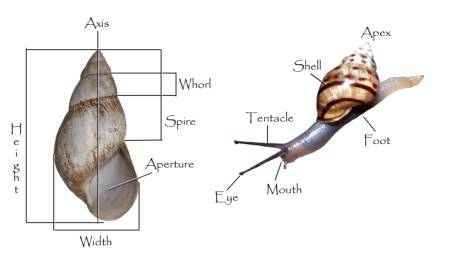
The phylum Mollusca is divided into 8 classes with varying number of species in them; the most important class is the Gastropoda comprising more than 80% of all living mollusc species. The species belonging to this class occurs in marine, freshwater and terrestrial habitat. Where as bivalves occurs both in freshwater as well as marine but not in terrestrial habitat. Rest six classes of mollusca are exclusively marine (Table 1).
Molluscs are very abundant and form an important link in the food chains. A large number are herbivores or grazers and hence are important in nutrient recycling along with the other soil invertebrates. Numerous molluscs are important food source for humans such as clams and snails. Some gastropods are pests and damage crops and others harbor disease-causing parasites such as rat lungworm and causes Schiostomasis in humans.
-
Annandale, N. and Prashad 1919. Fauna of Certain small streams in the Bombay Presidency. Records of Indian Museum , 16: 139.
-
Anonymous. 1910. Land and Freshwater Mollusca of India including south Arabia, Baluchistan, Afghanistan, Kashmir, Nepal, Ceylon. Conchologia Indica 2, Pp XI London.
-
Aravind, N.A., K. P. Rajashekhar and N. A. Madhyastha. 2005. Species diversity, endemism and distribution of land snails of the Western Ghats, India. Records of the Western Australian Museum, Supplement 68 : 31–38.
-
Beddome, R. H. 1875. Description of some new operculated land shells from southern India and Ceylon. Proceedings of Zoological Society of London , 1875: 442-953.
-
Beddome, R. H. 1891. Description of some new land shells from Indian region. Proceedings of Zoological Society of London, 1891: 313-315.
-
Beddome, R. H. 1906. Notes on Indian and Ceylonese species of Glessula Proceedings of Malacological Society of London, 7: 160-172.
-
Blanford, W. T. 1870. Contribution to Indian Malacology, No XI, description of new species of Paludomus, Cremnoconchus, Cyclostoma and of Helicidae from various parts of India. Journal of Asiatic Society of Bengal , 39: 9-25.
-
Blanford, W. T. 1880. Contribution to Indian Malacology, No. XII. Description of new land and freshwater shells from southern and Western India, Burma the Andamans Islands. Journal of Asiatic Society of Bengal , 492: 181-222.
-
Blanford, W. T. and H. H. Godwin-Austen. 1908 . The Fauna of British India– Including Ceylon and Burma– Mollusca I. Taylor and Francis, London.
-
Bogan, A. E. and W. R. Hoeh. 2000. On becoming cemented: evolutionary relationships among the genera in the freshwater bivalve family Etheriidae (Bivalvia: Unionoida), In: The Evolutionary Biology of the Bivalvia. Eds: Harper E.M., J. D. Taylor and J.A. Crame. Geological society, London, pp 159-168.
-
Ganesh, T., D. R. Priyadarsanan, M. S. Devy, N. A. Aravind and D. Rao. 2002. Assessment of Biodiversity of Lesser-known and Functionally Important Groups in Rajiv Gandhi (Nagarahole) National Park . Report: Submitted to Karnataka Forest Department, Bangalore, India.
-
Godwin-Austen, H. H. 1882. Land and freshwater mollusca of India, including South Arabia, Baluchistan, Afghanistan, Kashmir, Nepal, Burma, Pegu, Tenasserim, Malaya Peninsula, Ceylon and other islands of the Indian Ocean; Supplementary to Masers Theobald and Hanley's Conchologica Indica . Taylor and Francis, London.
-
Gude, G. K. 1906. Further remarks on the genus Chloritis with description of eleven new species. Proceedings of Zoological Society of London , 7: 105-118.
-
Gude, G. K. 1914. The Fauna of British India– Including Ceylon and Burma – Mollusca II. Taylor and Francis, London.
-
Gude, G. K. 1921. The Fauna of British India– Including Ceylon and Burma– Mollusca III. Taylor and Francis, London.
-
Madhyastha, N. A. 2001. Pseudomulleria dalyi ( Acostea dalyi ): a rare cemented bivalve of Western Ghats. Zoos' Print Journal, 16: 573.
-
Madhyastha, N. A. and Kamalesh D. Mumbrekar. 2006. Endemic bivalves of the Western Ghats, India. Tentacle, 14: 23-24.
