, base cuneate, margin distantly serrate. Verticils axillary and terminal, distantly arranged, rarely superposed, very dense, many-flowered, bracts-linear, ciliate. Nutlets 3 mm long, smooth, brown, truncate at apex1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: September-January |
Leucas lavandulifolia Sm.
Vernacular name: Thumbe
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves subserrate, linear-lanceolate, membranous. Verticillasters 1-2, many-flowered. Upper lip shorter than lower lip1,2,3.
Native: Indo-malaya
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |

Source-2
|

|
Leucas martinicensis (Sw.) R. Br.
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Herb hairy. Leaves oblong, blade serrate. Flowers in either terimal or axillary verticillasters. Corolla white with both lips equal. Fruit is a nutlet1,2,3.
Native: South America, Caribbean
Flowering and fruit: All Season |
Leucas sp
Family: Lamiaceae |
|

|
Madhuca latifolia (Roxb.) J.F. Macbr.
Vernacular name: Ippe, Helippe
Family: Sapotaceae
Description: Trees up to 20 m high, brak grey. Leaves simple, alternate, clustered at the end of branchlets, stipules lateral, lanceolate. Flowers bisexual, creamy, axillary. Fruit a berry, ovoid, greenish, fleshy, tawny-tomentose without. Seeds 21,2,5.
Flowering and fruit: December-July |
Mangifera indica L.
Vernacular name: Mavina mara
Family: Anacardiaceae
Description: Evergreen tree. Leaves are simple, oblong-lanceolate, acute or acuminate at apex. Flowers are small, bisexual, brone on much-branched panciles. Fruit is a single-seeded fleshy drupe1,2,3,5.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: January - June |

|

|
Maytenus emarginata (Willd.) Ding Hou
Vernacular name: Thanasimale
Family: Celastraceae
Description: Climbing shrub. Leaves glabrous, obtuse and serrate, subcoriaceous. Fruit capsule globose, 0.5 cm long1,2,3.
Native: Indomalesia
Flowering and fruit: December - February |
Melia dubia Cav.
Vernacular name: Bettada bevu mara
Family: Meliaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves compound with tooth leaflets. Flowers small, greenish-yellow in much branched inflorescence. Fruit are green, ellipsoidal with a single seed covered by hard grey1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Tropical Asia, Angola, Australia; Flowering and fruit: January - February |

|

|
Memecylon umbellatum Burm.f.
Vernacular name: Mundi Alle
Family: Melastomataceae
Description: Tree. Leaf blade ovate-elliptic, nerves faintly visible. Calyx campanulate. Fruit berry to 5 mm in diameter1,2,3,5.
Native: India, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: March - July |
Merremia tridentata (L.) Hallier f.
Vernacular name: Prasarani
Family: Convolvulaceae
Description: Perennial spreading herbs. Leaves simple, variable, linear, spathulate, linear-hastate or oblong-obovate. Flowers axillary, solitary or 2 -3 flowered cyme. Fruits capsule ovoid, glabrous, 4-valved1,2,3,4.
Flowering and fruit: June-January |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Miliusa tomentosa (Roxb.) Finet & Gagnep.
Family: Annonaceae
Description: Tree. Leaf blade elliptic or ovate – lanceolate, acute, rounded at base. Flowers solitary or in leaf-opposed or terminal. Fruitlets stalked, subglobose, tomentose1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Nepal
Flowering and fruit: February – March |
Mimosa pudica L.
Vernacular name: Olamucchaga
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Prickly herb. Leaves alternate compound. Leaflets many on secondary rachis. Flowers aggregated into globose head. Fruit is a flat pod with constictions between seeds1,2,3,4.
Native: South America
Flowering and fruit: July - October |

|

Source-2
|
Mollugo pentaphylla L.
Family: Gisekiaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves linear-lanceolate to obovate, acute. Flowers white, numerous in lax corymbose cyme. Fruit capsule is oblong1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Tropical America
Flowering and fruit: July - January |
Morinda pubescens J. E. Smith
Family: Rubiaceae
Habit: Deciduous tree. Leaves simple, opposite, decussate, stipules interpetiolar, connate, sheathing, bifid at apex. Flowers bisexual, white, in terminal, globose heads, calyx limb truncate. Fruit a syncarp, 15-18 mm across, pyrenes 4. Seeds not winged1,2,3.4.
Flowering and fruit: March-June |

|

Source-2
|
Murdannia semiteres (Dalzell) Santapau
Family: Commelinaceae
Description: Small herb. Leaves simple, linear. Flowers are small, branched inflorescence. Fruit is a subglobose capsule1,2,3,5.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: July - October |
Naringi crenulata (Roxb.) Nicolson
Vernacular name: Kadubilvapatre
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Tree. Leaf rachis to 7 cm long, elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate, obtuse at apex, crenate. Cyme inflorescence. Fruit berry globose, bluish-black1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: September - December |

|

Source-2
|
Oldenlandia herbacea (L.) Roxb.
Vernacular name: Chaayaparpatika
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, rigid. Fruit capsule loculicidal with protruding crown1,2,3.
Native: Africa
Flowering and fruit: January-July |
Olea dioica Roxb.
Vernacular name: Bilisarole
Family: Oleaceae
Description: Evergreen tree. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, entire. Flower white1,2,3.
Native: Indian sub-continent
Flowering and fruit: January-February |

|

|
Oplismenus compositus (L.) P. Beauv.
Family: Poaceae
Description: Perennial grass. Leaves lanceolate, linear, acuminate, flat, thin, dull-green hairy. Inflorescence a paniculate raceme. Spikelets hairy, lanceolate, acuminate, greenis-purple. Awns longer than glumes, often reddish1,2,3.
Native: Pantropics; Flowering and fruit: August - October |
Panicum sp.
Family: Poaceae |
|

|
Parthenium hysterophorus L.
Family: Asteraceae
Description: Herb. Leaves pubescent, lobes entire, acute. Florets white.ligule in female floret supported by 2 hyaline wings at base1,2,3.
Native: West Indies, Central & North America
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |
Pavetta breviflora DC.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Tree. Branched smooth. Leaves elliptic, bluntly acuminate, narrowed to the short petiole. Flowers in corymbs of perfect cymes. Fruit black, containing one or two stones1,2,3.
Flowering and fruits: April-May; May-August. |

|

|
Pavonia odorata Willd.
Vernacular name: Balarakshi gida
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves orbicular – ovate, acute, usually cordate at base. Corolla 1.3 cm long, white or pink. Cocci smooth, pubescent1,2,3.
Native: East Tropical Africa, Peninsular India, Burma
Flowering and fruit: September - October |
Pennisetum sp
Family: Poaceae |
|

Source-2
|
Perotis indica (L.) Kuntze
Family: Poaceae
Description: Herb. Blade to 2*0.4 cm with glabrous sheath. Raceme slender, often purplish1,2,3.
Native: Indomalaysia
Flowering and fruit: August - October |
Phoenix sylvestris (L.) Roxb.
Family: Arecaceae
Description: A graceful palm with 16 m tall. Leaves 3-4.5 m long, greyish-greenm flowers small, fragrant, borne in spadices. Fruiting spadix about 90 cm long, bearing oblong-ellipsoid berries. Seeds 1.7 cm long, deeply grooved with rounded ends1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: April - December |

|

|
Phyllanthus emblicaL.
Vernacular name: Bettada nelli kaayi
Family: Phyllanthaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves apiculate obtuse, rounded or cordate at base, glaucous beneath. Flowers usually monoecious. Fruit fleshy more than 1.5 cm in diameter1,2,3.
Native: India, South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: July-February |
Phyllanthus simplex Retz.
Family: Phyllanthaceae
Description: An erect or diffuse herb. Leaves subsessile, closely placed and often overlapping, linear-oblong, obtuse or acute at apex. Fruit capsule depressed-globose, long-stalked1,2,3.
Flowering: More or less throughout the year. |

Source-15
|

Source-2
|
Polycarpaea corymbosa (L.) Lam.
Vernacular name: Poudaemullugida
Family: Caryophyllaceae
Description: An erect herb. Leaves simple, linear, hairy and opposite in whorls. Flowers are small in compact bunches of white. Fruit is a capsule1,2,3.
Native: Africa, Asia, Australia
Flowering and fruit: August - March |
Polygala elongata Klein ex Willd.
Family: Polygalaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves linear, lanceolate, elliptic, linear. Flowers are usually in terminal raceme. Fruit is a rhomboidal capsule1,2,3.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: August - January |

Source-2
|

|
Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre
Vernacular name: Hongemara
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Medium-sized deciduous tree. Leaves are imparipinnate with 2-3 pairs of broad leaflets. Flowers are in short clusters, pea-like. Fruit is a flattened, oval, woody pod that dehisces at both ends1,2,3.
Native: India |
Premna tomentosa Willd.
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Trees upto 15 m high. Leaves simple, opposite, estipulate, broadly ovate, base obtuse or cordate, apex acuminate, margin entire. Flowers bisexual, yellow, in terminal and axillary corymbs. Fruit a drupe, ovoid, 5-6 mm long. Seeds 41,2,3,4.
Flowering and fruit: February - April |

|

|
Psydrax umbellata (Wight) Bridson
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Medium tree. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, shortly acuminate, acute. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, shortly acuminate, acute. Umbel Inflorescence. Fruit drupe ovoid 1.5 cm long1,2,3,5.
Native: South India, Burma |
Pterocarpus marsupium Roxb.
Vernacular name: Benga mara
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Deciduous native tree. Leaves alternate, pinnately compound and entire leaflets. Flowers in terminal, highly branched. Fruit is winged one seeded pod1,2,3,4.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: August - October |