-
Madhyastha, N. A., G.M. Rajendra and S. Shanbhag. 2005. Banding polymorphism in Trachia vittata. Zoos' Print Journal 20: 1821-1822.
-
Madhyastha, N. A., R. G. Mavinkuruve and S. P. Shanbhag. 2004. Land snails of Western Ghats. In A. K. Gupta, A. Kumar and V. Ramakantha (eds), ENVIS Bulletin: Wildlife and Protected Areas, Conservation of Rainforest in India, 4 : 143–151.
-
Mavinkuruve, R. G., S. P. Shanbhag and N. A. Madhyastha. 2004. The land snails of Sharavathi wildlife sanctuary. Records of Zoological Survey of India, 104 (Parts 1-2): 123–131.
-
Mavinkurve, G. M., S. P. Shanbhag and N.A. Madhyastha. 2004. Non-marine molluscs of Western Ghats: a status review Zoos' Print Journal, 19: 1708-1711.
-
Mavinkurve, R.G., S. P. Shanbhag and N. A. Madhyastha. 2004. Checklist of terrestrial gastropods of Karnataka, India. Zoos' Print Journal, 19 : 1684–1686
-
Naggs, F. 1997. William Benson and the early study of land snails in British India and Ceylon. Archives of Natural History, 24 : 37–88.
-
Patil, S. G. and S. S. Talmale. 2005. A checklist of land and freshwater mollusca of Maharashtra state. Zoos' Print Journal, 20 : 1912-1913.
-
Prashad, B. 1931. Some noteworthy examples of parallel evolution in the molluscan faunas of southern eastern Asia and South America. Proceedings of Royal Society of Edinburgh , 51: 42-63
-
Preston, H. B. 1915. The fauna of British India. Vol IV. Mollusca (Freshwater Gastropoda and Pelecypoda). Taylor and Francis, London.
-
Ramakrishna and S. C. Mitra. 2002. Endemic land molluscs of India. Records of Zoological Survey of India, Occasional Paper, 196 : 1-65.
-
Rao, H. S. 1925. On Certain Succineid Molluscs from the Western Ghats, Bombay Presidency. Records of Indian Museum, 28: 385.
-
Rao, H. S. 1925. On the Habits of a Succineid Mollusca of Western Ghats. Records of Indian Museum, 27: 401.
-
Sathyamaurthi S. T. 1960. The land and freshwater mollusca in the collection of the Madras Government Museum. Bulletin of the Madras Government Museum, 6 : 1–174.
-
Seddon, M. B. 2000. Molluscan diversity and impact of large dams. Prepared for thematic review II.1: Dams, ecosystem functions and environmental restoration. IUCN Report.
-
Sivaramkrishnan K. G., Madhyastha N. A. and Subramanian K. A. 1998. Field guide to aquatic macro-invertebrates, CES, IISc, Banglore,
-
Smith, E. A. 1898. Description of Mulleria dalyi n.sp. from India. Proceedings of Malacalogical Society of London, 3: 13-116.
-
Subbarao, N. V. 1989. Freshwater Molluscs of India . Zoological Survey of India. Culcutta.
-
Subbarao, N. V. 1993. Freshwater Molluscs of India. In: Rao K.S. (Ed.). Recent Advances in Freshwater Biology. New Delhi. Anmol Publication. Vol. 2. pp. 187-202.
-
Subbarao, N. V. 1998. The Mollusca. In: Faunal Diversity in India. Ed: Alfred J. R. B., A. K. Das and A. K. Sanyal. ENVIS center, ZSI, Calcutta.
-
Subbarao, N. V. and S. C. Mitra. 1979. On the land and freshwater molluscs of Pune district, Maharastra. Records of Zoological Survey of India, 75 : 1-37.
-
Theobald, W. 1875. Descriptions of some new land and freshwater shells from India and Burmah. Journal of Asiatic Society of Bengal , 5: 184-189.
-
Theoblad, W. 1876. Catalogue of the land and freshwater shells of British India, pp.1-65.
-
T onapi , G. T . 1971. Studies on the freshwater and amphibious Mollusca of Poona with notes on their distribution -Part III. Journal of Bombay Natural History Society , 68: 115-126.
-
Tonapi, G. T. and L. Mulherkar. 1963. Studies on freshwater and amphibious molluscs of Poona with notes on their distribution-Part II. Journal of Bombay Natural History Society , 60 : 103-120.
Thanks to International Foundation for Science (IFS), Sweden for funding the work on impact of land use change on land snails of the Western Ghats, India.