|

|
Pterolobium hexapetalum (Roth) Sant. & Wagh
Vernacular name: Bada Bakka
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaf rachis 12-18 cm long. Calyx rose, Corolla yellowish-white. Pod pinkish-red. 5*1 cm1,2,3.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: August - February |
Rotala fimbriata Wt.
Common name: Lilac Tasselflower
Family: Lythraceae
Description: Slender herb. Leaves are decussate, lanceolate to oblong. Flowers small sessile either single or in groups of few. Fruits is elongate-ellipsoid1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: September – January |

|

|
Santalum album L.
Vernacular name: Srigandha mara
Family: Santalaceae
Description: A small evergreen semi-parasitic. Leaves are simple, opposite, shortly-stalked, glossy and elliptic. The flowers are bell-shaped small, purplish-brown1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: Appears once in late summer and again between October and December. |
Sarcostemma acidum (Roxb.) Voigt
Vernacular name: Hambukalli
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Climbing shrub. Lobed corolla, margin revolute. Style apex short conical, entire, not exerted1,2,3.
Native: Peninsular India
Flowering and fruit: August – February |

Source-2
|

Source-16
|
Schizachyrium exile (Hochst.) stapf
Family: Poaceae
Description: An annual herb. Culms upto 15 cm tall. Leafsheaths 1-3 cm long, glabrous, ligule membranous. Sessile spikelet dorsally compressed. Lower glume lanceolate, keeled, hairy1,2,3,5.
Flowering and fruit: August - December |
Schleichera oleosa (Lour.) Merr.
Vernacular name: Kendala
Family: Sapindaceae
Description: Amedium-sized tree. Leaves are large, compound with oblong leaflets, sessile. Flowers are small in panicles at the nodes. Fruit is grape or olive-shaped with a pointed beak, slightly prickly1,2,3,4.
Native: India ; Flowering and fruit: February - May |

Source-2
|

|
Semecarpus anacardium L.f.
Vernacular name: Kari geru
Family: Anacardiaceae
Description: Medium- sized deciduous tree. Leaves are large, coriaceous, obovate-oblong. Flowers in panicles, greenish-white, small and polygamous. Fruit is a resinous nut1,2,3,4.
Native: Sub Himalayan; Flowering and fruit: July - September |
Senna occidentalis (L.) Link
Vernacular name: Kola thagache
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves alternate, paripinnate with glands above pulvinus. Flowers solitary, axillary, 0.4 cm across. Pod flat, pubescent. 10-14 seeded, 2.5 cm long1,2,3,4,5.
Native: Central & South America
Flowering and fruit: October - February |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Senna siamea (Lam.) H.S. Irwin & Barneby
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Trees. Leaves long, estipulate, eglandular. Corymb in axillary and terminal panicles. Pod 15-25*1 cm flattened1,2,3,5.
Native: South East Asia
Flowering and fruit: March – February |
Setaria sp
Family: Poaceae |

|
Shorea roxburghii G. Don
Family: Dipterocarpaceae
Description: Trees upto 25 m bark, brownish to grey-brown, blaze creamy-yellow, fibrous. Leaves simple, alternate, stipule large, coriaceous, stout, glabrous. Flowers bisexual, light pink, in drooping axillary and terminal panicles. Fruit capsule, enclosed within accrescent sepals, wings oblong, unequal, obovoid1,2,3,5.
Native: Indo-Malesia; Flowering and fruit: February-June |
Sida acuta N. Burm.
Vernacular name: Dodda bindige gida
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Erect herbs, nearly glabrous. Petiole to 5mm long, ovate or linear-lanceolate. Calyx lobes triangular, acute cocci 7, shortly awned1,2,3,5.
Native: Pantropical; Flowering and fruit: August - February |

|

Source-2
|
Sida cordata (Burm. f.) Borss. Waalk.
Vernacular name: Bekkinatale gida
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves ovate, acute-acuminate, dentate. Flowers solitary axillary, in few-flowered racemes. Cocci 2-toothed and hairy at apex1,2,3,4.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Tropical Africa
Flowering and fruit: July - February |
Sida mysorensis Wight. & arn.
Vernacular name: Antututti
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Erect herb. Leaves ovate, acuminate, dentate. Flowers solitary axillary, or in racemes shorter than leaves. Cocci 2-toothed and hairy at apex1,2,3,4.
Native: India to Malesia; Flowering and fruit: January |

Source-17
|

|
Sida rhombifolia L.
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Subshrubs. Leaves 2-5*1.5-3.5 cm, rhomboid, apex acute, base acute or cuneate. Flowers axillary, solitary or in clusters, yellow, lobes triangular to 3 mm. tomentose outside. Schizocrap enclosed in calyx, semiorbicular, mericarps 8-10, awned at apex to 1 mm1,2,3,5.
Flowering and fruit: September - December |
Smilax sp
Family: Smilacaceae |
|

|
Sopubia delphinifolia (L.) G. Don
Family: Orobanchaceae
Description: Erect branching herb. Leaves opposite, pinnatifid, lobes linear, narrow. Flowers axillary, solitary, passing on to terminal few-flowered leafy racemes. Fruit a capsule, oblong, green, seeds numerous, oblong, minute, brown, slightly compressed1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July; October - January |
Spermacoce articularis L.f.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: A diffuse herb. Leaves elliptic to elliptic-oblong or obovate, subsessile. Flowers in axillary few-flowered clusters. Capsules hispid, obovoid. Seeds oblong1,2,3.
Flower: More or less throughout the year. |

|

Source-2
|
Spermacoce ocymoides Burm.f.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves elliptic-oblong, sparsely scabrous, base cuneate to attenuate, apex acute, subsessile. Flowers in axillary fascicle. Capsule truncate, dehiscing transversely1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July - December |
Spermacoce pusilla wall.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: An erect slender herb. Leaves linear-lanceolate, scabrid, lateral veins. Flowers minute, in dense axillary and terminal capitate clusters. Corolla pink, funnel-shaped. Capsules ellipsoidal, glabrescent1,2,3.
Flowering: August - September |

|

Source-18
|
Spermacoce stricta L.f.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Erect herb. Leaves opposite, simple, linear-lanceolate, ovate-oblong, thick, narrow, entire, acute or acuminate. Inflorescence an axillary condensed fascicle or head. Fruit capsule, narrow, glabrous. Seed ellipsoid or rounded, grooved1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: July – September |
Stachytarpheta jamaicensis (L.) Vahl
Family: Verbenaceae
Description: Herb. Leaves elliptic-ovate, obtuse or acute at apex, cuneate. Spikes upto 40 cm long. Corolla 8-11 mm long, blue-purple1,2,3.
Native: Tropical America
Flowering: More or less throughout the year. |

|

|
Stereospermum tetragonum DC.
Family: Bignoniaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves once-pinnate, leaf axis 12 cm long. Calyx 0.6 cm long, unequaly and shortly lobed. Corolla yellow, sparsely pubescent. Capsule 4-angled1,2,3.
Native: India, Burma, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: March - November |
Striga angustifolia (Don) Sald.
Family: Orobanchaceae
Description: Parasite herb. Leaves linear, scabrid, subopposite or alternate. Corolla white, exceeding calyx. Flowers axillary, solitary, passing on to terminal leafy spikes. Fruit a capsule, oblong-ellipsoid, loculicidal. Seeds minute, black, truncate1,2,3.
Native: Indomalaysia; Flowering and fruit: August - November |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Strychnos potatorum L.f.
Vernacular name: Chilu
Family: Loganiaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves elliptic, acute at both ends. Cymes usually on old wood. Corolla tube longer than lobes. Fruit 1-1.5 cm wide1,2,3.
Native: Burma, Central & Peninsular India, Sri Lanka
Flowers: September - June |
Syzygium cumini (L.) Skeels
Vernacular name: Neerale
Family: Myrtaceae
Description: Tall tree. Leaves simple, elliptic, lush-green and leathery with insect galls. Numerous flowers aggregate into dense cluster with long stamens. Fruit is globose to oblong, single-seeded berries1,2,3.
Native: South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: February - September |

|

Source-2
|
Syzygium salicifolium (Wight) J. Graham
Vernacular name: Simpi neerale
Family: Myrtaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves shortly petiolate, subcoriaceous, linear elliptic. Cyme panicled, axillary or extra-axillary. Flower small, white. Berry oblong to 1.5 cm long1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: February - May |
Tamarindus indica L.
Vernacular name: Hunase mara
Family: Fabaceae
Description: A medium to large size deciduous tree. Leaves are pinnately compound with small leaflets. Flowers are small many, pale green and colour. Fruit is a bean like pod fleshy, green at first1,2,3.
Native: Tropical Africa
Flowering and fruit: Late Summer |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Tarenna asiatica (L.) Kuntze ex K. Schum.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, shortly acuminate, rounded. Corolla tube shorter than lobes. Fruit berry 2 mm across, globose1,2,3.
Native: Indomalaysia
Flowering and fruit: August – March |
Tectona grandis L.f.
Vernacular name: Thega mara
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves are large, opposite pairs with variable shapes. Flowers are small white, sweet-scented. Fruit is hard and enveloped by bladder like calyx1,2,3.
Native: South-east Asia; Flowering and fruit: June - October |

|

|
Tephrosia purpurea (L.) Pers.
Vernacular name: Kolingii
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Undershrubs. Leaf rachis 6 cm long, leaflets oblanceolate. Raceme many flowered. Corolla pink. Pod slightly curved, glabrous. 4 seeded1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Old World Tropics; Flowering and fruit: All Seasons |
Terminalia arjuna (Roxb. ex DC.) Wight & Arn.
Vernacular name: Holimathi
Family: Combretaceae
Description: A large evergreen tree. Leaves are simple, oblong, crenulate and leathery in texture, petiole glandular. Flowers are small, white and are borne on catkins. Fruit is ovoid with 5-7 angles or wings1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and Fruit: May - February |

|

|
Terminalia bellirica (Gaertn.) Roxb.
Vernacular name: Shanti mara
Description: Tree upto 15 m. Leaves clustered at ends of branchlets, coriaceous, broadly elliptic to elliptic- obovate. Spikes clustered towards apex, simple. Flowers creamy-white. Calyx hairy. Fruits ovoid, slightly 5-ridged, brown-pubescent1,2,3.
Native: Indomalaya |
Terminalia chebula Retz.
Vernacular name: Anile kaayi mara
Family: Combretaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves elliptic-oblong, obtuse or acute at apex, rounded at base. Spike simple or branched. Flowers pale yellow, disc densely villous. Fruit elliptic-ovoid, glabrous1,2,3.
Native: India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka; Flowering and fruit: February - November |

|

Source-19
|
Terminalia elliptica Willd.
Family: Combretaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves simple, opposite to subopposite, exstipulate. Flowers bisexual, dull yellow, in terminal and axillary paniculate spikes. Fruit drupe, coriaceous1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: April-May |
Terminalia paniculata Roth
Vernacular name: Hanalu mara
Family: Combretaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves subopposite or upper ones alternate, lamina elliptic-oblong, with sessile glands at base beneath. Flowers white, calyx hairy outside. Fruit brownish –red, unequally 3 winged1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: August - January |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Themeda triandra Forssk.
Family: Poaceae
Description: Perennial grass. Culms robust, densely tufted. Leaves narrowly linear, acuminate. Fascicles inflorescence drooping. Spikelets show conspicuous awns1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Pantropics
Flowering and fruit: October – December |
Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam.
Vernacular name: Dodda kaadu menasu
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Slender prickly shrub. Leaves alternate, 3-foliate, leaflets obovate, crenate, glabrous, gland-dotted. Inflorescence a panicle, elongated. Flowers unisexual. Fruit a berry, sub-globose, fleshy, 5-6 lobed1,2,3.
Native: Africa; Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |

|

|
Tribulus terrestris L.
Vernacular name: Neggele mullu
Family: Zygophyllaceae
Description: Procumbent herb. Leaves opposite, compound. Flowers pedicelled, solitary, axillary, sepals 5, acute. Mericarp with 2 large and 2 smaller spines1,2,3.
Native: Paleotropics |
Trichodesma zeylanica (L.) R. Br.
Family: Boraginaceae
Description: Erect herb. Leaves lanceolate, hairy with a sharp tip. Flowers are clusters at branch ends, pale blue and spread like a wheel. Fruits are ovoid nutlets1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Malaya, Australia, Mascarene Island
Flowering and fruit: September - March |

Source-20
|

Source-2
|
Tridax procumbens L.
Vernacular name: Kari balli
Family: Asteraceae
Description: Perennial hairy herb. Leaves simple alternate. Flowers heterogamous heads. Fruit tiny, dark with a crown of hairs1,2,3.
Native: Central America
Flowering and fruit: Year long |
Triumfetta annua L.
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Herbs. Leaves ovate, acuminate, serrate dentate, membranous. Flowers in axillary few-flowered cymes. Fruits glabrous, 1.3 cm1,2,3.
Native: Tropical Africa to Malesia
Flowering and fruit: November - December |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Tylophora indica (Burm. F.) Merr.
Vernacular name: Aadu muttada balli
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Twiners. Leaves simple, opposite, elliptic to ovate. Inflorescence is compound umbellate lateral cyme. Fruit is a cylindrical follicle1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: May - September |
Vangueria spinosa (Roxb. ex Link) Roxb.
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves arranged opposite or whorls of three. Flowers cymes occur in leaf axils. Flowers small, greenish-white. Fruit is small size1,2,3.
Flower: March - April |

|

|
Ventilago madraspatana Gaertn.
Vernacular name: Aithaala beelu
Family: Rhamnaceae
Description: Liana. Leaves oblong – elliptic, acute or shortly acuminate, calyx tomentose. Disc villous around the style. Fruit calyx only covering base of nut1,2,3.
Native: Sri Lanka, Myanmar; Flowering and fruit: December - February |
Vitex altissima L.f.
Vernacular name: Bharanige
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: A large dry deciduous and semi evergreen forests. Leaves are compound with three or five leaflets. Flowers are numerous on branched inflorescence, small. Fruit are small and purplish-black when ripe1,2,3.
Native: Tropical Asia; Flowering and fruit: October - December |

|

Source-2
|
Vitex negundo L.
Vernacular name: Lakki gida
Family: Lamiaceae
Description: A large shrub. Leaves are with 3-5 leaflets, lanceolate, acute. Flowers are small in stalked bunches with bluish-purple 5-lobed petals. Fruits are globose black berries1,2,3.
Native: India, Nepal, Bhutan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka
Flowering and fruit: More or less throughout the year |
Vitis auriculata Wall.
Family: Vitaceae
Description: Huge Climber. Leaves 5-foliate, leaflet ovate, elliptic-lanceolate, stipules, 5-foliate. Flowers greenish-white in axillary umbels. Fruit berries 1.5 cm long, glabrescent. Seeds rugose, 2 –pitted, furrowed1,6.
Flowering and fruit: May-November |

Source- 21
|

|
Waltheria indica L.
Vernacular name: Ottatti gida
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Subshrub. Leaves simple, alternateand stipulate with characteristic. Flowers in axillary or terminal fascicles. Fruit is a capsule1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: August - January |
Wrightia arborea (Dennst.) Mabb.
Vernacular name: Benki gida
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, elliptic or obovatem shortly acuminate at apex. Flowers in short corymbose tomentose cyme. Carpels connate into cylindrical capsule with two longitudinal groove1,2,3.
Flowering and fruit: April - September |

|

|
Wrightia tinctoria
Vernacular name: Hale neeli kodumurki
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: A small deciduous tree. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate, acute or acuminate at apex, acute at base, glabrous or puberulous beneath. Flowers in axillary or terminal lax, spreading cymes. Follicles 2, cylindrical, cohering at the apex1,2,3.
Flower: March - April |

|
Xylia xylocarpa (Roxb.) Taub.
Vernacular name: Jambe
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Unarmed tree. Leaflets 3-5 pairs, elliptic-lanceolate, acuminate, with glands in between. Corolla yellowish-white. Pod brown-pubescent, axe-shaped1,2,3.
Native: Indomalesia; Flowers: March – May, Fruit: May - January |
Ziziphus mauritiana Lam.
Vernacular name: Bugari mara
Family: Rhamnaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves simple, elliptic-ovate to orbicular, palmately nerved with stipules modified into hooked spines. Flowers small, in axillary clusters. Fruit is orange red berry1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: December - January |
 Source-2 Source-2
|

|
Ziziphus oenoplia (L.) Mill.
Vernacular name: Choori mullu
Family: Rhamnaceae
Description: A ferruginous prickly shrub with recurved prickles. Leaves are ovate, 3-4 nerved with tomentum. Flowers are axillary, sessile, 10-lobed yellowish disc at th ecentre. Fruit is a drupe1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, Pantropics; Flowering and fruit: April- June |
Zornia gibbosa Span.
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Diffuse herb. Leaflets lanceolate, acute. Calyx 0.25 cm long. Corolla yellow, 0.5 cm long. Pod 2-5 jointed2,3.
Native: Tropics
Flowering and fruit: June - November |

|

|
Feronia elephantum
Vernacular name: Belada mara
Family: Rutaceae
Description: Deciduous thorny tree. Leaves pinnately compound. Flowers small. Fruits are large globes, size of a tennis ball1,2,3.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: March - April |
Osbeckia sp
Family: Melastomaceae |
|

Source-2
|
Dodonaea viscosa
Family: Sapindaceae
Description: Small tree. Leaves simple, linear-oblong, oblanceolate. Inflorescence is panicle of racemes. Flowers are polygamous, corolla is white. Fruit is a capsule 1.5 cm broad with wings1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka Tropics
Flowering and fruit: October - March |
Cipadessa fruticosa
Vernacular name: Sidigolla
Family: Meliaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaf rachis to 27 cm long, leaflets 9-13, elliptic to elliptic-lanceolate, acuminate. Sepals sparsely pubescent, seeds not winged, exarillate1,2,3.
Native: Indomalesia; Flowering and fruit: Year long |

|

Source-2
|
Desmodium pulchellum
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Erect undershrubs. Leaves 3-foliate, leaflets elliptic-ovate, repand, obtuse, apiculate, tomentose beneath. Flowers 3-5, hidden by orbicular bractd. Pod with 1-3 round, reticulate, glabrous joints1,2,3.
Native: China, Indomalesia
Flowering and fruit: December - January |
Flemingia strobilifera
Vernacular name: Kanpoothi
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaf 1-foliate, ovate-lanceolate. Peduncle zig-zag. Calyx 0.6 cm long wings shorter than keel. Pod 2-seeded1,2,3.
Native: Indomalesia
Flowering and fruit: November – March. |

Source-2
|

Source-22
|
Oxytenanthera stocksii
Family: Poaceae
Description: An erect bamboo. Culms upto 9 m high and 2.5 – 3.8 cm in diameter. Leaves linear-lanceolate, base rounded or cuneate, tip ending in a setaceous point. Inflorescence a large panicle of spicate heads1,2,3. |
Hemidesmus indicus
Vernacular name: Anantha beru
Family: Apocynaceae
Description: Climber. Leaves simple, opposite, decussate, narrow or broadly oblong. Flowers are crowded in subsessile. Fruit is a follicle and sseeds are brownish-white hairs1,2,3.
Native: India, Sri Lanka; Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |

|

Source-2
|
Ficus benghalensis
Vernacular name: Aladamara
Family: Moraceae
Description: Evergreen tree. Leaves are leathery, simple, alternate, ovate with prominent veins. Figs about 2 cm diameter1,2,3.
Native: India
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |
Hybanthus enneaspermus
Vernacular name: Purusharathna
Family: Violaceae
Description: Branching herb. Leaves are linear-lanceolate with shallowly-crenate margin. Flowers axillary, long-petioled, bilipped. Fruit is a capsule1,2,3.
Native: Tropics, South Asia; Flowering and fruit: July -December |

Source-2
|

Source-23
|
Crotalaria striata
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Glabrescent undershrubs. Leaves 3-foliolate, leaflets usually elliptic, acute-mucronate, membranous. Raceme terminal, many flowered. Pod glabrescent, exserted1,2,3.
Native: Africa
Flowering and fruit: September - April |
Schefflera venulosa
Family: Araliaceae
Description: Large woody straggling shrub or a tree. Leaves palmately compound, leaflets elliptic lanceolate. Inflorescence is an umbel. Flowers are 5-merous. Fruits is a schizocarp1,2,3.
Native: Indo-Malaysia and Tropical Australia
Flowering and fruit: April - June |
 Source-2 Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Solanum torvum
Vernacular name: Sundekkayi
Family: Solanaceae
Description: Large shrub with prickles on stem. Leaves ovate-lanceolate, hairy and shallowly lobed. Flowers corymbose cymes. Fruits a globose berry and is green1,2,3.
Native: West Indies
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year. |
Acacia catechu
Vernacular name: Kachhu
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves compound with many leaflets and spines on either side of leaf base. Flowers small, white or pale yellow. Pod many seeded2.
Native: India; Flowering and fruit: June-October |

Source-2
|

Source-2
|
Stereospermum chelonoides
Family: Bignoniaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves imparipinnate, leaflets 5-9 number, base acute. Flowers purple dull, fragrant, in large axillary panicles. Fruit capsule terete2.
Native: Myanmar
Flowering and fruit: September - February |
Phoenix acaulis
Family: Arecaeae
Description: Palm. Leaves fibrous, acanthophylls closely arranged in more than one plane. Staminate inflorescences not extending. Fruit obovoid, ripening from green with scarlet. Seed elongate in shape29.
|
 Source- 24 Source- 24
|
 Source-2 Source-2
|
Cassia tora
Vernacular name: Chagache
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Annual shrubby herbs. Leaves with subulate glands between the leaflets, obovate-oblong, obtuse. Flowers in axillary pairs. Fruit pod2.
Native: Tropics; Flowering and fruit: August – November2 |
Cassia auriculata
Vernacular name:Honambre gida
Family: Fabaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves pinnately compound with glands opposite to leaflets. Flowers in corymbose racemes are golden yellow. Fruit pod, long and dehiscent2.
Native: South America; Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year. |

Source - 7
|

Source-25
|
Grewia tiliifolia
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Large tree. Leaves simple, alternate, lateral, auricled. Flowers bisexual, yellow, in axillary umbels. Fruit drupe, globose to subglobose2.
Flowering and fruit: February - June |
Randia dumetorum
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: An armed large shrub or small tree. Leaves simple, obovate, entire, opposite decussate. Flower white turning yellow in axillary fascicles. Fruit berry globose ovoid to ellipsoid26.
Flowering: January - July |

Source-26
|
 Source-27 Source-27
|
Randia uliginosa
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves simple, opposite, decussate, glabrous above and pubescent and glaucous beneath. Flowers bisexual, white, solitary. Fruit a berry, ovoid or ellipsoid27.
Flowering and fruit: August – March |
Kydia calycina
Vernacular name: Bellaka
Family: Malvaceae
Description: Tree. Leaves ovoate- orbicular, lobes, glaucous beneath. Panicles axillary and terminal. Petals spathulate. Fruit capsule7.
Native: Indian sub-continent; Flowering and fruit: September - January7 |

Source-2
|

Source-28
|
Lagerstroemia lanceolata
Family: Lythraceae
Description: Large deciduous tree. Leaves simple, elliptic, entire, opposite. Flowers in terminal panicles. Fruit capsule ellipsoid, brownish28.
Flowering and fruit: March - May |
Adina cordifolia
Vernacular name: Anavu
Family: Rubiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaves simple, orbicular to cordate, with an acuminate tip. Flowers small, yellow and aggregated in heads. Fruit capsule2.
Native: India, Sri Lanka, China; Flowering and fruit: March - June |

|

Source-29
|
Stereospermum xylocarpum
Vernacular name: Ambalahude
Family: Bignoniaceae
Description: Large deciduous tree. Leaves opposite, double –pinnate, elliptic, flowers funnel shaped, white. Fruit capsule29.
Flowering: March - April |
Odina wodier
Vernacular name: Ajjashringi
Family: Anacardiaceae
Description: Deciduous tree. Leaflets subsessile, ovate-elliptic, acuminate at apex, glabrous above. Yellow colour corolla. Fruit drupe2.
Flowering and fruit: January- May |

Source- 7
|

Source-2
|
Ficus infectoria
Vernacular name: Basarimara
Family: Moraceae
Description: Medium-sized deciduous tree. Leaves large, elliptic, acute. Figs stalked, larger2.
Native: India, South-east Asia
Flowering and fruit: October – November |
Solanum ferox
Family: Solanaceae
Description: Shurb found on the coast line of Southern India. It is wild brinjal30. |
 Source-2 Source-2
|

Source- 31
|
Solanum indicum
Family: Solanaceae
Description: Armed with short spines, stellately tomentose. Leaf shallowly lobed, ovate, Cyme short, few-many-flowered. Blue color corolla. Fruit berries globose, yellow2.
Flowering and fruit: Throughout the year |
Asparagus racemosus
Vernacular name: Shataavari
Family: Asparagaceae
Description: climbing shrub. Leaves reduced, spinescent scales. Cladodes slightly compressed. Spines longer, decurved. Flowers white, small.
Flowering and fruit: July-August |
 Source- 32 Source- 32
|

|
Clematis gouriana
Vernacular name: Thalejadari
Family: Ranunculaceae
Description: Climbing herb. Leaflets ovate, acute at apex, rounded at base, nerves tomentose below. Flowers white, 1 cm across, obtuse. Fruit achene, ovoid2.
Flowering and fruit: November-March |
Jasminum arborescens
Vernacular name: Vishamallige
Family: Oleaceae
Description: Shrub. Leaves ovate, elliptic or rarely ovate-lanceolate. Flowers white, 7-flowered trichotomous cyme. Berry solitary, globose or ellipsoid2.
Flowering and fruit: March - May |
 Source-33 Source-33
|

|
Terminalia tomentosa
Family: Combretaceae
Description: Bark rough, deeply cracked. Leaves thinly coriaceous, elliptic-lanceolate, acute at apex. Fruit elliptic, glabrous, thick wings.
Native: India |
Reference:
- Flora of Bangalore District, S V Ramaswamy, B A Razi, Published by the Director, Prasaranga, University of Mysore, Manasagangotri, Mysore – 570012, pp L+740
- Digital Flora of Karnataka (http://florakarnataka.ces.iisc.ac.in/hjcb2/)
- Indian Biodiversity Portal (http://indiabiodiversity.org/)
- eFloras.org (http://efloras.org/)
- Flowers of India (http://www.flowersofindia.net/)
- Flora of District Andhra Pradesh, India, Ranga Reddi (https://books.google.co.in/books?id=0tI7vIpJJxgC&pg=PA55&lpg=PA55&dq=Vitis+auriculata&source=bl&ots=N7Ef3xflWl&sig=DzWxDy6Ol2sIUrKKubDAWl1dJ1Q&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwjZpe_B6OTJAhWTHY4KHdd1CncQ6AEIRDAM#v=onepage&q=Vitis%20auriculata&f=false)
- http://tanamanherbalindo.blogspot.in/2014/05/sereh-andropogon-nardus-l.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Echinochloa_colona#/media/File:Echinochloa_colona.jpg
- http://www.ibin.gov.in/ibin/components/com_ibin/species_html/Dactyloctenium%20aegyptium/Dactyloctenium%20aegyptium1.jpg
- http://regionalconservation.org/ircs/database/plants/PlantPage.asp?TXCODE=Eleuindi
- http://www.discoverlife.org/mp/20q?search=Bulbostylis+barbata
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/13899
- http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=KYPU#
- http://www.inaturalist.org/observations/21602
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/266558
- https://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp/project/africa_dojo/FakaraPlants/Contents/Species_pages/Schizexi.html
- http://gardenbreizh.org/photos/karlostachys/photo-249096.html
- http://flora.indianbiodiversity.org/file/7497
- http://www.flickriver.com/photos/tags/terminaliacoriacea/interesting/
- http://flora.indianbiodiversity.org/flora/angiosperm/boraginaceae/trichodesma/trichodesma-zeylanicum
- https://www.flickr.com/photos/66499264@N05/9802851304
- http://www.bambooworldindia.com/bambooinkerala.php
- https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Crotalaria_striata_07342.JPG
- http://www.fruitipedia.com/Dwarf_date_palm_phonix_acaulis.htm
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/31410
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/31701
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/231317
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/31487
- http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Padri%20Tree.html
- https://books.google.co.in/books?id=d9UBAAAAYAAJ&pg=PA460&dq=Solanum+%2B+india&hl=en&sa=X&ei=2PSCU5XgKIWSuASpz4Jw&ved=0CCwQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=Solanum%20%2B%20india&f=false
- http://parisaramahiti.kar.nic.in/medicinal_plants_new/med%20plants/p173.html
- http://indiabiodiversity.org/species/show/32039
- http://www.flowersofindia.net/catalog/slides/Navamallika.html